12 Replaying a Database Workload
This chapter describes how to replay a database workload on the test system and contains the following sections:
Tip:
Before you can replay a database workload, you must first:
-
Capture the workload on the production system, as described in Capturing a Database Workload
-
Preprocess the captured workload, as described in Preprocessing a Database Workload
12.1 Steps for Replaying a Database Workload
12.1.1 Setting Up the Replay Directory
The captured workload must have been preprocessed and copied to the replay system. A directory object for the directory to which the preprocessed workload is copied must exist in the replay system.
12.1.2 Restoring the Database
DUPLICATE capabilities to create the test database. For more information, see "Prerequisites for Capturing a Database Workload".
After the database is created with the appropriate application data on the replay system, perform the system change you want to test, such as a database or operating system upgrade. The primary purpose of Database Replay is to test the effect of system changes on a captured workload. Therefore, the system changes you make should define the test you are conducting with the captured workload.
12.1.3 Resolving References to External Systems
-
Database links
It is typically not desirable for the replay system to interact with other databases. Therefore, you should reconfigure all database links to point to an appropriate database that contains the data needed for replay.
-
External tables
All external files specified using directory objects referenced by external tables need to be available to the database during replay. The content of these files should be the same as during capture, and the filenames and directory objects used to define the external tables should also be valid.
-
Directory objects
You should reconfigure any references to directories on the production system by appropriately redefining the directory objects present in the replay system after restoring the database.
-
URLs
URLs/URIs that are stored in the database need to be configured so that Web services accessed during the workload capture will point to the proper URLs during replay. If the workload refers to URLs that are stored in the production system, you should isolate the test system network during replay.
-
E-mails
To avoid resending E-mail notifications during replay, any E-mail server accessible to the replay system should be configured to ignore requests for outgoing E-mails.
Tip:
To avoid impacting other production systems during replay, Oracle strongly recommends running the replay within an isolated private network that does not have access to the production environment hosts.
12.1.4 Connection Remapping
During workload capture, connection strings used to connect to the production system are captured. In order for the replay to succeed, you need to remap these connection strings to the replay system. The replay clients can then connect to the replay system using the remapped connections.
For Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) databases, you can map all connection strings to a load balancing connection string. This is especially useful if the number of nodes on the replay system is different from the capture system. Alternatively, if you want to direct workload to specific instances, you can use services or explicitly specify the instance identifier in the remapped connection strings.
12.1.5 User Remapping
During workload capture, the username of the database user or schema used to connect to the production system is captured. You can choose to remap the captured username to that of a new user or schema.
12.1.6 Specifying Replay Options
12.1.6.1 Specifying the Synchronization Method
The synchronization parameter controls the synchronization method used for database replay.
If the parameter is set to TIME, the replay will use the same wall-clock timing as the capture. All database session login times will be replayed exactly as the capture. Likewise, all timing between transactions within database sessions will be preserved and replayed as captured. This synchronization method will produce good replays for most workloads.
If this parameter is set to SCN, the COMMIT order in the captured workload will be observed during replay and all replay actions will be executed only after all dependent COMMIT actions have completed. This synchronization method may introduce significant delays for some workloads. If this is the case, it is recommended to use TIME as the synchronization parameter.
If this parameter is set to OBJECT_ID, all replay actions will be executed only after all relevant COMMIT actions have completed. Relevant COMMIT actions must meet the following criteria:
-
Issued before the given action in the workload capture
-
Modified at least one of the database objects for which the given action is referencing, either implicitly or explicitly
Setting this parameter to OBJECT_ID allows for more concurrency during workload replays for COMMIT actions that do not reference the same database objects during workload capture.
12.1.6.2 Controlling Session Connection Rate
connect_time_scale parameter enables you to scale the elapsed time between the time when the workload capture began and each session connects. You can use this option to manipulate the session connect time during replay with a given percentage value. The default value is 100, which will attempt to connect all sessions as captured. Setting this parameter to 0 will attempt to connect all sessions immediately.
12.1.6.3 Controlling Request Rate Within a Session
think_time_scale parameter to scale user think time during replay.
If user calls are being executed slower during replay than during capture, you can make the database replay attempt to catch up by setting the think_time_auto_correct parameter to TRUE. This will make the replay client shorten the think time between calls, so that the overall elapsed time of the replay will more closely match the captured elapsed time.
If user calls are being executed faster during replay than during capture, setting the think_time_auto_correct parameter to TRUE will not change the think time. The replay client will not increase the think time between calls to match the captured elapsed time.
12.1.7 Using Filters with Workload Replay
By default, all captured database calls are replayed during workload replay. You can use workload filters to specify which database calls to include in or exclude from the workload during workload replay.
Workload replay filters are first defined and then added to a replay filter set so they can be used in a workload replay. There are two types of workload filters: inclusion filters and exclusion filters. Inclusion filters enable you to specify database calls that will be replayed. Exclusion filters enable you to specify database calls that will not be replayed. You can use either inclusion filters or exclusion filters in a workload replay, but not both. The workload filter is determined as an inclusion or exclusion filter when the replay filter set is created.
12.1.8 Setting Up Replay Clients
wrc located in the $ORACLE_HOME/bin directory) where each thread submits a workload from a captured session. Before replay begins, the database will wait for replay clients to connect. At this point, you need to set up and start the replay clients, which will connect to the replay system and send requests based on what has been captured in the workload.Before starting replay clients, ensure that the:
-
Replay client software is installed on the hosts where it will run
-
Replay clients have access to the replay directory
-
Replay directory contains the preprocessed workload capture
-
Replay user has the correct user ID, password, and privileges (the replay user needs the DBA role and cannot be the
SYSuser) -
Replay clients are not started on a system that is running the database
-
Replay clients read the capture directory on a file system that is different from the one on which the database files reside
To do this, copy the capture directory to the system where the replay client will run. After the replay is completed, you can delete the capture directory.
After these prerequisites are met, you can proceed to set up and start the replay clients using the wrc executable. The wrc executable uses the following syntax:
wrc [user/password[@server]] MODE=[value] [keyword=[value]]
The parameters user, password and server specify the username, password and connection string used to connect to the replay database. The parameter mode specifies the mode in which to run the wrc executable. Possible values include replay (the default), calibrate, and list_hosts. The parameter keyword specifies the options to use for the execution and is dependent on the mode selected. To display the possible keywords and their corresponding values, run the wrc executable without any arguments.
The following sections describe the modes that you can select when running the wrc executable:
12.1.8.1 Calibrating Replay Clients
Since one replay client can initiate multiple sessions with the database, it is not necessary to start a replay client for each session that was captured. The number of replay clients that need to be started depends on the number of workload streams, the number of hosts, and the number of replay clients for each host.
To estimate the number of replay clients and hosts that are required to replay a particular workload, run the wrc executable in calibrate mode.
