Lesson: Using Swing Components
Section: How to Use Various Components
How to Use Progress Bars
Sometimes a task running within a program might take a while to complete. A user-friendly program provides some indication to the user that the task is occurring, how long the task might take, and how much work has already been done. One way of indicating work, and perhaps the amount of progress, is to use an animated image.
Another way of indicating work is to set the wait cursor, using the
Cursor class and the Component-defined
setCursor method. For example, the following code makes the wait cursor be displayed when the cursor is over container (including any components it contains that have no cursor specified):
container.setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.WAIT_CURSOR));
To convey how complete a task is, you can use a progress bar like this one:
Sometimes you can't immediately determine the length of a long-running task, or the task might stay stuck at the same state of completion for a long time. You can show work without measurable progress by putting the progress bar in indeterminate mode. A progress bar in indeterminate mode displays animation to indicate that work is occurring. As soon as the progress bar can display more meaningful information, you should switch it back into its default, determinate mode. In the Java look and feel, indeterminate progress bars look like this:
Swing provides three classes to help you use progress bars:
-
JProgressBar - A visible component to graphically display how much of a total task has completed. See Using Determinate Progress Bars for information and an example of using a typical progress bar. The section Using Indeterminate Mode tells you how to animate a progress bar to show activity before the task's scope is known.
-
ProgressMonitor - Not a visible component. Instead, an instance of this class monitors the progress of a task and pops up a dialog if necessary. See How to Use Progress Monitors for details and an example of using a progress monitor.
-
ProgressMonitorInputStream - An input stream with an attached progress monitor, which monitors reading from the stream. You use an instance of this stream like any of the other input streams described in
Basic I/O. You can get the stream's progress monitor with a call to
getProgressMonitorand configure it as described in How to Use Progress Monitors.
After you see a progress bar and a progress monitor in action, Deciding Whether to Use a Progress Bar or a Progress Monitor can help you figure out which is appropriate for your application.
Using Determinate Progress Bars
Here's a picture of a small demo application that uses a progress bar to measure the progress of a task that runs in its own thread:
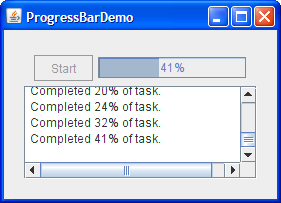
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run the ProgressBar Demo using
Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

The following code, from
ProgressBarDemo.java, creates and sets up the progress bar:
//Where member variables are declared: JProgressBar progressBar; ... //Where the GUI is constructed: progressBar = new JProgressBar(0, task.getLengthOfTask()); progressBar.setValue(0); progressBar.setStringPainted(true);
The constructor that creates the progress bar sets the progress bar's minimum and maximum values. You can also set these values with setMinimum and setMaximum. The minimum and maximum values used in this program are 0 and the length of the task, which is typical of many programs and tasks. However, a progress bar's minimum and maximum values can be any value, even negative. The code snippet also sets the progress bar's current value to 0.
The call to setStringPainted causes the progress bar to display, within its bounds, a textual indication of the percentage of the task that has completed. By default, the progress bar displays the value returned by its getPercentComplete method formatted as a percent, such as 33%. Alternatively, you can replace the default with a different string by calling setString. For example,
if (/*...half way done...*/)
progressBar.setString("Half way there!");
When the user clicks Start, an instance of the inner class Task is created and executed.
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt) {
startButton.setEnabled(false);
setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.WAIT_CURSOR));
done = false;
task = new Task();
task.addPropertyChangeListener(this);
task.execute();
}
Task is a subclass of
javax.swing.SwingWorker. The Task instance does three important things for ProgressBarDemo:
- The instance invokes the
doInBackgroundin a separate thread. This is where the long-running task is actually executed. Using a background thread instead of the event-dispatching thread prevents the user interface from freezing while the task is running. - When the background task is complete, the instance invokes the
donemethod in the event-dispatching thread. - The instance maintains a bound property,
progress, that is updated to indicate the progress of the task. ThepropertyChangemethod is invoked each timeprogresschanges.
