CREATE ROLE
Purpose
Use the CREATE ROLE statement to create a role, which is a set of privileges that can be granted to users or to other roles. You can use roles to administer database privileges. You can add privileges to a role and then grant the role to a user. The user can then enable the role and exercise the privileges granted by the role.
A role contains all privileges granted to the role and all privileges of other roles granted to it. A new role is initially empty. You add privileges to a role with the GRANT statement.
If you create a role that is NOT IDENTIFIED or is IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY or BY password, then Oracle Database grants you the role with ADMIN OPTION. However, if you create a role IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY, then the database does not grant you the role. A global role cannot be granted to a user or role directly. Global roles can be granted only through enterprise roles.
See Also:
-
GRANT for information on granting roles
-
ALTER USER for information on enabling roles
-
ALTER ROLE and DROP ROLE for information on modifying or removing a role from the database
-
SET ROLE for information on enabling and disabling roles for the current session
-
Oracle Database Security Guide for general information about roles
-
Oracle Database Enterprise User Security Administrator's Guide for details on enterprise roles
Prerequisites
You must have the CREATE ROLE system privilege.
To specify the CONTAINER clause, you must be connected to a multitenant container database (CDB). To specify CONTAINER = ALL, the current container must be the root. To specify CONTAINER = CURRENT, the current container must be a pluggable database (PDB).
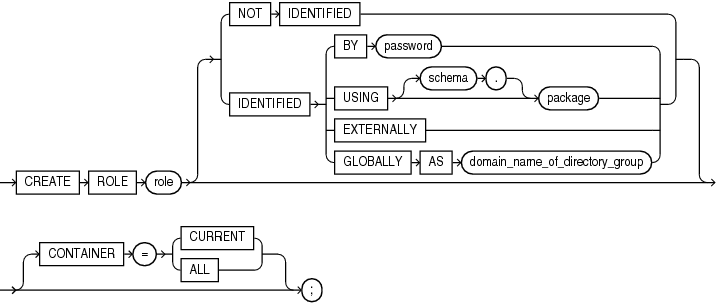
Syntax
create_role::=
Semantics
role
Specify the name of the role to be created. The name must satisfy the requirements listed in "Database Object Naming Rules". Oracle recommends that the role contain at least one single-byte character regardless of whether the database character set also contains multibyte characters. The maximum length of the role name is 30 bytes. The maximum number of user-defined roles that can be enabled for a single user at one time is 148.
In a non-CDB, a role name cannot begin with C## or c##.
In a CDB, the requirements for a role name are as follows:
-
The name of a common role must begin with characters that are a case-insensitive match to the prefix specified by the
COMMON_USER_PREFIXinitialization parameter. By default, the prefix isC##. -
The name of a local role must not begin with characters that are a case-insensitive match to the prefix specified by the
COMMON_USER_PREFIXinitialization parameter. Regardless of the value ofCOMMON_USER_PREFIX, the name of a local role can never begin withC##orc##.
Note:
If the value of COMMON_USER_PREFIX is an empty string, then there are no requirements for common or local role names with one exception: the name of a local role can never begin with C## or c##. Oracle recommends against using an empty string value because it might result in conflicts between the names of local and common roles when a PDB is plugged into a different CDB, or when opening a PDB that was closed when a common user was created.
Some roles are defined by SQL scripts provided on your distribution media.
NOT IDENTIFIED Clause
Specify NOT IDENTIFIED to indicate that this role is authorized by the database and that no password is required to enable the role.
IDENTIFIED Clause
Use the IDENTIFIED clause to indicate that a user must be authorized by the specified method before the role is enabled with the SET ROLE statement.
BY password
You can create a local role with a password with the BY password clause. This means that you must specify the password to the database at the time you enable the role.
The password can contain any characters from the database character set except the NULL character (CHR(0)) and the double-quote. The password is syntactically an identifier, and may need to be enclosed in double-quotes as required by the "Database Object Naming Rules". You must ensure that your database, and the clients that need to enable the role are configured to support all the characters comprising the password.
You can enable password-protected roles in a proxy session. Both secure application role and password-protected roles provide a secure method for enabling a role in a session. Oracle recommends using secure password roles instead of password protected roles in instances where the password has to be maintained and transmitted over insecure channels, or if more than one person needs to know the password. Password-protected roles in a proxy session are suitable for situations where automation is used to set the role.
USING package
The USING package clause lets you create a secure application role, which is a role that can be enabled only by applications using an authorized package. If you do not specify schema, then the database assumes the package is in your own schema.
See Also:
Oracle Database Security Guide for information on creating a secure application role
EXTERNALLY
Specify EXTERNALLY to create an external role. An external user must be authorized by an external service, such as an operating system or third-party service, before enabling the role.
Depending on the operating system, the user may have to specify a password to the operating system before the role is enabled.
GLOBALLY
Specify GLOBALLY to create a global role . A global user must be authorized to use the role by the enterprise directory service before the role is enabled at login.
Specify GLOBALLY with AS to map a directory group to a global role when using centrally managed users. The directory group is identified by its domain name.
Example: Map a Directory User to a Global User
CREATE USER scott_global IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY AS ‘cn=scott taylor,ou=sales,dc=abccorp,dc=com’;
This effectively maps a directory user named ‘scott taylor’ in the ‘sales’ organization unit of the abccorp.com domain to a database global user ‘scott_global’.
CONTAINER Clause
The CONTAINER clause applies when you are connected to a CDB. However, it is not necessary to specify the CONTAINER clause because its default values are the only allowed values.
-
To create a common role, you must be connected to the root. You can optionally specify
CONTAINER=ALL, which is the default when you are connected to the root. -
To create a local role, you must be connected to a PDB. You can optionally specify
CONTAINER=CURRENT, which is the default when you are connected to a PDB.
Examples
Creating a Role: Example
The following statement creates the role dw_manager:
CREATE ROLE dw_manager;
Users who are subsequently granted the dw_manager role will inherit all of the privileges that have been granted to this role.
You can add a layer of security to roles by specifying a password, as in the following example:
CREATE ROLE dw_manager IDENTIFIED BY warehouse;
Users who are subsequently granted the dw_manager role must specify the password warehouse to enable the role with the SET ROLE statement.
The following statement creates global role warehouse_user:
CREATE ROLE warehouse_user IDENTIFIED GLOBALLY;
The following statement creates the same role as an external role:
CREATE ROLE warehouse_user IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY;
The following statement creates local role role1 in the current PDB. The current container must be a PDB when you issue this statement:
CREATE ROLE role1 CONTAINER = CURRENT;
The following statement creates common role c##role1. The current container must be the root when you issue this statement:
CREATE ROLE c##role1 CONTAINER = ALL;