In calibrate mode, the wrc executable accepts the following keywords:
-
replaydirspecifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory. -
process_per_cpuspecifies the maximum number of client processes that can run per CPU. The default value is 4. -
threads_per_processspecifies the maximum number of threads that can run within a client process. The default value is 50.
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in calibrate mode:
%> wrc mode=calibrate replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable is executed to estimate the number of replay clients and hosts that are required to replay the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory. In the following sample output, the recommendation is to use at least 21 replay clients divided among 6 CPUs:
Workload Replay Client: Release 12.1.0.0.1 - Production on Fri Sept 30 13:06:33 2011 Copyright (c) 1982, 2011, Oracle. All rights reserved. Report for Workload in: /oracle/replay/ ----------------------- Recommendation: Consider using at least 21 clients divided among 6 CPU(s). Workload Characteristics: - max concurrency: 1004 sessions - total number of sessions: 1013 Assumptions: - 1 client process per 50 concurrent sessions - 4 client process per CPU - think time scale = 100 - connect time scale = 100 - synchronization = TRUE
12.1.8.2 Starting Replay Clients
wrc executable in replay mode on the hosts where they are installed. Once started, each replay client will initiate one or more sessions with the database to drive the workload replay.
In replay mode, the wrc executable accepts the following keywords:
-
useridandpasswordspecify the user ID and password of a replay user for the replay client. If unspecified, these values default to thesystemuser. -
serverspecifies the connection string that is used to connect to the replay system. If unspecified, the value defaults to an empty string. -
replaydirspecifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory. -
workdirspecifies the directory where the client logs will be written. This parameter is only used with thedebugparameter for debugging purposes. -
debugspecifies whether debug data will be created. Possible values include:-
onDebug data will be written to files in the working directory
-
offNo debug data will be written (the default value)
Note:
Before running the
wrcexecutable in debug mode, contact Oracle Support for more information. -
-
connection_overridespecifies whether to override the connection mappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview. If set toTRUE, connection remappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview will be ignored and the connection string specified using theserverparameter will be used. If set toFALSE, all replay threads will connect using the connection remappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview. This is the default setting. -
walletdirpoints to the location of the auto-login software keystore directory. The default value is an empty string.walletdiris mandatory during the replay of an encrypted workload capture. For a non-encrypted capture,walletdirmust not be set and it defaults to an empty string.
Note:
-
For an encrypted workload capture, you must set the password using the
oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption(case-sensitive) identifier. The password is stored in the auto-login software keystore. -
During replay of encrypted workload capture, you must set up a separate client-side software keystore. For example:
rm -rf keystore_location mkdir keystore_location mkstore -wrl keystore_location -create mkstore -wrl keystore_location -createEntry 'oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption' secret_key mkstore -wrl keystore_location -createSSOsecret_keymust match thesecret_keythat was used in the server-side software keystore which was created during the encryption of the workload capture.
After all replay clients have connected, the database will automatically distribute workload capture streams among all available replay clients and workload replay can begin. You can monitor the status of the replay clients using the V$WORKLOAD_REPLAY_THREAD view. After the replay finishes, all replay clients will disconnect automatically.
Example: Running wrc executable in replay mode for a non-encrypted capture
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in replay mode:
%> wrc system/password@test mode=replay replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable starts the replay client to replay the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory.
Example: Running wrc executable in replay mode for an encrypted capture
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in replay mode for an encrypted workload capture:
%> wrc system/password@test mode=replay replaydir=./replay walletdir=/tmp/replay_encrypt_cwalletIn this example, the wrc executable starts the replay client to replay the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory. walletdir points to the location of the auto-login software keystore directory.
12.1.8.3 Displaying Host Information
You can display the hosts that participated in a workload capture and workload replay by running the wrc executable in list_hosts mode.
In list_hosts mode, the wrc executable accepts the keyword replaydir, which specifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory.
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in list_hosts mode:
%> wrc mode=list_hosts replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable is executed to list all hosts that participated in capturing or replaying the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory. In the following sample output, the hosts that participated in the workload capture and three subsequent replays are shown:
Workload Replay Client: Release 12.1.0.0.1 - Production on Fri Sept 30
13:44:48 2011
Copyright (c) 1982, 2011, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Hosts found:
Capture:
prod1
prod2
Replay 1:
test1
Replay 2:
test1
test2
Replay 3:
testwin
12.2 Replaying a Database Workload Using Enterprise Manager
This section describes how to replay a database workload using Enterprise Manager.
The primary tool for replaying database workloads is Oracle Enterprise Manager. If Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can also replay database workloads using APIs, as described in "Replaying a Database Workload Using APIs".
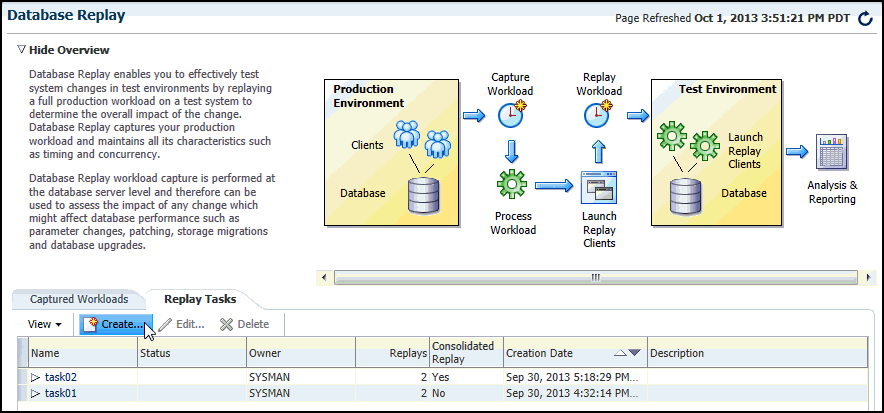
To replay a database workload using Enterprise Manager:
-
From the Enterprise menu of the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control console, select Quality Management, then Database Replay.
If the Database Login page appears, log in as a user with administrator privileges.
The Database Replay page appears.
-
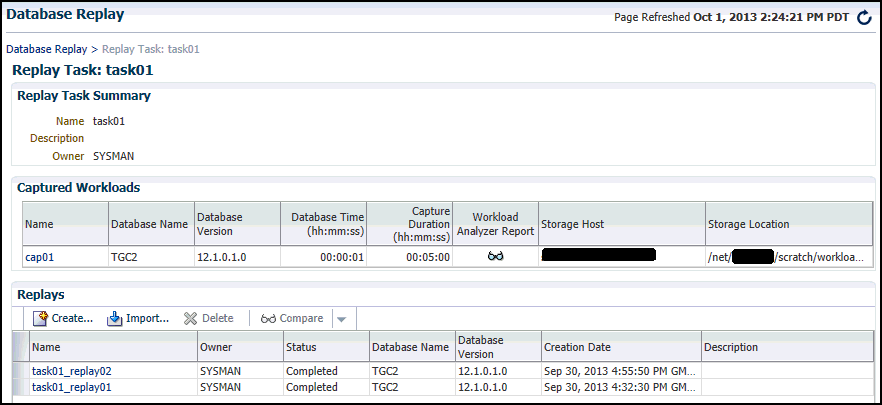
Select the Replay Tasks tab, then click the link for the desired replay task in the table.
