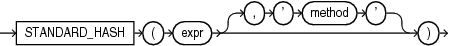STANDARD_HASH
Syntax
Purpose
STANDARD_HASH computes a hash value for a given expression using one of several hash algorithms that are defined and standardized by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. This function is useful for performing authentication and maintaining data integrity in security applications such as digital signatures, checksums, and fingerprinting.
You can use the STANDARD_HASH function to create an index on an extended data type column. Refer to "Creating an Index on an Extended Data Type Column" for more information.
-
The
exprargument determines the data for which you want Oracle Database to compute a hash value. There are no restrictions on the length of data represented byexpr, which commonly resolves to a column name. Theexprcannot be aLONGor LOB type. It cannot be a user-defined object type. All other data types are supported forexpr. -
The optional
methodargument lets you specify the name of the hash algorithm to be used. Valid algorithms areSHA1,SHA256,SHA384,SHA512, andMD5. If you omit this argument, thenSHA1is used.
The function returns a RAW value.
Note:
The STANDARD_HASH function is not identical to the one used internally by Oracle Database for hash partitioning.