6 Creating a PDB from Scratch
Use the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement to create a PDB in a CDB using the files of the PDB seed (PDB$SEED).
You can also use this statement to create an application PDB in an application container using the files of an application seed or the PDB seed.
This chapter contains the following topics:
- About Creating a PDB from Scratch
Use theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement to create a new PDB by using the files of the PDB seed or an application PDB from the files of an application seed or the PDB seed. - Creating a PDB
Using theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement, you can create a PDB from the PDB seed, and you can create an application PDB from an application seed or the PDB seed. - Creating a PDB: Examples
These examples create a new PDB namedsalespdband asalesadmlocal administrator given different factors.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement
Parent topic: Creating and Removing PDBs and Application Containers
6.1 About Creating a PDB from Scratch
Use the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement to create a new PDB by using the files of the PDB seed or an application PDB from the files of an application seed or the PDB seed.
The statement copies these files to a new location and associates them with the new PDB. The following figure illustrates how this technique creates a new PDB in a CDB with the CDB root as the current container.
Figure 6-1 Create a PDB in the CDB Root Using the PDB$SEED Files
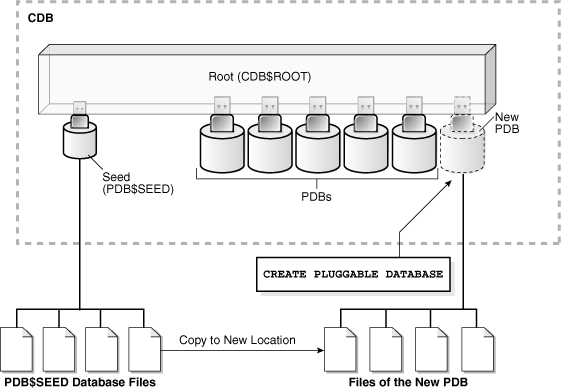
Description of "Figure 6-1 Create a PDB in the CDB Root Using the PDB$SEED Files"
The following figure illustrates how this technique creates a new application PDB in an application container with the application root as the current container.
Figure 6-2 Create a PDB in an Application Root Using the Application Seed Files
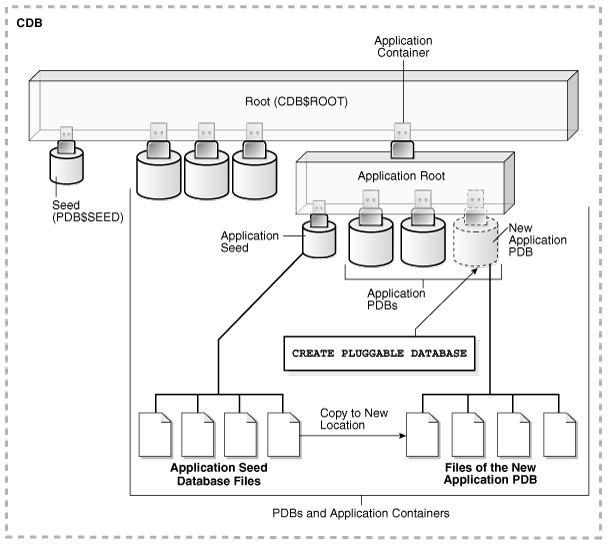
Description of "Figure 6-2 Create a PDB in an Application Root Using the Application Seed Files"
See Also:
When an application container includes an application seed, and a CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement is run in the application root to create an application PDB from the seed, the application PDB is created using the application seed. However, when an application container does not include an application seed, and a CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement is run in the application root to create an application PDB from the seed, the application PDB is created using the PDB seed (PDB$SEED ).
When you create a new PDB or application PDB from the seed, you must specify an administrator for the PDB or application PDB in the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement. The statement creates the administrator as a local user in the PDB and grants the PDB_DBA role locally to the administrator.
Before creating a PDB using the PDB seed or an application seed, address the questions that apply to creating a PDB from the seed in Table 5-3. The table describes which CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE clauses you must specify based on different factors.
See Also:
Parent topic: Creating a PDB from Scratch
6.2 Creating a PDB
Using the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, you can create a PDB from the PDB seed, and you can create an application PDB from an application seed or the PDB seed.
Prerequisites
Before creating a PDB from the PDB seed (PDB$SEED) or an application PDB from an application seed or the PDB seed, complete the prerequisites described in "General Prerequisites for PDB Creation".
To create a PDB:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the CDB root or an application root.
When the current container is the CDB root, the PDB is created in the CDB using the files of the PDB seed.
When the current container is an application root, the application PDB is created in the application container using the files of the application seed. If there is no application seed in the application container, then the application PDB is created in the application container using the files of the PDB seed.
-
Run the
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement, and specify a local administrator for the PDB. Specify other clauses when they are required.After you create the PDB, it is in mounted mode, and its status is
NEW. You can view the open mode of a PDB by querying theOPEN_MODEcolumn in theV$PDBSview. You can view the status of a PDB by querying theSTATUScolumn of theCDB_PDBSorDBA_PDBSview.A new default service is created for the PDB. The service has the same name as the PDB and can be used to access the PDB. Oracle Net Services must be configured properly for clients to access this service.
-
Open the new PDB in read/write mode.
You must open the new PDB in read/write mode for Oracle Database to complete the integration of the new PDB into the CDB. An error is returned if you attempt to open the PDB in read-only mode. After the PDB is opened in read/write mode, its status is
NORMAL. -
Back up the PDB.