The Replay Task page for the replay appears.
-
Click Create in the Replays section to create the replay.
The Create Replay pop-up appears.
-
Provide a required Name and optional description, then click the Target Database icon.
The Search and Select: Targets pop-up appears.
-
Choose the appropriate database, then click Select.
-
Click OK in the Create Replay pop-up.
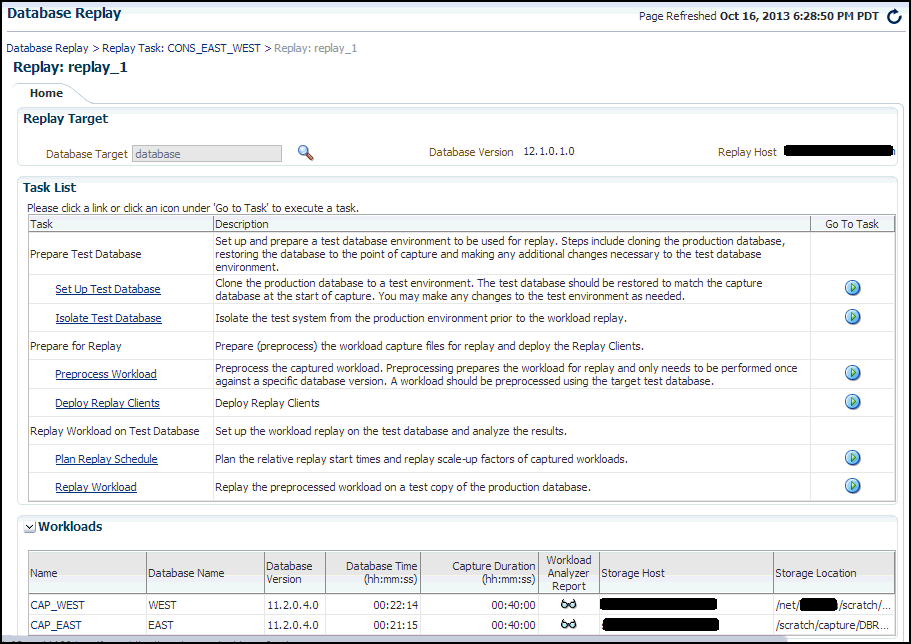
The Database Replay page for your replay appears, which includes a Task List with a link to perform the replay.
-
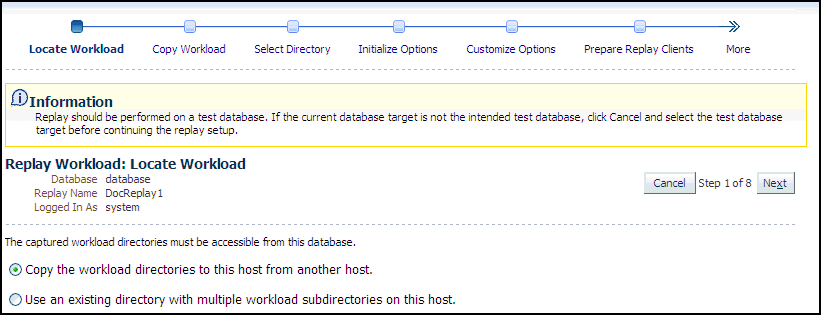
Click the link for the Replay Workload task.
The Replay Workload: Locate Workload page appears.
-
Select the desired workload location option.
If you have not previously copied the workload from its storage location to the replay location where the replay clients can access it, select the option to copy the workload. Otherwise, select the option to use the existing replay directory that contains the workload to be replayed.
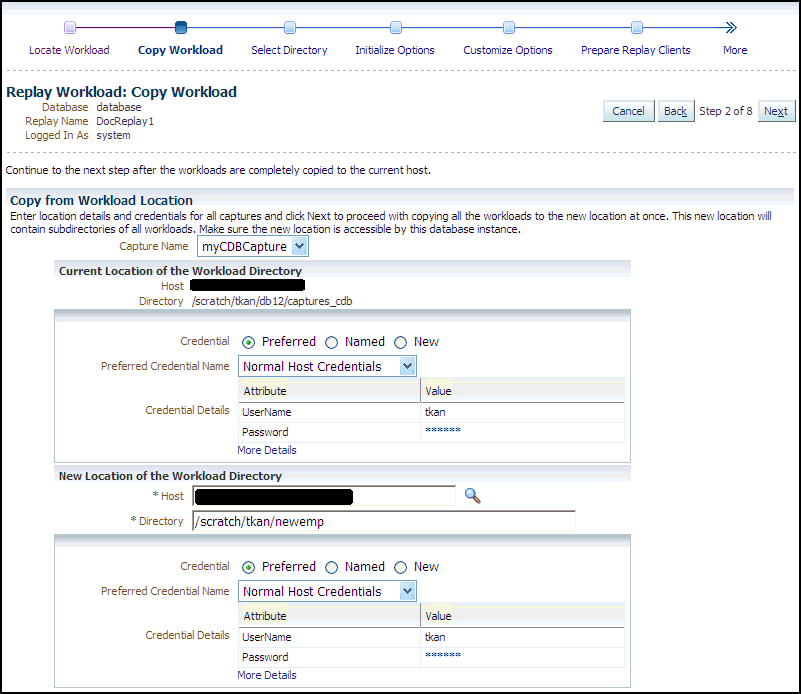
Click Next to display the Replay Workload: Copy Workload page.
-
Provide the required credentials and the new location of the workload directory to which you want to copy the workload, then click Next.
-
There are multiple source workloads for a consolidated replay, so multiple source credentials might be needed for the current location of the workload directory. For more information on consolidated replays, see "Using Consolidated Database Replay with Enterprise Manager."
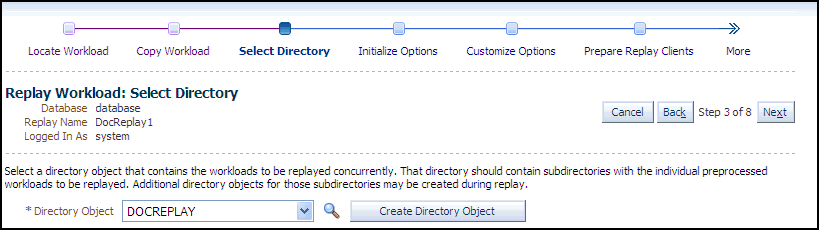
The system responds by displaying a progress bar graph during processing, then displays the Replay Workload: Select Directory page after the copy operation concludes.
-
-
Specify the Directory Object, or create a new Directory Object that points to the location that contains the workload. If you chose to copy from the workload location to a new location in the previous step, make sure that the directory object points to the exact location you specified in the New Location of the Workload Directory section.
