TO_CHAR (datetime)
Syntax
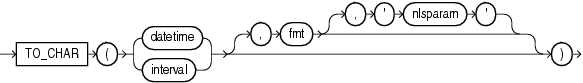
to_char_date::=
Purpose
TO_CHAR (datetime) converts a datetime or interval value of DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND, or INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH data type to a value of VARCHAR2 data type in the format specified by the date format fmt. If you omit fmt, then date is converted to a VARCHAR2 value as follows:
-
DATEvalues are converted to values in the default date format. -
TIMESTAMPandTIMESTAMPWITHLOCALTIMEZONEvalues are converted to values in the default timestamp format. -
TIMESTAMPWITHTIMEZONEvalues are converted to values in the default timestamp with time zone format. -
Interval values are converted to the numeric representation of the interval literal.
Refer to "Format Models" for information on datetime formats.
The 'nlsparam' argument specifies the language in which month and day names and abbreviations are returned. This argument can have this form:
'NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = language'
If you omit 'nlsparam', then this function uses the default date language for your session.
See Also:
You can use this function in conjunction with any of the XML functions to generate a date in the database format rather than the XML Schema standard format.
See Also:
-
Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide for information about formatting of XML dates and timestamps, including examples
-
"XML Functions" for a listing of the XML functions
-
Appendix C in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for the collation derivation rules, which define the collation assigned to the character return value of this function
Examples
The following example uses this table:
CREATE TABLE date_tab ( ts_col TIMESTAMP, tsltz_col TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, tstz_col TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE);
The example shows the results of applying TO_CHAR to different TIMESTAMP data types. The result for a TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE column is sensitive to session time zone, whereas the results for the TIMESTAMP and TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE columns are not sensitive to session time zone:
ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = '-8:00'; INSERT INTO date_tab VALUES ( TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00'); INSERT INTO date_tab VALUES ( TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00'); SELECT TO_CHAR(ts_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS ts_date, TO_CHAR(tstz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF TZH:TZM') AS tstz_date FROM date_tab ORDER BY ts_date, tstz_date; TS_DATE TSTZ_DATE ------------------------------ ------------------------------------- 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE, TO_CHAR(tsltz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS tsltz FROM date_tab ORDER BY sessiontimezone, tsltz; SESSIONTIM TSLTZ ---------- ------------------------------ -08:00 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = '-5:00'; SELECT TO_CHAR(ts_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS ts_col, TO_CHAR(tstz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF TZH:TZM') AS tstz_col FROM date_tab ORDER BY ts_col, tstz_col; TS_COL TSTZ_COL ------------------------------ ------------------------------------- 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE, TO_CHAR(tsltz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS tsltz_col FROM date_tab ORDER BY sessiontimezone, tsltz_col; 2 3 4 SESSIONTIM TSLTZ_COL ---------- ------------------------------ -05:00 01-DEC-1999 13:00:00.000000 -05:00 02-DEC-1999 13:00:00.000000
The following example converts an interval literal into a text literal:
SELECT TO_CHAR(INTERVAL '123-2' YEAR(3) TO MONTH) FROM DUAL; TO_CHAR ------- +123-02
Using TO_CHAR to Format Dates and Numbers: Example
The following statement converts date values to the format specified in the TO_CHAR function:
WITH dates AS (
SELECT date'2015-01-01' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-01-10' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-02-01' d FROM dual