See
Worker Threads and SwingWorker in
Concurrency in Swing for more information about SwingWorker.
The background task in ProgressBarDemo simulates a real task by reporting random amounts of progress at random intervals. The propertyChange method responds to changes in the the task's progress property by updating the progress bar:
public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) {
if (!done) {
int progress = task.getProgress();
progressBar.setValue(progress);
taskOutput.append(String.format(
"Completed %d%% of task.\n", progress));
}
When the background task is complete, the task's done method resets the progress bar:
public void done() {
//Tell progress listener to stop updating progress bar.
done = true;
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
startButton.setEnabled(true);
setCursor(null); //turn off the wait cursor
progressBar.setValue(progressBar.getMinimum());
taskOutput.append("Done!\n");
}
Note that the done method sets the done field to true, preventing propertyChange from making further updates to the progress bar. This is necessary because the final updates to the progress property may occcur after done is invoked.
Using Indeterminate Mode
In ProgressBarDemo2 indeterminate mode is set until actual progress begins:
public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) {
if (!done) {
int progress = task.getProgress();
if (progress == 0) {
progressBar.setIndeterminate(true);
taskOutput.append("No progress yet\n");
} else {
progressBar.setIndeterminate(false);
progressBar.setString(null);
progressBar.setValue(progress);
taskOutput.append(String.format(
"Completed %d%% of task.\n", progress));
}
}
}
The other changes in the code are related to string display. A progress bar that displays a string is likely to be taller than one that doesn't, and, as the demo designers, we've arbitarily decided that this progress bar should display a string only when it's in the default, determinate mode. However, we want to avoid the layout ugliness that might result if the progress bar changed height when it changed modes. Thus, the code leaves in the call to setStringPainted(true) but adds a call to setString("") so that no text will be displayed. Later, when the progress bar switches from indeterminate to determinate mode, invoking setString(null) makes the progress bar display its default string.
One change we did not make was removing the call to progressBar.setValue from the progress event handler. The call doesn't do any harm because an indeterminate progress bar doesn't use its value property, except perhaps to display it in the status string. In fact, keeping the progress bar's data as up-to-date as possible is a good practice, since some look and feels might not support indeterminate mode.
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run the ProgressBar2 Demo using
Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

- Push the Start button. Note that the progress bar starts animating as soon as the button is pressed, and then switches back into determinate mode (like ProgressBarDemo).
How to Use Progress Monitors
Now let's rewrite ProgressBarDemo to use a progress monitor instead of a progress bar. Here's a picture of the new demo program, ProgressMonitorDemo:
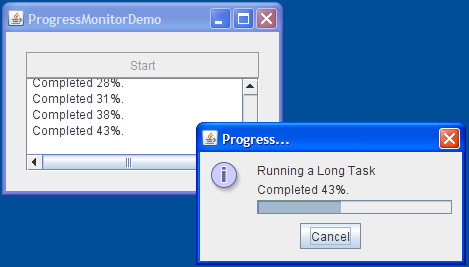
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run the ProgressMonitor Demo using
Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

- Push the Start button. After a certain amount of time, the program displays a progress dialog.
- Click the OK button. Note that the task continues even though the dialog is gone.
- Start another task. After the dialog pops up, click the Cancel button. The dialog goes away and the task stops.
A progress monitor cannot be used again, so a new one must be created each time a new task is started. This program creates a progress monitor each time the user starts a new task with the Start button.
Here's the statement that creates the progress monitor:
progressMonitor = new ProgressMonitor(ProgressMonitorDemo.this,
"Running a Long Task",
"", 0, task.getLengthOfTask());
This code uses ProgressMonitor's only constructor to create the monitor and initialize several arguments:
- The first argument provides the parent component to the dialog popped up by the progress monitor.