The system responds by displaying a Capture Summary. You can expand the Capture Details section to see the workload profile and workload filters. You can also generate a Workload Capture Analyzer Report and Database Capture Report. The Capture Summary does not appear for consolidated replays.
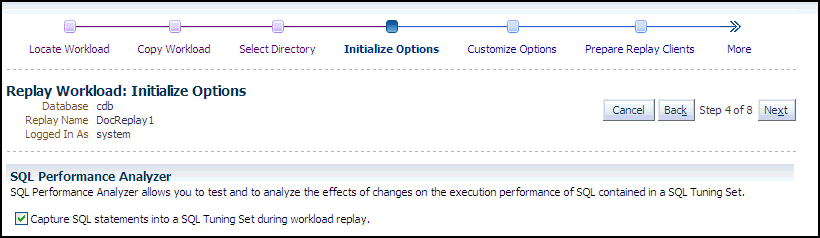
Click Next to display the Replay Workload: Initialize Options page.
-
In the SQL Performance Analyzer section, retain or disable the Capture SQL Statements option, which is enabled by default and recommended. You can disable this option if you do not want to compare SQL tuning sets at the end of the replay.
-
The SQL Performance Analyzer can initiate an impact analysis of environmental changes on the performance of SQL statements within a SQL Tuning Set. You can create and analyze SQL Performance Analyzer tasks to test the effects of a database upgrade, initialization parameter change, Exadata simulation, or custom experiments. A task compares the effects of before-trial changes with after-trial changes.
Although Database Replay provides an analysis of how a change affects your entire system, you can use a SQL tuning set in conjunction with the SQL Performance Analyzer to gain a more SQL-centric analysis of how the change affects SQL statements and execution plans.
By capturing a SQL tuning set during workload replay, you can use SQL Performance Analyzer to compare this SQL tuning set to another SQL tuning set captured during workload capture, without having to re-execute the SQL statements. This enables you to obtain a SQL Performance Analyzer report and compare the SQL performance, before and after change, while running Database Replay.
-
In the Identify Source section, initial replay options refer to the connection mappings and parameters on the Customize Options page. Connections are captured along with the workload.
Note:
This section does not appear for consolidated replays or Oracle RAC.
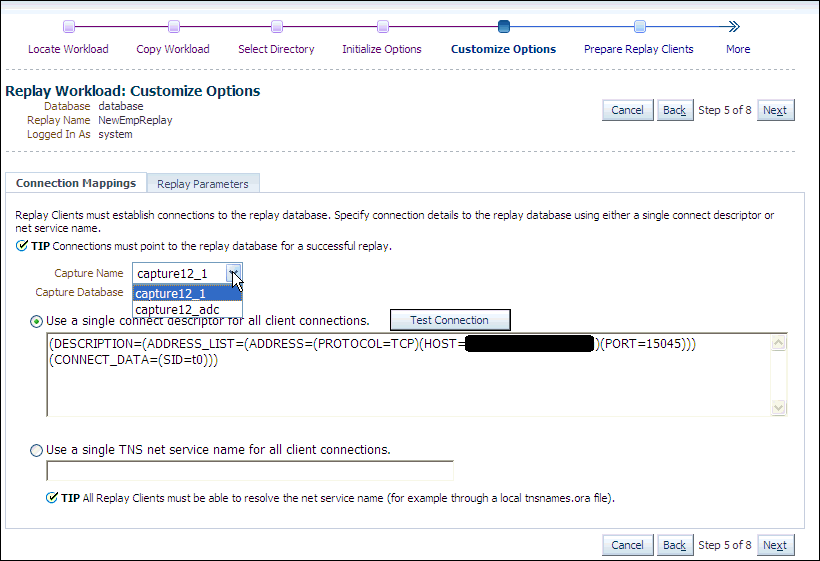
Click Next to display the Replay Workload: Customize Options page.
-
-
Remap captured connection strings to connection strings that point to the replay system. Note that you need to remap each capture connection. For example, in the illustration above, you would need to remap the connection for both capture12_1 and capture12_adc.
(You can remap connections per workload for consolidated replay. There is a Capture Name drop-down to choose the workload.)
Click the Connection Mappings tab. There are several methods you can use to remap captured connection strings. You can choose to:
-
Use a single connect descriptor for all client connections by selecting this option and entering the connect descriptor you want to use. The connect descriptor should point to the replay system.
To test the connection, click Test Connection. If the connect descriptor is valid, an Information message is displayed to inform you that the connection was successful.
-
Use a single TNS net service name for all client connections by selecting this option and entering the net service name you want to use. All replay clients must be able to resolve the net service name, which can be done using a local
tnsnames.orafile. -
Use a separate connect descriptor or net service name for each client connect descriptor captured in the workload by selecting this option and, for each capture system value, entering a corresponding replay system value that the replay client will be use. If you selected the "Use replay options from a previous replay" option in the Initialize Options step, the "Use a separate connect descriptor" option is selected, and the previous replay system values appear in the text field below.
Note:
This option does not apply to consolidated replays.
-
-
Specify the replay options using the replay parameters, which control some aspects of the replay.
To modify the replay behavior, click the Replay Parameters tab and enter the desired values for each replay parameter. Using the default values is recommended. For information about setting the replay parameters, see .
After setting the replay parameters, click Next.
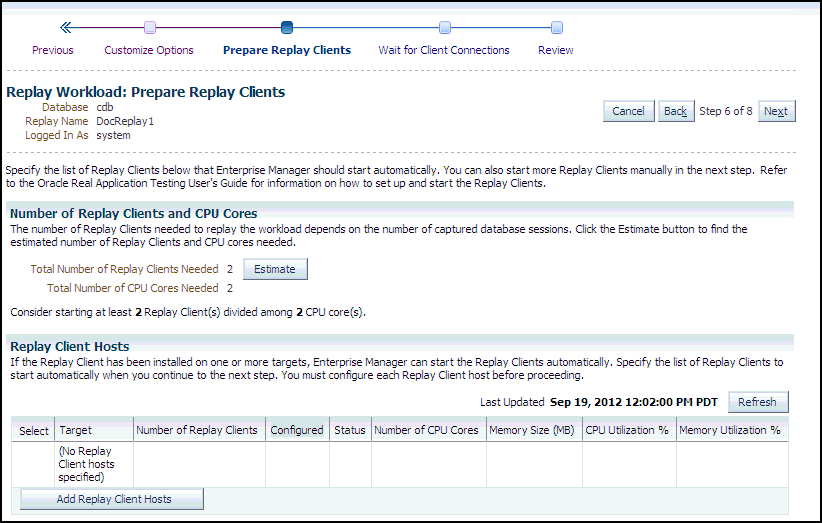
The Replay Workload: Prepare Replay Clients page appears.
-
Ensure that the replay clients are prepared for replay:
Before proceeding, the replay clients must be set up.
-
Click Estimate to determine how many replay clients and CPUs are required for the replay.
