CREATE PFILE
Purpose
Use the CREATE PFILE statement to export either a binary server parameter file or the current In-Memory parameter settings into a text initialization parameter file. Creating a text parameter file is a convenient way to get a listing of the current parameter settings being used by the database, and it lets you edit the file easily in a text editor and then convert it back into a server parameter file using the CREATE SPFILE statement.
Upon successful execution of this statement, Oracle Database creates a text parameter file on the server. In an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment, it will contain all parameter settings of all instances. It will also contain any comments that appeared on the same line with a parameter setting in the server parameter file.
Note on Creating Text Parameter Files in a CDB
When you create a text parameter file in a multitenant container database (CDB), the current container can be the root or a PDB.
-
If the current container is the root, then the database creates a text file that contains the parameter settings for the root.
-
If the current container is a PDB, then the database creates a text file that contains the parameter settings for the PDB. In this case you must specify a
pfile_name.
See Also:
-
CREATE SPFILE for information on server parameter files
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for additional information on text initialization parameter files and binary server parameter files
-
Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide for information on using server parameter files in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment
Prerequisites
You must have one of the following system privileges to execute this statement:
-
SYSDBA -
SYSDG -
SYSOPER -
SYSBACKUP -
SYSASM -
SYSRAC
You can execute this statement either before or after instance startup.
Restrictions
You cannot overwrite OS files as a SYSDG, SYSOPER, or SYSRAC user.
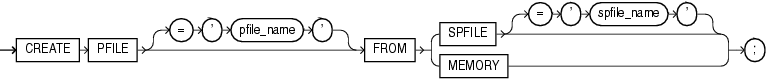
Syntax
create_pfile::=
Semantics
pfile_name
Specify the name of the text parameter file you want to create. If you do not specify pfile_name, then Oracle Database uses the platform-specific default initialization parameter file name. pfile_name can include a path prefix. If you do not specify such a path prefix, then the database adds the path prefix for the default storage location, which is platform dependent.
spfile_name
Specify the name of the binary server parameter from which you want to create a text file.
-
If you specify
spfile_name, then the file must exist on the server. If the file does not reside in the default directory for server parameter files on your operating system, then you must specify the full path. -
If you do not specify
spfile_name, then the database uses the spfile that is currently associated with the instance, usually the one that was used a startup. If no spfile is associated with the instance, then the database looks for the platform-specific default server parameter file name. If that file does not exist, then the database returns an error.
See Also:
the appropriate operating-system-specific documentation for default parameter file names
MEMORY
Specify MEMORY to create a pfile using the current system-wide parameter settings. In an Oracle RAC environment, the created file will contain the parameter settings from each instance.
Examples
Creating a Parameter File: Example
The following example creates a text parameter file my_init.ora from a binary server parameter file s_params.ora:
CREATE PFILE = 'my_init.ora' FROM SPFILE = 's_params.ora';
Note:
Typically you will need to specify the full path and filename for parameter files on your operating system. Refer to your Oracle operating system documentation for path information.