- The second argument is a string that describes the nature of the task being monitored. This string is displayed on the dialog. see The Progress Monitoring API for details about this argument.
- The third argument is another string that provides a changeable status note. The example uses an empty string to indicate that the dialog should make space for a changeable status note, but that the note is initially empty. If you provide
nullfor this argument, the note is omitted from the dialog. The example updates the note each time theprogressproperty changes. It updates the monitor's current value at the same time:int progress = task.getProgress(); String message = String.format("Completed %d%%.\n", progress); progressMonitor.setNote(message); progressMonitor.setProgress(progress); taskOutput.append(message); - The last two arguments provide the minimum and maximum values, respectively, for the progress bar displayed in the dialog.
By default, a progress monitor waits a minium of 500 milliseconds before deciding whether to pop up the dialog. It also waits for the progress to become more than the minimum value. If it calculates that the task will take more than 2000 milliseconds to complete, the progress dialog appears. To adjust the minimum waiting period, invoke setMillisToDecidedToPopup. To adjust the minimum progress time required for a dialog to appear, invoke setMillisToPopup.
By the simple fact that this example uses a progress monitor, it adds a feature that wasn't present in the version of the program that uses a progress bar: The user can cancel the task by clicking the Cancel button on the dialog. Here's the code in the example that checks to see if the user canceled the task or if the task exited normally:
if (progressMonitor.isCanceled() || task.isDone()) {
progressMonitor.close();
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
if (progressMonitor.isCanceled()) {
task.cancel(true);
taskOutput.append("Task canceled.\n");
} else {
taskOutput.append("Task completed.\n");
}
startButton.setEnabled(true);
}
Note that the progress monitor doesn't itself cancel the task. It provides the GUI and API to allow the program to do so easily.
Deciding Whether to Use a Progress Bar or a Progress Monitor
Use a progress bar if:
- You want more control over the configuration of the progress bar. If you are working directly with a progress bar, you can set it to be indeterminate, make it display vertically, provide a string for it to display, register change listeners on it, and provide it with a bounded range model to control the progress bar's minimum, maximum, and current values.
- The program needs to display other components along with the progress bar.
- You need more than one progress bar. With some tasks, you need to monitor more than one parameter. For example, an installation program might monitor disk space usage in addition to how many files have been successfully installed.
- You need to reuse the progress bar. A progress bar can be reused; a progress monitor cannot. Once the progress monitor has decided to display a dialog (or not), the progress monitor cannot do it again.
Use a progress monitor if:
- You want an easy way to display progress in a dialog.
- The running task is secondary and the user might not be interested in the progress of the task. Progress monitor provides a way for the user to dismiss the dialog while the task is still running.
- You want an easy way for the task to be cancelled. Progress monitor provides a GUI for the user to cancel the task. All you have to do is call progress monitor's
isCanceledmethod to find out if the user pressed the Cancel button. - Your task displays a short message periodically while running. The progress monitor dialog provides the
setNotemethod so that the task can provide further information about what it's doing. For example, an installation task might report the name of each file as it's installed. - The task might not take a long time to complete. You decide at what point a running task is taking long enough to warrant letting the user know about it. Progress monitor won't pop up a dialog if the task completes within the timeframe you set.
If you decide to use a progress monitor and the task you are monitoring is reading from an input stream, use the
ProgressMonitorInputStream class.
The Progress Monitoring API
The following tables list the commonly used API for using progress bars and progress monitors. Because JProgressBar is a subclass of JComponent, other methods you are likely to call on a JProgressBar are listed in The JComponent Class. Note that ProgressMonitor is a subclass of Object and is not a visual component.