-
Click Add Replay Client Hosts to add a host or hosts for the replay clients. (If you do not want to add any replay client hosts, you can still continue and start the replay clients from the command line outside of Enterprise Manager).
The Search and Select: Replay Client Host pop-up appears.
-
Specify a Target Name and then click Go, or just click Go to display the entire list of available hosts.
-
Choose a host and then click Select.
-
-
When the host name appears in the Target column of the Replay Client Hosts table, specify the number of replay clients recommended from the estimate results, then make sure that the number of CPUs listed for the host satisfies the minimum recommendation in the estimate results. You should start at least one replay client per captured workload.
-
In the Configured column, click the No link to configure the replay client host in the pop-up that appears.
-
Click Apply after you have finished providing input in the pop-up. The Configured column now displays Yes in the Replay Client Hosts table.
-
-
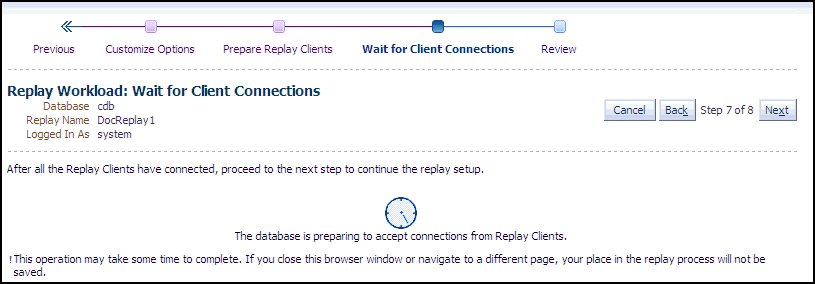
Click Next to start the replay clients and display the Replay Workload: Wait for Client Connections page.
Note:
If you have reached this step in the process from the Enterprise menu, you also need to enter credentials for the replay job and for the replay result storage host.
-
As replay clients are started, the replay client connections are displayed in the Client Connections table.
-
The text below the clock changes if a replay client is connected.
-
The Client Connections table is populated when at least one replay client is connected.
When all replay clients have connected, enter host credentials at the bottom of the page to start the replay job, then click Next to display the Replay Workload: Review page.
-
-
Review the options and parameters that have been defined for the workload replay.
-
The value for Connected Replay Clients must be at least 1 in order to successfully submit the Replay Workload job.
-
The Submit button is enabled only if at least one replay client is connected.
-
-
If everything appears as you have intended, click Submit to submit the replay job.
After the replay starts, the Home tab of the Database Replay page for this replay reappears with a system message that states "The workload replay has started."
12.3 Setting Up the Replay Schedule and Parameters Using Enterprise Manager
This feature is available for Cloud Control Database plug-in 12.1.0.5 and later releases.
This feature enables you to accomplish the following tasks:
-
Offset instances so that they execute at different time intervals
You can adjust the relative replay start time of each workload instance to align the average active sessions peak times for scheduled instances of Capture workloads. This alignment of the workload peaks potentially maximizes the load on the system, so that you can experiment with how the test system responds under different workload conditions.
-
Scale up the replay workload by adding instances of the captured workload
Each added instance is replayed independently of the other instances.
When you scale up a workload by specifying multiple instances of it, the default and recommended configuration is to replay the DML statements in one of the instances. All of the additional instances will only replay the query (ready-only) statements.
For example, if a workload has a SQL Insert to an employee database, you normally would want to have only one instance that executes the Insert, and the others would bypass user calls that modify the database with this Insert. However, you can override the default setting of an instance by unchecking the Replay Query-only check box to replay all statements in the workload.
To access the Plan Replay Schedule page:
-
From the Database Replay home page, click on the Replay Tasks tab.
-
Click on the name of an existing replay task with more than one workload to navigate to the Replay Task page.
-
Click Create to create a new replay.
-
Provide the requisite information in the Create Replay pop-up, then click OK.
The new replay appears in the Replays table.
-
Click the name of your new replay in the Replays table.
A Task List now appears in the Replay page.
-
Click the Plan Replay Schedule link.
The Plan Replay Schedule page appears.
To scale up a replay:
-
In the drop-down next to the Add Workload Instance button, select the Capture workload for which you want to add an instance.
-
Click Add Workload Instance to add the instance.
To schedule the time intervals:
-
From the Replay Delay column, either leave the default value of 0 for the first capture instance, or adjust the number of minutes desired before the instance starts to execute.
-
Repeat the step above for each capture instance until you have set all of the values to represent how you want the performance spikes to execute for your testing needs.
To auto-align workload peaks:
-
Click the Auto-align button.
To specify query-only instances:
-
For each instance that you want to be query-only, enable the Replay Query-only check box.
To review the updated schedule:
-
From the Replay Task tab of the Database Replay page, click the Replay task link containing your scheduled replay.
The Replay Task page appears.
-
Click the scheduled replay in the Replays table.
-
Select the Review tab in the Replay page.
12.4 Monitoring Workload Replay Using Enterprise Manager
-
Monitor or stop an active workload replay
-
View a completed workload replay
If Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can monitor workload replay using APIs and views, as described in "Monitoring Workload Replay Using APIs".
This section contains the following topics:
12.4.1 Monitoring an Active Workload Replay
This section describes how to monitor an active workload replay using Enterprise Manager.
To monitor an active workload replay:
12.5 Importing a Replay External to Enterprise Manager
A replay to be imported can be running in the test database, or the replay can be completed and the replay directory stored on a file system.
This feature is available for Cloud Control Database plug-in 12.1.0.5 and later releases.
To import a replay external to Enterprise Manager:
-
From the Database Replay page, click the Replay Tasks tab, then select the desired replay task.
The Replay Task page appears.
-
Click Import in the Replays section.
The Import Replay: Source page appears
-
Select one of the three choices available to import a replay, then click Next.
-
Import one or more completed Replays from a directory in the file system
This option typically applies for a replay created using an API, in which you now want to import it to Enterprise Manager for subsequent processing. In this case, Enterprise Manager may not be necessarily managing the replay database.
-
Import one or more completed Replays from a database target
In this case, Enterprise Manager is probably already managing the replay database. The replay could have been done on this database, or it could have been loaded in as would be the case for the option above.
-
Attach to a Replay of this Replay task running in a database target
This option is similar to the option above, except this replay is still in progress, rather than one that has already completed.
The Import Replay: Database page appears.
-
-
Click the search icon next to the Database Target field and select a database from the pop-up that appears.
Note:
The target version of the database reading the replay must be at least as high as the one you used in the replay task. For instance, if the replay task used Oracle Database 12x, the database you select to read the replay must be at least version 12x.
-
The system now requests database and host credentials.
-
In the previous step, if you chose to import one or more completed replays from a directory in the file system, the system also requires a workload location.
-
The replay task can determine if this is a consolidated replay based on the number of workloads contained in the replay task. If this is a consolidated replay, this step asks you to enter a consolidated replay directory for the workload location.
