JSON_VALUE
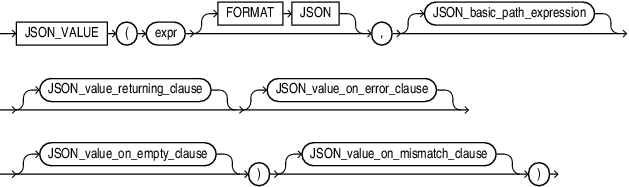
Syntax
JSON_basic_path_expression::=
(JSON_basic_path_expression: See SQL/JSON Path Expressions)
JSON_value_returning_clause::=
JSON_value_return_type::=
JSON_value_return_object_instance ::=
JSON_value_on_error_clause::=
JSON_value_on_empty_clause::=
Purpose
The SQL/JSON function JSON_VALUE finds a specified scalar JSON value in JSON data and returns it as a SQL value.
See Also:
Appendix C in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for the collation derivation rules, which define the collation assigned to the value returned by this function when it is a character value
expr
Use this clause to specify the JSON data to be evaluated. For expr, specify an expression that evaluates to a text literal. If expr is a column, then the column must be of data type VARCHAR2, CLOB, or BLOB. If expr is null, then the function returns null.
If expr is not a text literal of well-formed JSON data using strict or lax syntax, then the function returns null by default. You can use the JSON_value_on_error_clause to override this default behavior. Refer to the JSON_value_on_error_clause.
FORMAT JSON
You must specify FORMAT JSON if expr is a column of data type BLOB.
JSON_basic_path_expression
Use this clause to specify a SQL/JSON path expression. The function uses the path expression to evaluate expr and find a scalar JSON value that matches, or satisfies, the path expression. The path expression must be a text literal. See Oracle Database JSON Developer's Guide for the full semantics of JSON_basic_path_expression.
JSON_value_returning_clause
Use this clause to specify the data type and format of the value returned by this function.
RETURNING
Use the RETURNING clause to specify the data type of the return value. If you omit this clause, then JSON_VALUE returns a value of type VARCHAR2(4000).
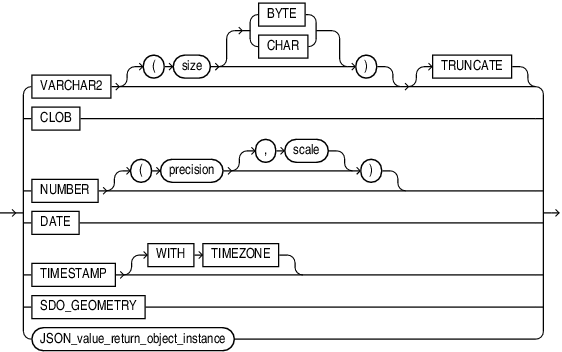
JSON_value_return_type ::=
You can use JSON_value_return_type to specify the following data types:
-
VARCHAR2[(size[BYTE,CHAR])]If you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function can be a character or number value. A number value will be implicitly converted to a
VARCHAR2. When specifying theVARCHAR2data type elsewhere in SQL, you are required to specify a size. However, in this clause you can omit the size. In this case,JSON_VALUEreturns a value of typeVARCHAR2(4000).Specify the optional
TRUNCATEclause immediately afterVARCHAR2(N)to truncate the return value toNcharacters, if the return value is greater thanNcharacters. -
CLOBSpecify this data type to return a character large object containing single-byte or multi-byte characters.
-
NUMBER[(precision[,scale])]If you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function must be a number value. The scalar value returned can also be a JSON Boolean value. Note however, that returning
NUMBERfor a JSON Boolean value is deprecated. -
DATEIf you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function must be a character value that can be implicitly converted to a
DATEdata type. -
TIMESTAMPIf you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function must be a character value that can be implicitly converted to a
TIMESTAMPdata type. -
TIMESTAMPWITHTIMEZONEIf you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function must be a character value that can be implicitly converted to a
TIMESTAMPWITHTIMEZONEdata type. -
SDO_GEOMETRYThis data type is used for Oracle Spatial and Graph data. If you specify this data type, then
exprmust evaluate to a text literal containing GeoJSON data, which is a format for encoding geographic data in JSON. If you specify this data type, then the scalar value returned by this function must be an object of typeSDO_GEOMETRY. -
JSON_value_return_object_instance
If
JSON_VALUEtargets a JSON object, and you specify a user-defined SQL object type as the return type, thenJSON_VALUEreturns an instance of that object type in object_type_name.For examples see Using JSON_VALUE To Instantiate a User-Defined Object Type Instance
See Also:
-
SQL/JSON Function JSON_VALUE for a conceptual understanding.
