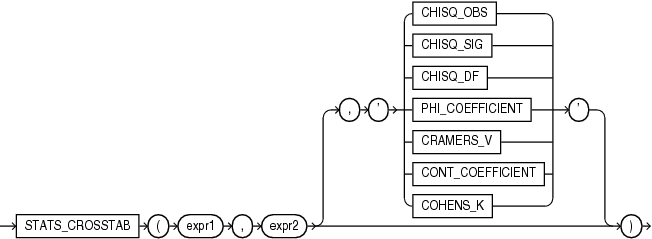
STATS_CROSSTAB
Syntax
Purpose
Crosstabulation (commonly called crosstab) is a method used to analyze two nominal variables. The STATS_CROSSTAB function takes two required arguments: expr1 and expr2 are the two variables being analyzed. The optional third argument lets you specify the meaning of the NUMBER value returned by this function, as shown in Table 7-4. For this argument, you can specify a text literal, or a bind variable or expression that evaluates to a constant character value. If you omit the third argument, then the default is 'CHISQ_SIG'.
See Also:
Appendix C in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for the collation determination rules for STATS_CROSSTAB
Table 7-4 STATS_CROSSTAB Return Values
| Argument | Return Value Meaning |
|---|---|
|
|
Observed value of chi-squared |
|
|
Significance of observed chi-squared |
|
|
Degree of freedom for chi-squared |
|
|
Phi coefficient |
|
|
Cramer's V statistic |
|
|
Contingency coefficient |
|
|
Cohen's kappa |
STATS_CROSSTAB Example
The following example determines the strength of the association between gender and income level:
SELECT STATS_CROSSTAB
(cust_gender, cust_income_level, 'CHISQ_OBS') chi_squared,
STATS_CROSSTAB
(cust_gender, cust_income_level, 'CHISQ_SIG') p_value,
STATS_CROSSTAB
(cust_gender, cust_income_level, 'PHI_COEFFICIENT') phi_coefficient
FROM sh.customers;
CHI_SQUARED P_VALUE PHI_COEFFICIENT
----------- ---------- ---------------
251.690705 1.2364E-47 .067367056