-
-
Provide the requisite input for the step above, then click Next.
The Import Replay: Replay page appears.
-
If you chose "Import one or more completed Replays from a directory in the file system" in step 3, this page provides a Load Replay button.
-
If you chose “Import one or more completed Replays from a database target" or “Attach to a Replay of this Replay task running in a database target" in step 3, this page provides a Discover Replay button.
-
-
Click either Load Replay or Discover Replay, depending on which button is available in accordance with your selection in step 3.
The system displays one or more replays, if found, in the Discovered Replays table.
-
Either click Next to load the replay, or select one or more replays, then click Next to continue importing the replays.
The Import Replay: Review page appears.
-
If everything appears as you have intended, click Submit.
The Database Replay page reappears and displays a message stating that the job was submitted successfully. The Status column in the table for your imported replay will show In Progress.
Tip:
You can check on the job's progress by clicking on the replay name that you just submitted in the Review step. A Replay Summary page appears, and you can click the Database Replay Import Job link to see the progress of the job execution steps.
12.6 Replaying a Database Workload Using APIs
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY package. You can also use Oracle Enterprise Manager to replay a database workload, as described in "Replaying a Database Workload Using Enterprise Manager".
Replaying a database workload using the DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY package is a multi-step process that involves:
See Also:
-
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about the
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAYpackage
12.6.1 Initializing Replay Data
To initialize replay data:
-
Use the
INITIALIZE_REPLAYprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.INITIALIZE_REPLAY (replay_name => 'dec06_102', replay_dir => 'dec06', plsql_mode => 'top_level'); END; /In this example, the
INITIALIZE_REPLAYprocedure loads preprocessed workload data from thedec06directory into the database.The
INITIALIZE_REPLAYprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
replay_namerequired parameter specifies a replay name that can be used with other APIs to retrieve settings and filters of previous replays. -
The
replay_dirrequired parameter specifies the directory that contains the workload capture that will be replayed. -
The optional
plsql_modeparameter specifies the PL/SQL replay mode.These two values can be set for the
plsql_modeparameter:-
top_level: Only top-level PL/SQL calls. This is the default value. -
extended: SQL executed inside PL/SQL or top-level PL/SQL if there is no SQL recorded inside. Non-PL/SQL calls will be replayed in the usual manner.
-
-
Note:
To run INITIALIZE_REPLAY on an encrypted workload capture, you need to set the password using the oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption (case-sensitive) identifier. The password is stored in a software keystore. You can find whether a workload capture is encrypted or not from DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURES view.
See Also:
-
"Preprocessing a Database Workload Using APIs" for information about preprocessing a workload capture
-
"Steps for Replaying a Database Workload" for information preparing the test system
12.6.2 Remapping Connections
DBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAP view.
To remap connections:
-
Use the
REMAP_CONNECTIONprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.REMAP_CONNECTION (connection_id => 101, replay_connection => 'dlsun244:3434/bjava21'); END; /In this example, the connection that corresponds to the connection ID 101 will use the new connection string defined by the
replay_connectionparameter.The
REMAP_CONNECTIONprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
connection_idrequired parameter is generated when initializing replay data and corresponds to a connection from the workload capture. -
The
replay_connectionrequired parameter specifies the new connection string that will be used during workload replay.
-
See Also:
12.6.3 Remapping Users
DBA_WORKLOAD_USER_MAP view.
To remap users:
-
Use the
SET_USER_MAPPINGprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.SET_USER_MAPPING (capture_user => 'PROD', replay_user => 'TEST'); END; /In this example, the
PRODuser used during capture is remapped to theTESTuser during replay.The
SET_USER_MAPPINGprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
capture_userrequired parameter specifies the username captured during the time of the workload capture. -
The
replay_userrequired parameter specifies the username to which the captured user is remapped during replay. If this parameter is set toNULL, then the mapping is disabled.
-
See Also:
12.6.4 Setting Workload Replay Options
To prepare workload replay on the replay system:
-
Use the
PREPARE_REPLAYprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.PREPARE_REPLAY (synchronization => 'OBJECT_ID', capture_sts => TRUE, sts_cap_interval => 300); END; /In this example, the
PREPARE_REPLAYprocedure prepares a replay that has been previously initialized. A SQL tuning set will also be captured in parallel with the workload replay.The
PREPARE_REPLAYprocedure uses the following parameters:-
The
synchronizationrequired parameter controls the type of synchronization used during workload replay.If the parameter is set to
TIME, the replay will use the same wall-clock timing as the capture. All database session login times will be replayed exactly as the capture. Likewise, all timing between transactions within database sessions will be preserved and replayed as captured. This synchronization method will produce good replays for most workloads.If this parameter is set to
SCN(the default value), theCOMMITorder in the captured workload will be observed during replay and all replay actions will be executed only after all dependentCOMMITactions have completed. This synchronization method may introduce significant delays for some workloads. If this is the case, it is recommended to useTIMEas the synchronization parameter.If this parameter is set to
OBJECT_ID, all replay actions will be executed only after all relevantCOMMITactions have completed. RelevantCOMMITactions must meet the following criteria:-
Issued before the given action in the workload capture
-
Modified at least one of the database objects for which the given action is referencing, either implicitly or explicitly
Setting this parameter to
OBJECT_IDcan allow for more concurrency during workload replays forCOMMITactions that do not reference the same database objects during workload capture. -
-
The
connect_time_scaleparameter scales the elapsed time from when the workload capture started to when the session connects with the specified value and is interpreted as a % value. Use this parameter to increase or decrease the number of concurrent users during replay. The default value is 100. -
The
think_time_scaleparameter scales the elapsed time between two successive user calls from the same session and is interpreted as a % value. Setting this parameter to 0 will send user calls to the database as fast as possible during replay. The default value is 100. -
The
think_time_auto_correctparameter corrects the think time (based on thethink_time_scaleparameter) between calls when user calls take longer to complete during replay than during capture. This parameter can be set to eitherTRUEorFALSE. Setting this parameter toTRUEreduces the think time if the workload replay is taking longer than the workload capture. The default value isTRUE. -
The
scale_up_multiplierparameter defines the number of times the workload is scaled up during replay. Each captured session will be replayed concurrently for as many times as specified by this parameter. However, only one session in each set of identical replay sessions will execute both queries and updates. The rest of the sessions will only execute queries. -
The
capture_stsparameter specifies whether to capture a SQL tuning set in parallel with the workload replay. If this parameter is set toTRUE, you can capture a SQL tuning set during workload replay and use SQL Performance Analyzer to compare it to another SQL tuning set without having to re-execute the SQL statements. This enables you to obtain a SQL Performance Analyzer report and compare the SQL performance—before and after the change—while running Database Replay. You can also export the resulting SQL tuning set with its AWR data using theEXPORT_AWRprocedure, as described in "Exporting AWR Data for Workload Replay".This feature is not supported for Oracle RAC. Workload replay filters that are defined using
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAYdo not apply to the SQL tuning set capture. The default value for this parameter isFALSE. -
The
sts_cap_intervalparameter specifies the duration of the SQL tuning set capture from the cursor cache in seconds. The default value is 300. Setting the value of this parameter below the default value may cause additional overhead with some workloads and is not recommended.