A PDB cannot be recovered unless it is backed up.
A local user with the name of the specified local administrator is created and granted the PDB_DBA common role locally in the PDB. If this user was not granted administrator privileges during PDB creation, then use the SYS and SYSTEM common users to administer to the PDB.
Note:
If an error is returned during PDB creation, then the PDB being created might be in an UNUSABLE state. You can check a PDB's state by querying the CDB_PDBS or DBA_PDBS view, and you can learn more about PDB creation errors by checking the alert log. An unusable PDB can only be dropped, and it must be dropped before a PDB with the same name as the unusable PDB can be created.
See Also:
-
"Modifying the Open Mode of One or More PDBs" for more information
-
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User’s Guide for information about backing up a PDB
Parent topic: Creating a PDB from Scratch
6.3 Creating a PDB: Examples
These examples create a new PDB named salespdb and a salesadm local administrator given different factors.
In addition to creating the salespdb PDB, this statement grants the PDB_DBA role to the PDB administrator salesadm and grants the specified predefined Oracle roles to the PDB_DBA role locally in the PDB.
In each example, the root to which the new PDB belongs depends on the current container when the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement is run:
-
When the current container is the CDB root, the new PDB is created in the CDB root.
-
When the current container is an application root in an application container, the new PDB is created as an application PDB in the application root.
This section contains the following examples:
- Creating a PDB Using No Clauses: Example
This example shows the simplest way to create a PDB. - Creating a PDB and Granting Predefined Oracle Roles to the PDB Administrator: Example
This example uses theROLESparameter to grant a predefined role. - Creating a PDB Using Multiple Clauses: Example
This example creating a PDB using theSTORAGE,DEFAULT TABLESPACE,PATH_PREFIX, andFILE_NAME_CONVERTclauses.
Parent topic: Creating a PDB from Scratch
6.3.1 Creating a PDB Using No Clauses: Example
This example shows the simplest way to create a PDB.
This example assumes the following factors:
-
Storage limits are not required for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is not required. -
The PDB does not require a default tablespace.
-
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The
FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause and theCREATE_FILE_DESTclause are not required.Either Oracle Managed Files is enabled for the CDB, or the
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is set. The files associated with the PDB seed or application seed will be copied to a new location based on the Oracle Managed Files configuration or the initialization parameter setting. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required. -
No predefined Oracle roles need to be granted to the
PDB_DBArole.
The following statement creates the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb ADMIN USER salesadm IDENTIFIED BY password;
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for information about using Oracle Managed Files
-
Oracle Database Reference for information about the
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter -
Oracle Database Security Guide for guidelines about choosing passwords
Parent topic: Creating a PDB: Examples
6.3.2 Creating a PDB and Granting Predefined Oracle Roles to the PDB Administrator: Example
This example uses the ROLES parameter to grant a predefined role.
This example assumes the following factors:
-
Storage limits are not required for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is not required. -
The PDB does not require a default tablespace.
-
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The
FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause and theCREATE_FILE_DESTclause are not required.Either Oracle Managed Files is enabled, or the
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is set. The files associated with the PDB seed or application seed will be copied to a new location based on the Oracle Managed Files configuration or the initialization parameter setting. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required. -
The
PDB_DBArole should be granted the following predefined Oracle role locally:DBA.
The following statement creates the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb
ADMIN USER salesadm IDENTIFIED BY password
ROLES=(DBA);
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for information about using Oracle Managed Files
-
Oracle Database Reference for information about the
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter -
Oracle Database Security Guide for guidelines about choosing passwords
Parent topic: Creating a PDB: Examples
6.3.3 Creating a PDB Using Multiple Clauses: Example
This example creating a PDB using the STORAGE, DEFAULT TABLESPACE, PATH_PREFIX, and FILE_NAME_CONVERT clauses.
This example assumes the following factors:
-
Storage limits must be enforced for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is required. Specifically, all tablespaces that belong to the PDB must not exceed 2 gigabytes. -
A default permanent tablespace is required for any non-administrative users for which you do not specify a different permanent tablespace. Specifically, this example creates a default permanent tablespace named
saleswith the following characteristics:-
The single data file for the tablespace is
sales01.dbf, and the statement creates it in the/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdbdirectory. -
The
SIZEclause specifies that the initial size of the tablespace is 250 megabytes. -
The
AUTOEXTENDclause enables automatic extension for the file.
-
-
The path prefix must be added to the PDB directory object paths. Therefore, the
PATH_PREFIXclause is required. In this example, the path prefix/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/is added to the PDB’s directory object paths. -
The
CREATE_FILE_DESTclause will not be used, Oracle Managed Files is not enabled, and thePDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is not set. Therefore, theFILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is required. Specify the location of the data files for the PDB seed or application seed on your system. In this example, Oracle Database copies the files from/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseedto/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required. -
No predefined Oracle roles need to be granted to the
PDB_DBArole.
The following statement creates the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb
ADMIN USER salesadm IDENTIFIED BY password
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G)
DEFAULT TABLESPACE sales
DATAFILE '/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/sales01.dbf' SIZE 250M AUTOEXTEND ON
PATH_PREFIX = '/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/'
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/pdbseed/', '/disk1/oracle/dbs/salespdb/');
See Also:
-
"Example 19-7" to learn how to view the location of the data files for the PDB seed or application seed
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the
DEFAULT TABLESPACEclause -
Oracle Database Security Guide for guidelines about choosing passwords
Parent topic: Creating a PDB: Examples