)
SELECT d "Original Date",
to_char(d, 'dd-mm-yyyy') "Day-Month-Year",
to_char(d, 'hh24:mi') "Time in 24-hr format",
to_char(d, 'iw-iyyy') "ISO Year and Week of Year"
FROM dates;
The following statement converts date and timestamp values to the format specified in the TO_CHAR function:
WITH dates AS (
SELECT date'2015-01-01' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-01-10' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-02-01' d FROM dual union
SELECT timestamp'2015-03-03 23:44:32' d FROM dual union
SELECT timestamp'2015-04-11 12:34:56' d FROM dual
)
SELECT d "Original Date",
to_char(d, 'dd-mm-yyyy') "Day-Month-Year",
to_char(d, 'hh24:mi') "Time in 24-hr format",
to_char(d, 'iw-iyyy') "ISO Year and Week of Year",
to_char(d, 'Month') "Month Name",
to_char(d, 'Year') "Year"
FROM dates;
The following statement extracts the datetime fields specified in the EXTRACT function from the input datetime expressions:
WITH dates AS (
SELECT date'2015-01-01' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-01-10' d FROM dual union
SELECT date'2015-02-01' d FROM dual union
SELECT timestamp'2015-03-03 23:44:32' d FROM dual union
SELECT timestamp'2015-04-11 12:34:56' d FROM dual
)
SELECT extract(minute from d) minutes,
extract(hour from d) hours,
extract(day from d) days,
extract(month from d) months,
extract(year from d) years
FROM dates;
The following statement displays the input numbers as per the format specified in the TO_CHAR function:
WITH nums AS (
SELECT 10 n FROM dual union
SELECT 9.99 n FROM dual union
SELECT 1000000 n FROM dual --one million
)
SELECT n "Input Number N",
to_char(n),
to_char(n, '9,999,999.99') "Number with Commas",
to_char(n, '0,000,000.000') "Zero-padded Number",
to_char(n, '9.9EEEE') "Scientific Notation"
FROM nums;
The following statement converts the input numbers as per the format specified in the TO_CHAR function:
WITH nums AS (
SELECT 10 n FROM dual union
SELECT 9.99 n FROM dual union
SELECT .99 n FROM dual union
SELECT 1000000 n FROM dual --one million
)
SELECT n "Input Number N",
to_char(n),
to_char(n, '9,999,999.99') "Number with Commas",
to_char(n, '0,000,000.000') "Zero_padded Number",
to_char(n, '9.9EEEE') "Scientific Notation",
to_char(n, '$9,999,990.00') Monetary,
to_char(n, 'X') "Hexadecimal Value"
FROM nums;
The following statement converts the input numbers as per the format specified in the TO_CHAR function:
WITH nums AS (
SELECT 10 n FROM dual union
SELECT 9.99 n FROM dual union
SELECT .99 n FROM dual union
SELECT 1000000 n FROM dual --one million
)
SELECT n "Input Number N",
to_char(n),
to_char(n, '9,999,999.99') "Number with Commas",
to_char(n, '0,000,000.000') "Zero_padded Number",
to_char(n, '9.9EEEE') "Scientific Notation",
to_char(n, '$9,999,990.00') Monetary,
to_char(n, 'XXXXXX') "Hexadecimal Value"
FROM nums;
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Using TO_CHAR to Format Dates and Numbers
TO_CHAR (datetime) Function: Example
The following statements create a table named empl_temp and populate it with employee details:
CREATE TABLE empl_temp
(
employee_id NUMBER(6),
first_name VARCHAR2(20),
last_name VARCHAR2(25),
email VARCHAR2(25),
hire_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE,
job_id VARCHAR2(10),
clob_column CLOB
);
INSERT INTO empl_temp
VALUES(111,'John','Doe','example.com','10-JAN-2015','1001','Experienced Employee');
INSERT INTO empl_temp
VALUES(112,'John','Smith','example.com','12-JAN-2015','1002','Junior Employee');
INSERT INTO empl_temp
VALUES(113,'Johnnie','Smith','example.com','12-JAN-2014','1002','Mid-Career Employee');
INSERT INTO empl_temp
VALUES(115,'Jane','Doe','example.com','15-JAN-2015','1005','Executive Employee');The following statement displays dates by using the short and long formats:
SELECT hire_date "Default",
TO_CHAR(hire_date,'DS') "Short",
TO_CHAR(hire_date,'DL') "Long"FROM empl_temp
WHERE employee_id IN (111, 112, 115);
Default Short Long
---------- ---------- --------------------------
10-JAN-15 1/10/2015 Saturday, January 10, 2015
12-JAN-15 1/12/2015 Monday, January 12, 2015
15-JAN-15 1/15/2015 Thursday, January 15, 2015Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Using the TO_CHAR Function