-
For more information about setting these parameters, see "Specifying Replay Options".
See Also:
12.6.5 Defining Workload Replay Filters and Replay Filter Sets
This section contains the following topics:
See Also:
12.6.5.1 Adding Workload Replay Filters
This section describes how to add a new filter to be used in a replay filter set.
To add a new filter:
-
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.ADD_FILTER ( fname => 'user_ichan', fattribute => 'USER', fvalue => 'ICHAN'); END; /In this example, the
ADD_FILTERprocedure adds a filter named user_ichan, which can be used to filter out all sessions belonging to the user name ICHAN.The
ADD_FILTERprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
fnamerequired parameter specifies the name of the filter that will be added. -
The
fattributerequired parameter specifies the attribute on which the filter will be applied. Valid values include PROGRAM, MODULE, ACTION, SERVICE, USER, and CONNECTION_STRING. You must specify a valid captured connection string that will be used during replay as the CONNECTION_STRING attribute. -
The
fvaluerequired parameter specifies the value for the corresponding attribute on which the filter will be applied. It is possible to use wildcards such as % with some of the attributes, such as modules and actions.
Once all workload replay filters are added, you can create a replay filter set that can be used when replaying the workload.
-
12.6.5.2 Deleting Workload Replay Filters
This section describes how to delete workload replay filters.
To delete workload replay filters:
-
Use the
DELETE_FILTERprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.DELETE_FILTER (fname => 'user_ichan'); END; /
In this example, the
DELETE_FILTERprocedure removes the filter named user_ichan.The
DELETE_FILTERprocedure in this example uses thefnamerequired parameter, which specifies the name of the filter to be removed.
12.6.5.3 Creating a Replay Filter Set
After the workload replay filters are added, you can create a set of replay filters to use with workload replay. When creating a replay filter set, all workload replay filters that were added since the previous replay filter set was created will be used.
To create a replay filter set:
-
Use the
CREATE_FILTER_SETprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.CREATE_FILTER_SET ( replay_dir => 'apr09', filter_set => 'replayfilters', default_action => 'INCLUDE'); END; /In this example, the
CREATE_FILTER_SETprocedure creates a replay filter set named replayfilters, which will replay all captured calls for the replay stored in theapr09directory, except for the part of the workload defined by the replay filters.The
CREATE_FILTER_SETprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
replay_dirparameter specifies the directory where the replay to be filtered is stored -
The
filter_setparameter specifies the name of the filter set to create -
The
default_actionparameter determines if every captured database call should be replayed and whether the workload replay filters should be considered as inclusion or exclusion filters.If this parameter is set to
INCLUDE, all captured database calls will be replayed, except for the part of the workload defined by the replay filters. In this case, all replay filters will be treated as exclusion filters, since they will define the part of the workload that will not be replayed. This is the default behavior.If this parameter is set to
EXCLUDE, none of the captured database calls will be replayed, except for the part of the workload defined by the replay filters. In this case, all replay filters will be treated as inclusion filters, since they will define the part of the workload that will be replayed.
-
12.6.5.4 Using a Replay Filter Set
Once the replay filter set is created and the replay is initialized, you can use the replay filter set to filter the replay in the replay_dir directory.
To use a replay filter set:
-
Use the
USE_FILTER_SETprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.USE_FILTER_SET (filter_set => 'replayfilters'); END; /
In this example, the
USE_FILTER_SETprocedure uses the filter set named replayfilters.The
USE_FILTER_SETprocedure in this example uses thefilter_setrequired parameter, which specifies the name of the filter set to be used in the replay.
12.6.6 Setting the Replay Timeout Action
When a replay timeout action is enabled, a user call will exit with an ORA-15569 error if it is delayed beyond the conditions specified by the replay timeout action. The aborted call and its error are reported as error divergence.
To set a replay timeout:
-
Use the
SET_REPLAY_TIMEOUTprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.SET_REPLAY_TIMEOUT ( enabled => TRUE, min_delay => 20, max_delay => 60, delay_factor => 10); END; /In this example, the
SET_REPLAY_TIMEOUTprocedure defines a replay timeout action that will abort a user call if the delay during replay is more than 60 minutes, or if the delay during replay is over 20 minutes and the elapsed time is 10 times greater than the capture elapsed time.The
SET_REPLAY_TIMEOUTprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
enabledparameter specifies if the replay timeout action is enabled or disabled. The default value isTRUE. -
The
min_delayparameter defines the lower bound value of call delay in minutes. The replay timeout action is only activated when the delay is over this value. The default value is 10. -
The
max_delayparameter defines the upper bound value of call delay in minutes. The replay timeout action is activated and issues an error when the delay is over this value. The default value is 120. -
The
delay_factorparameter defines a factor for the call delays that are between the values ofmin_delayandmax_delay. The replay timeout action issues an error when the current replay elapsed time is higher than the multiplication of the capture elapsed time and this value. The default value is 8.
-
To retrieve the replay timeout action setting:
-
Use the
GET_REPLAY_TIMEOUTprocedure:DECLARE enabled BOOLEAN; min_delay NUMBER; max_delay NUMBER; delay_factor NUMBER; BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.GET_REPLAY_TIMEOUT(enabled, min_delay, max_delay, delay_factor); END; /The
GET_REPLAY_TIMEOUTprocedure in this example returns the following parameters:-
The
enabledparameter returns whether the replay timeout action is enabled or disabled. -
The
min_delayparameter returns the lower bound value of call delay in minutes. -
The
max_delayparameter returns the upper bound value of call delay in minutes. -
The
delay_factorparameter returns the delay factor.
-
12.6.7 Starting a Workload Replay
-
Preprocess the captured workload, as described in "Preprocessing a Database Workload Using APIs"
-
Initialize the replay data, as described in "Initializing Replay Data"
-
Specify the replay options, as described in "Setting Workload Replay Options"
-
Start the replay clients, as described in "Starting Replay Clients"
Note:
Once a workload replay is started, new replay clients will not be able to connect to the database. Only replay clients that were started before the START_REPLAY procedure is executed will be used to replay the captured workload.
To start a workload replay:
Note:
Starting with Oracle Database Release 19c, the DBA_RAT_CAPTURE_SCHEMA_INFO view provides login_schema and current_schema information for SQL statements. During a replay in the extended mode, if you encounter the ORA-00942: table or view does not exist error, then use the DBA_RAT_CAPTURE_SCHEMA_INFO and DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE_SQLTEXT views to find the tables on which the error happened. Then grant the necessary privileges on the tables to the users who hit the error and retry the replay; this may fix the problem.