-
Refer to "Data Types" for more information on the preceding data types.
-
If the data type is not large enough to hold the return value, then this function returns null by default. You can use the
JSON_value_on_error_clauseto override this default behavior. Refer to the JSON_value_on_error_clause.
ASCII
Specify ASCII to automatically escape any non-ASCII Unicode characters in the return value, using standard ASCII Unicode escape sequences.
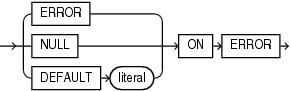
JSON_value_on_error_clause
Use this clause to specify the value returned by this function when the following errors occur:
-
expris not well-formed JSON data using strict or lax JSON syntax -
A nonscalar value is found when the JSON data is evaluated using the SQL/JSON path expression
-
No match is found when the JSON data is evaluated using the SQL/JSON path expression. You can override the behavior for this type of error by specifying the
JSON_value_on_empty_clause. -
The return value data type is not large enough to hold the return value
You can specify the following clauses:
-
NULLONERROR- Returns null when an error occurs. This is the default. -
ERRORONERROR- Returns the appropriate Oracle error when an error occurs. -
DEFAULTliteralONERROR- Returnsliteralwhen an error occurs. The data type ofliteralmust match the data type of the value returned by this function.
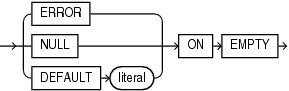
JSON_value_on_empty_clause
Use this clause to specify the value returned by this function if no match is found when the JSON data is evaluated using the SQL/JSON path expression. This clause allows you to specify a different outcome for this type of error than the outcome specified with the JSON_value_on_error_clause.
You can specify the following clauses:
-
NULLONEMPTY- Returns null when no match is found. -
ERRORONEMPTY- Returns the appropriate Oracle error when no match is found. -
DEFAULTliteralONEMPTY- Returnsliteralwhen no match is found. The data type ofliteralmust match the data type of the value returned by this function.
If you omit this clause, then the JSON_value_on_error_clause determines the value returned when no match is found.
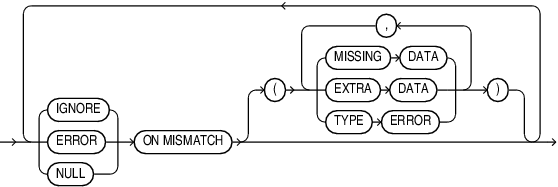
JSON_value_on_mismatch_clause
You can use the JSON_value_on_mismatch_clause in two ways: generally or case by case.
Use it generally to apply to all error cases like extra data, missing data, and type errors.
Use it case by case by specifying different ON MISMATCH clauses for each case. For example:
IGNORE ON MISMATCH (EXTRA DATA)ERROR ON MISMATCH ( MISSING DATA, TYPE ERROR)Examples
The following query returns the value of the member with property name a. Because the RETURNING clause is not specified, the value is returned as a VARCHAR2(4000) data type:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{a:100}', '$.a') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
100
The following query returns the value of the member with property name a. Because the RETURNING NUMBER clause is specified, the value is returned as a NUMBER data type:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{a:100}', '$.a' RETURNING NUMBER) AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
----------
100
The following query returns the value of the member with property name b, which is in the value of the member with property name a:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{a:{b:100}}', '$.a.b') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
100
The following query returns the value of the member with property name d in any object:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{a:{b:100}, c:{d:200}, e:{f:300}}', '$.*.d') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
200
The following query returns the value of the first element in an array:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('[0, 1, 2, 3]', '$[0]') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
0
The following query returns the value of the third element in an array. The array is the value of the member with property name a.
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{a:[5, 10, 15, 20]}', '$.a[2]') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
15
The following query returns the value of the member with property name a in the second object in an array:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('[{a:100}, {a:200}, {a:300}]', '$[1].a') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
200
The following query returns the value of the member with property name c in any object in an array:
SELECT JSON_VALUE('[{a:100}, {b:200}, {c:300}]', '$[*].c') AS value
FROM DUAL;
VALUE
-----
300
The following query attempts to return the value of the member that has property name lastname. However, such a member does not exist in the specified JSON data, resulting in no match. Because the ON ERROR clause is not specified, the statement uses the default NULL ON ERROR and returns null.
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{firstname:"John"}', '$.lastname') AS "Last Name"
FROM DUAL;
Last Name
---------
The following query results in an error because it attempts to return the value of the member with property name lastname, which does not exist in the specified JSON. Because the ON ERROR clause is specified, the statement returns the specified text literal.
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{firstname:"John"}', '$.lastname'
DEFAULT 'No last name found' ON ERROR) AS "Last Name"
FROM DUAL;
Last Name
---------
No last name found