Lesson: Using Swing Components
Section: Using Text Components
Text Component Features
The
JTextComponent class is the foundation for Swing text components. This class provides the following customizable features for all of its descendants:
- A model, known as a document, that manages the component's content.
- A view, which displays the component on screen.
- A controller, known as an editor kit, that reads and writes text and implements editing capabilities with actions.
- Support for infinite undo and redo.
- A pluggable caret and support for caret change listeners and navigation filters.
See the example called TextComponentDemo to explore these capabilities. Although the TextComponentDemo example contains a customized instance of JTextPane, the capabilities discussed in this section are inherited by all JTextComponent subclasses.
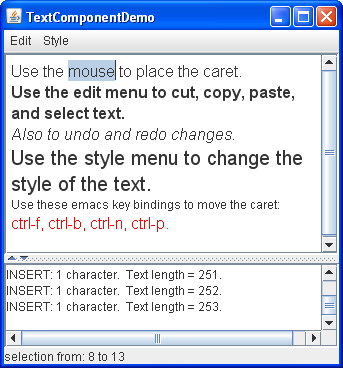
The upper text component is the customized text pane. The lower text component is an instance of JTextArea, which serves as a log that reports all changes made to the contents of the text pane. The status line at the bottom of the window reports either the location of the selection or the position of the caret, depending on whether text is selected.
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run TextComponentDemo using
Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

- Use the mouse to select text and place the cursor in the text pane. Information about the selection and cursor is displayed at the bottom of the window.
- Enter text by typing on the keyboard. You can move the caret around using the arrow keys on the keyboard or the four emacs key bindings: Ctrl-B (backward one character), Ctrl-F (forward one character), Ctrl-N (down one line), and Ctrl-P (up one line).
- Open the Edit menu, and use its menu items to edit text in the text pane. Make a selection in the text area at the bottom of the window. Because the text area is not editable, only some of the Edit menu's commands, like copy-to-clipboard, work. It is important to note though, that the menu operates on both text components.
- Use the items in the Style menu to apply different styles to the text in the text pane.
Using the TextComponentDemo example as a reference point, this section covers the following topics:
- Associating Text Actions With Menus and Buttons
- Associating Text Actions With Key Strokes
- Implementing Undo and Redo
- Concepts: About Documents
- Implementing a Document Filter
- Listening for Changes on a Document
- Listening for Caret and Selection Changes
- Concepts: About Editor Kits
Associating Text Actions With Menus and Buttons
All Swing text components support standard editing commands such as cut, copy, paste, and insert characters. Each editing command is represented and implemented by an Action object. (To learn more about actions see
How to Use Actions.) Actions allow you to associate a command with a GUI component, such as a menu item or button, and therefore build a GUI around a text component.
You can invoke the getActions method on any text component to receive an array containing all actions supported by this component. It is also possible to load the array of actions into a HashMap so your program can retrieve an action by name. Here is the code from the TextComponentDemo example that takes the actions from the text pane and loads them into a HashMap.
private HashMap<Object, Action> createActionTable(JTextComponent textComponent) {
HashMap<Object, Action> actions = new HashMap<Object, Action>();
Action[] actionsArray = textComponent.getActions();
for (int i = 0; i < actionsArray.length; i++) {
Action a = actionsArray[i];
actions.put(a.getValue(Action.NAME), a);
}
return actions;
}
Here is the method for retrieving an action by its name from the hash map:
private Action getActionByName(String name) {
return actions.get(name);
}
You can use both methods verbatim in your programs.
The following code shows how the cut menu item is created and associated with the action of removing text from the text component.
protected JMenu createEditMenu() {
JMenu menu = new JMenu("Edit");
...
menu.add(getActionByName(DefaultEditorKit.cutAction));
...
This code gets the action by name using the handy method shown previously. It then adds the action to the menu. That is all you need to do. The menu and the action take care of everything else. Note that the name of the action comes from
DefaultEditorKit. This kit provides actions for basic text editing and is the superclass for all the editor kits provided by Swing. So its capabilities are available to all text components unless thay are overridden by a customization.
For efficiency, text components share actions. The Action object returned by getActionByName(DefaultEditorKit.cutAction) is shared by the uneditable JTextArea at the bottom of the window. This sharing characteristic has two important ramifications:
- Generally, you should not modify
Actionobjects you get from editor kits. If you do, the changes affect all text components in your program. Actionobjects can operate on other text components in the program, sometimes more than you intended. In this example, even though it is not editable, theJTextAreashares actions with theJTextPane. (Select some text in the text area, then choose the cut-to-clipboard menu item. You will hear a beep because the text area is not editable.) If you do not want to share, instantiate theActionobject yourself.DefaultEditorKitdefines a number of usefulActionsubclasses.