12.6.8 Pausing a Workload Replay
12.6.11 Retrieving Information About Workload Replays
To retrieve information about workload replays:
-
Call the
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.GET_REPLAY_INFOfunction.The
GET_REPLAY_INFOfunction first imports a row into theDBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview, which contains information about the workload capture. By default, it then only imports information for replays that have not been previously loaded into theDBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAYSview. This function returns thecap_idof the capture directory (for a consolidated capture directory, thecap_idreturned is0), which can be associated with theCAPTURE_IDcolumn in theDBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAYSview to access the information retrieved.The
GET_REPLAY_INFOfunction uses the following parameters:-
The
replay_dirrequired parameter, which specifies the name of the workload replay directory object. -
The
load_divergenceoptional parameter, which specifies if divergence data is loaded. The default value for this parameter isFALSE. To load divergence data, which imports rows for every replay attempt retrieved from the replay directory into theDBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCEview, set this parameter toTRUE. Alternatively, you can use theLOAD_DIVERGENCEprocedure to selectively load divergence data for a single replay or all replays in a directory object after the replay information is retrieved, as described in "Loading Divergence Data for Workload Replay".
-
Example 12-1 Retrieving information about workload replay
The following example shows how to retrieve information about the workload captures and the history of the workload replay attempts for the replay directory object named jul14, and to validate that the information is retrieved.
DECLARE
cap_id NUMBER;
BEGIN
cap_id := DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.GET_REPLAY_INFO(replay_dir => 'jul14');
SELECT capture_id
FROM dba_workload_replays
WHERE capture_id = cap_id;
END;
/
12.6.12 Loading Divergence Data for Workload Replay
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCE view, which displays information about diverged calls and errors during replay attempts. You can choose to load divergence data for either a single workload replay or all workload replays in a given directory object.
To load divergence data for workload replay:
-
Call the
WORKLOAD_REPLAY.LOAD_DIVERGENCEprocedure using one of the following parameters:-
The
replay_idparameter specifies the ID of the workload replay for which you want to load divergence data. Use this parameter if you only want to load divergence data for a single workload replay. -
The
replay_dirparameter specifies the name of the directory object (the value is case-sensitive). Use this parameter if you want to load divergence data for all workload replays in a given directory object.
-
-
To check the loading status of divergence data, query the
DIVERGENCE_LOAD_STATUScolumn in theDBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAYSview.A value of
TRUEindicates that the divergence data is loaded, and a value ofFALSEindicates that it has not been loaded.
Example 12-2 Loading divergence data for a single workload replay
The following example shows how to load divergence data for the workload replay with a replay_id value of 12, and to validate that the divergence data is loaded.
DECLARE
rep_id NUMBER;
BEGIN
rep_id := DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.LOAD_DIVERGENCE (replay_id => 12);
SELECT divergence_load_status
FROM dba_workload_replays
WHERE capture_id = rep_id;
END;
/
12.6.13 Deleting Information About Workload Replays
GET_REPLAY_INFO function, as described in "Retrieving Information About Workload Replays".
To delete information about workload replays:
-
Call the
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.DELETE_REPLAY_INFOprocedure using thereplay_idparameter.-
The
replay_idparameter specifies the ID of the workload replay for which you want to delete replay information. Use this parameter if you only want to delete information for a single workload replay.
-
-
By default, deleting information about workload replays does not remove the data from disk.
Example 12-3 Deleting information about workload replay
The following example deletes information retrieved about the workload captures and the history of the workload replay attempts for the workload replay with an ID of 2. The replay data is not deleted from disk, and thus can be retrieved by calling the GET_REPLAY_INFO function, as described in "Retrieving Information About Workload Replays".
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.DELETE_REPLAY_INFO (replay_id => 2); END; /
12.6.14 Exporting AWR Data for Workload Replay
To export AWR data:
-
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.EXPORT_AWR (replay_id => 1); END; /
In this example, the AWR snapshots that correspond to the workload replay with a replay ID of 1 are exported, along with any SQL tuning set that may have been captured during workload replay.
The
EXPORT_AWRprocedure uses thereplay_idrequired parameter, which specifies the ID of the replay whose AWR snapshots will be exported.
Note:
This procedure works only if the corresponding workload replay was performed in the current database and the AWR snapshots that correspond to the original replay time period are still available.
12.6.15 Importing AWR Data for Workload Replay
To import AWR data:
-
CREATE USER capture_awr SELECT DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.IMPORT_AWR (replay_id => 1, staging_schema => 'capture_awr') FROM DUAL;In this example, the AWR snapshots that correspond to the workload replay with a capture ID of 1 are imported using a staging schema named
capture_awr.The
IMPORT_AWRprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
replay_idrequired parameter specifies the ID of the replay whose AWR snapshots will be import. -
The
staging_schemarequired parameter specifies the name of a valid schema in the current database which can be used as a staging area while importing the AWR snapshots from the replay directory to theSYSAWRschema.
-
Note:
This function fails if the schema specified by the staging_schema parameter contains any tables with the same name as any of the AWR tables.
12.7 Monitoring Workload Replay Using APIs
This section contains the following topics:
12.7.1 Retrieving Information About Diverged Calls
During replay, any error and data discrepancies between the replay system and the capture system are recorded as diverged calls.
To retrieve information about a diverged call—including its SQL identifier, SQL text, and bind values—call the GET_DIVERGING_STATEMENT function using the following parameters:
-
Set the
replay_idparameter to the ID of the replay in which the call diverged -
Set the
stream_idparameter to the stream ID of the diverged call -
Set the
call_counterparameter to the call counter of the diverged call
To view these information about a diverged call, use the DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCE view. The following example illustrates a function call:
DECLARE r CLOB; ls_stream_id NUMBER; ls_call_counter NUMBER; ls_sql_cd VARCHAR2(20); ls_sql_err VARCHAR2(512); CURSOR c IS SELECT stream_id, call_counter FROM DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCE WHERE replay_id = 72; BEGIN OPEN c; LOOP FETCH c INTO ls_stream_id, ls_call_counter; EXIT when c%notfound; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (ls_stream_id||''||ls_call_counter); r:=DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.GET_DIVERGING_STATEMENT(replay_id => 72, stream_id => ls_stream_id, call_counter => ls_call_counter); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (r); END LOOP; END; /
See Also:
-
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about the
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAYpackage
12.7.2 Monitoring Workload Replay Using Views
-
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview lists all the workload captures that have been captured in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_FILTERSview lists all workload filters for workload captures defined in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAYSview lists all the workload replays that have been replayed in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCEview enables you to view information about diverged calls, such as the replay identifier, stream identifier, and call counter. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_DIV_SUMMARYview displays a summary of the replay divergence information in theDBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCEview. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_FILTER_SETview lists all workload filters for workload replays defined in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview lists the connection mapping information for workload replay. -
The
V$WORKLOAD_REPLAY_THREADview lists information about all sessions from the replay clients.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for information about these views