The API for monitoring progress falls into these categories:
- Creating the Progress Bar
- Setting or Getting the Progress Bar's Constraints/Values
- Controlling the Progress Bar's Appearance
- Creating the Progress Monitor
- Configuring the Progress Monitor
- Terminating the Progress Monitor
| Constructor | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
JProgressBar() JProgressBar(int, int) |
Create a horizontal progress bar. The no-argument constructor initializes the progress bar with a minimum and initial value of 0 and a maximum of 100. The constructor with two integer arguments specifies the minimum and maximum values. |
|
JProgressBar(int) JProgressBar(int, int, int) |
Create a progress bar with the specified orientation, which can be either JProgressBar.HORIZONTAL or JProgressBar.VERTICAL. The optional second and third arguments specify minimum and maximum values. |
| JProgressBar(BoundedRangeModel) | Create a horizontal progress bar with the specified range model. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
void setValue(int) int getValue() |
Set or get the current value of the progress bar. The value is constrained by the minimum and maximum values. |
| double getPercentComplete() | Get the percent complete for the progress bar. |
|
void setMinimum(int) int getMinimum() |
Set or get the minimum value of the progress bar. |
|
void setMaximum(int) int getMaximum() |
Set or get the maximum value of the progress bar. |
|
void setModel(BoundedRangeModel) BoundedRangeModel getModel() |
Set or get the model used by the progress bar. The model establishes the progress bar's constraints and values, so you can use it directly as an alternative to using the individual set/get methods listed above. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| void setIndeterminate(boolean) | By specifying true, put the progress bar into indeterminate mode. Specifying false puts the progress bar back into its default, determinate mode. |
|
void setOrientation(int) int getOrientation() |
Set or get whether the progress bar is vertical or horizontal. Acceptable values are JProgressBar.VERTICAL or JProgressBar.HORIZONTAL. |
|
void setBorderPainted(boolean) boolean isBorderPainted() |
Set or get whether the progress bar has a border. |
|
void setStringPainted(boolean) boolean isStringPainted() |
Set or get whether the progress bar displays a percent string. By default, the value of the percent string is the value returned by getPercentComplete formatted as a percent. You can set the string to be displayed with setString. |
|
void setString(String) String getString() |
Set or get the percent string. |
| Method or Constructor | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ProgressMonitor(Component, Object, String, int, int) | Create a progress monitor. The Component argument is the parent for the monitor's dialog. The Object argument is a message to put on the option pane within the dialog. The value of this object is typically a String. The String argument is a changeable status note. The final two int arguments set the minimum and maximum values, respectively, for the progress bar used in the dialog. |
|
ProgressMonitor getProgressMonitor() (in ProgressMonitorInputStream) |
Gets a progress monitor that monitors reading from an input stream. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
void setMinimum(int) int getMinimum() |
Set or get the minimum value of the progress monitor. This value is used by the monitor to set up the progress bar in the dialog. |
|
void setMaximum(int) int getMaximum() |
Set or get the maximum value of the progress monitor. This value is used by the monitor to set up the progress bar in the dialog. |
| void setProgress(int) | Update the monitor's progress. |
void setNote(String)String getNote() |
Set or get the status note. This note is displayed on the dialog. To omit the status note from the dialog, provide null as the third argument to the monitor's constructor. |
void setMillisToDecideToPopup(int)int getMillisToDecideToPopup() |
Set or get the time after which the monitor should decide whether to popup a dialog. |
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
void close() |
Close the progress monitor. This disposes of the dialog. |
boolean isCanceled() |
Determine whether the user pressed the Cancel button. |
Examples that Monitor Progress
This following examples use JProgressBar or ProgressMonitor.
| Example | Where Described | Notes |
|---|---|---|
ProgressBarDemo |
This section | Uses a basic progress bar to show progress on a task running in a separate thread. |
ProgressBarDemo2 |
This section | Uses a basic progress bar to show progress on a task running in a separate thread. |
ProgressMonitorDemo |
This section | Modification of the previous example that uses a progress monitor instead of a progress bar. |
If you are programming in JavaFX, see Progress Bar and Progress Indicator.