Here is the code that creates the Style menu and puts the Bold menu item in it:
protected JMenu createStyleMenu() {
JMenu menu = new JMenu("Style");
Action action = new StyledEditorKit.BoldAction();
action.putValue(Action.NAME, "Bold");
menu.add(action);
...
The StyledEditorKit provides Action subclasses to implement editing commands for styled text. You will note that instead of getting the action from the editor kit, this code creates an instance of the BoldAction class. Thus, this action is not shared with any other text component, and changing its name will not affect any other text component.
Associating Text Actions With Key Strokes
In addition to associating an action with a GUI component, you can also associate an action with a key stroke by using a text component's input map. Input maps are described in How to Use Key Bindings.
The text pane in the TextComponentDemo example supports four key bindings not provided by default.
- Ctrl-B to move the caret backward one character
- Ctrl-F to move the caret forward one character
- Ctrl-N to move the caret down one line
- Ctrl-P to move the caret up one line
The following code adds the Ctrl-B key binding to the text pane. The code for adding the other three bindings listed above is similar.
InputMap inputMap = textPane.getInputMap();
KeyStroke key = KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_B,
Event.CTRL_MASK);
inputMap.put(key, DefaultEditorKit.backwardAction);
First, the code obtains the text component's input map. Next, it finds a
KeyStroke object representing the Ctrl-B key sequence. Finally, the code binds the key stroke to the Action that moves the cursor backward.
Implementing Undo and Redo
Implementing undo and redo has two parts:
- Remembering undoable edits.
- Implementing the undo and redo commands and providing a user interface for them.
Part 1: Remembering Undoable Edits
To support undo and redo, a text component must remember each edit that occurs, the order of edits, and what is needed to undo each edit. The example program uses an instance of the
UndoManager class to manage its list of undoable edits. The undo manager is created where the member variables are declared:
protected UndoManager undo = new UndoManager();
Now, let us look at how the program discovers undoable edits and adds them to the undo manager.
A document notifies interested listeners whenever an undoable edit occurs on the document content. An important step in implementing undo and redo is to register an undoable edit listener on the document of the text component. The following code adds an instance of MyUndoableEditListener to the text pane's document:
doc.addUndoableEditListener(new MyUndoableEditListener());
The undoable edit listener used in our example adds the edit to the undo manager's list:
protected class MyUndoableEditListener
implements UndoableEditListener {
public void undoableEditHappened(UndoableEditEvent e) {
//Remember the edit and update the menus
undo.addEdit(e.getEdit());
undoAction.updateUndoState();
redoAction.updateRedoState();
}
}
Note that this method updates two objects: undoAction and redoAction. These are the action objects attached to the Undo and Redo menu items, respectively. The next step shows you how to create the menu items and how to implement the two actions. For general information about undoable edit listeners and undoable edit events, see How to Write an Undoable Edit Listener.
Note:
By default, each undoable edit undoes a single character entry. It is possible with some effort to group edits so that a series of key strokes is combined into one undoable edit. Grouping edits in this manner would require you to define a class that intercepts undoable edit events from the document, combining them if appropriate and forwarding the results to your undoable edit listener.
Part 2: Implementing the Undo and Redo Commands
The first step in implementing undo and redo is to create the actions to put in the Edit menu.
JMenu menu = new JMenu("Edit");
//Undo and redo are actions of our own creation
undoAction = new UndoAction();
menu.add(undoAction);
redoAction = new RedoAction();
menu.add(redoAction);
...
The undo and redo actions are implemented by custom AbstractAction subclasses: UndoAction and RedoAction, respectively. These classes are inner classes of the example's primary class.
When the user invokes the undo command, the actionPerformed method of the UndoAction class is called:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
undo.undo();
} catch (CannotUndoException ex) {
System.out.println("Unable to undo: " + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
}
updateUndoState();
redoAction.updateRedoState();
}
This method calls the undo manager's undo method and updates the menu items to reflect the new undo/redo state.
Similarly, when the user invokes the redo command, the actionPerformed method of the RedoAction class is called:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
undo.redo();
} catch (CannotRedoException ex) {
System.out.println("Unable to redo: " + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
}
updateRedoState();
undoAction.updateUndoState();
}
This method is similar to undo, except that it calls the undo manager's redo method.
Much of the code in the UndoAction and RedoAction classes is dedicated to enabling and disabling the actions as appropriate of the current state, and changing the names of the menu items to reflect the edit to be undone or redone.
Note:
The implementation of undo and redo in the TextComponentDemo example was taken from the NotePad demo that comes with the JDK software. Many programmers will also be able to copy this implementation of undo/redo without modification.
Concepts: About Documents
Like other Swing components, a text component separates its data (known as the model) from its view of the data. If you are not yet familiar with the model-view split used by Swing components, refer to Using Models.
A text component's model is known as a document and is an instance of a class that implements the
Document interface. A document provides the following services for a text component:
- Contains the text. A document stores the textual content in
Elementobjects, which can represent any logical text structure, such as paragraphs, or text runs that share styles. We do not describeElementobjects here. - Provides support for editing the text through the
removeandinsertStringmethods. - Notifies document listeners and undoable edit listeners of changes to the text.
- Manages
Positionobjects, which track a particular location within the text even as the text is modified. - Allows you to obtain information about the text, such as its length, and segments of the text as a string.
The Swing text package contains a subinterface of Document,
StyledDocument, that adds support for marking up the text with styles. One JTextComponent subclass, JTextPane, requires that its document be a StyledDocument rather than merely a Document.
The javax.swing.text package provides the following hierarchy of document classes, which implement specialized documents for the various JTextComponent subclasses:
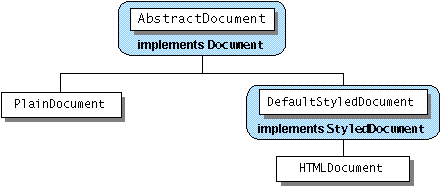
A PlainDocument is the default document for text fields, password fields, and text areas. PlainDocument provides a basic container for text where all the text is displayed in the same font. Even though an editor pane is a styled text component, it uses an instance of PlainDocument by default. The default document for a standard JTextPane is an instance of DefaultStyledDocument — a container for styled text in no particular format. However, the document instance used by any particular editor pane or text pane depends on the type of content bound to it. If you use the setPage method to load text into an editor pane or text pane, the document instance used by the pane might change. Refer to How to Use Editor Panes and Text Panes for details.
Although you can set the document of a text component, it is usually easier to allow it to set automatically, and if necessary, use a document filter to change how the text component's data is set. You can implement certain customizations either by installing a document filter or by replacing a text component's document with one of your own. For example, the text pane in the TextComponentDemo example has a document filter that limits the number of characters the text pane can contain.
Implementing a Document Filter
To implement a document filter, create a subclass of
DocumentFilter and then attach it to a document using the setDocumentFilter method defined in the AbstractDocument class. Although it is possible to have documents that do not descend from AbstractDocument, by default Swing text components use AbstractDocument subclasses for their documents.
The TextComponentDemo application has a document filter,
DocumentSizeFilter, that limits the number of characters that the text pane can contain. Here is the code that creates the filter and attaches it to the text pane's document:
...//Where member variables are declared:
JTextPane textPane;
AbstractDocument doc;
static final int MAX_CHARACTERS = 300;
...
textPane = new JTextPane();
...
StyledDocument styledDoc = textPane.getStyledDocument();
if (styledDoc instanceof AbstractDocument) {
doc = (AbstractDocument)styledDoc;
doc.setDocumentFilter(new DocumentSizeFilter(MAX_CHARACTERS));
}
To limit the characters allowed in the document, DocumentSizeFilter overrides the DocumentFilter class's insertString method, which is called each time that text is inserted into the document. It also overrides the replace method, which is most likely to be called when the user pastes in new text. In general, text insertion can result when the user types or pastes in new text, or when the setText method is called. Here is the DocumentSizeFilter class's implementation of the insertString method:
public void insertString(FilterBypass fb, int offs,
String str, AttributeSet a)
throws BadLocationException {
if ((fb.getDocument().getLength() + str.length()) <= maxCharacters)
super.insertString(fb, offs, str, a);
else
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
}
The code for replace is similar. The
FilterBypass parameter to the methods defined by the DocumentFilter class is simply an object that enables the document to be updated in a thread-safe way.
Because the preceding document filter is concerned with additions to the document's data, it only overrides the insertString and replace methods. Most document filters would override DocumentFilter's remove method as well.
Listening for Changes on a Document
You can register two different types of listeners on a document: document listeners and undoable edit listeners. This subsection describes document listeners. For information about undoable edit listeners, refer to Implementing Undo and Redo.
A document notifies registered document listeners of changes to the document. Use a document listener to create a reaction when text is inserted or removed from a document, or when the text style changes.
The TextComponentDemo program uses a document listener to update the change log whenever a change is made to the text pane. The following line of code registers an instance of the MyDocumentListener class as a listener on the text pane's document:
doc.addDocumentListener(new MyDocumentListener());
Here is the implementation of the MyDocumentListener class:
protected class MyDocumentListener implements DocumentListener {
public void insertUpdate(DocumentEvent e) {
displayEditInfo(e);
}
public void removeUpdate(DocumentEvent e) {
displayEditInfo(e);
}
public void changedUpdate(DocumentEvent e) {
displayEditInfo(e);
}
private void displayEditInfo(DocumentEvent e) {
Document document = (Document)e.getDocument();
int changeLength = e.getLength();
changeLog.append(e.getType().toString() + ": "
+ changeLength + " character"
+ ((changeLength == 1) ? ". " : "s. ")
+ " Text length = " + document.getLength()
+ "." + newline);
}
}
The listener implements three methods for handling three different types of document events: insertion, removal, and style changes. StyledDocument instances can fire all three types of events. PlainDocument instances fire events only for insertion and removal. For general information about document listeners and document events, see How to Write a Document Listener.
Remember that the document filter for this text pane limits the number of characters allowed in the document. If you try to add more text than the document filter allows, the document filter blocks the change and the listener's insertUpdate method is not called. Document listeners are notified of changes only if the change has already occurred.
You may want to change the document's text within a document listener. However, you should never modify the contents of a text component from within a document listener. If you do, the program will likely deadlock. Instead, you can use a formatted text field or provide a document filter.
Listening for Caret and Selection Changes
The TextComponentDemo program uses a caret listener to display the current position of the caret or, if text is selected, the extent of the selection.
The caret listener class in this example is a JLabel subclass. Here is the code that creates the caret listener label and makes it a caret listener of the text pane:
//Create the status area
CaretListenerLabel caretListenerLabel = new CaretListenerLabel(
"Caret Status");
...
textPane.addCaretListener(caretListenerLabel);
A caret listener must implement one method, caretUpdate, which is called each time the caret moves or the selection changes. Here is the CaretListenerLabel implementation of caretUpdate:
public void caretUpdate(CaretEvent e) {
//Get the location in the text
int dot = e.getDot();
int mark = e.getMark();
if (dot == mark) { // no selection
try {
Rectangle caretCoords = textPane.modelToView(dot);
//Convert it to view coordinates
setText("caret: text position: " + dot +
", view location = [" +
caretCoords.x + ", " + caretCoords.y + "]" +
newline);
} catch (BadLocationException ble) {
setText("caret: text position: " + dot + newline);
}
} else if (dot < mark) {
setText("selection from: " + dot + " to " + mark + newline);
} else {
setText("selection from: " + mark + " to " + dot + newline);
}
}
As you can see, this listener updates its text label to reflect the current state of the caret or selection. The listener gets the information to display from the caret event object. For general information about caret listeners and caret events, see How to Write a Caret Listener.
As with document listeners, a caret listener is passive. It reacts to changes in the caret or in the selection, but does not change the caret or the selection itself. If you want to change the caret or selection, use a navigation filter or a custom caret.
Implementing a navigation filter is similar to implementing a document filter. First, write a subclass of
NavigationFilter. Then attach an instance of the subclass to a text component with the setNavigationFilter method.
You might create a custom caret to customize the appearance of a caret. To create a custom caret, write a class that implements the
Caret interface — perhaps by extending the
DefaultCaret class. Then provide an instance of your class as an argument to the setCaret method on a text component.
Concepts: About Editor Kits
Text components use an EditorKit to tie the various pieces of the text component together. The editor kit provides the view factory, document, caret, and actions. An editor kit also reads and writes documents of a particular format. Although all text components use editor kits, some components hide theirs. You cannot set or get the editor kit used by a text field or text area. Editor panes and text panes provide the getEditorKit method to get the current editor kit and the setEditorKit method to change it.
For all components, the JTextComponent class provides the API for you to indirectly invoke or customize some editor kit capabilities. For example, JTextComponent provides the read and write methods, which invoke the editor kit's read and write methods. JTextComponent also provides a method, getActions, which returns all of the actions supported by a component.
The Swing text package provides the following editor kits:
-
DefaultEditorKit - Reads and writes plain text, and provides a basic set of editing commands. Details about how the text system treats newlines can be found in the
DefaultEditorKitAPI documentation. Briefly, the '\n' character is used internally, but the document or platform line separators are used when writing files. All the other editor kits are descendants of theDefaultEditorKitclass. -
StyledEditorKit - Reads and writes styled text, and provides a minimal set of actions for styled text. This class is a subclass of
DefaultEditorKitand is the editor kit used byJTextPaneby default. -
HTMLEditorKit - Reads, writes, and edits HTML. This is a subclass of
StyledEditorKit.
Each of the editor kits listed above has been registered with the JEditorPane class and associated with the text format that the kit reads, writes, and edits. When a file is loaded into an editor pane, the pane checks the format of the file against its registered kits. If a registered kit is found that supports that file format, the pane uses the kit to read the file, display, and edit it. Thus, the editor pane effectively transforms itself into an editor for that text format. You can extend JEditorPane to support your own text format by creating an editor kit for it, and then using JEditorPane's registerEditorKitForContentType to associate your kit with your text format.