10 Capturing a Database Workload
This chapter contains the following sections:
See Also:
"Workload Capture" for more information about how capturing a database workload fits within the Database Replay architecture
10.1 Prerequisites for Capturing a Database Workload
-
Recovery Manager (RMAN)
DUPLICATEcommand -
Snapshot standby
-
Data Pump Import and Export
This will allow you to restore the database on the replay system to the application state as of the workload capture start time.
If the database is protected by Database Vault, then you need to be authorized to use the DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE and DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY packages in a Database Vault environment before you can use Database Replay.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Vault Administrator’s Guide for information about using Database Replay in a Database Vault environment
-
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User’s Guide for information about duplicating databases with RMAN
-
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about managing snapshot standby databases
-
Oracle Database Utilities for information about using Data Pump
10.2 Setting Up the Capture Directory
For Oracle RAC, consider using a shared file system. Alternatively, you can set up one capture directory path that resolves to separate physical directories on each instance, but you will need to consolidate the files created in each of these directories into a single directory. For captures on an Oracle RAC database, Enterprise Manager only supports Oracle RAC configured with a shared file system. The entire content of the local capture directories on each instance (not only the capture files) must be copied to the shared directory before it can be used for preprocessing. For example, assume that you are:
-
Running an Oracle RAC environment in Linux with two database instances named
host1andhost2 -
Using a capture directory object named
CAPDIRthat resolves to/$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/captureon both instances -
Using a shared directory that resides in
/nfs/rac_capture
You will need to login into each host and run the following command:
cp -r /$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/capture/* /nfs/rac_capture
After this is done for both instances, the /nfs/rac_capture shared directory is ready to be preprocessed or masked.
10.3 Workload Capture Options
Proper planning before workload capture is required to ensure that the capture will be accurate and useful when replayed in another environment.
Before capturing a database workload, carefully consider the following options:
10.3.1 Restarting the Database
Before restarting the database, determine an appropriate time to shut down the production database before the workload capture when it is the least disruptive. For example, you may want to capture a workload that begins at 8:00 a.m. However, to avoid service interruption during normal business hours, you may not want to restart the database during this time. In this case, you should consider starting the workload capture at an earlier time, so that the database can be restarted at a time that is less disruptive.
Once the database is restarted, it is important to start the workload capture before any user sessions reconnect and start issuing any workload. Otherwise, transactions performed by these user sessions will not be replayed properly in subsequent database replays, because only the part of the transaction whose calls were executed after the workload capture is started will be replayed. To avoid this problem, consider restarting the database in RESTRICTED mode using STARTUP RESTRICT, which will only allow the SYS user to login and start the workload capture. By default, once the workload capture begins, any database instance that are in RESTRICTED mode will automatically switch to UNRESTRICTED mode, and normal operations can continue while the workload is being captured.
Only one workload capture can be performed at any given time. If you have a Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) configuration, workload capture is performed for the entire database. Once you enable capture for one of the Oracle RAC nodes, workload capture is started on all database instances (the workload capture process is Oracle RAC aware). Although it is not required, restarting all instances in a Oracle RAC configuration before workload capture is recommended to avoid capturing ongoing transactions.
To restart all instances in a Oracle RAC configuration before workload capture:
- Shut down all the instances.
- Restart all the instances.
- Start workload capture.
- Connect the application and start the user workload.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide for information about restricting access to an instance at startup
10.3.2 Using Filters with Workload Capture
Inclusion filters enable you to specify user sessions that will be captured in the workload. This is useful if you want to capture only a subset of the database workload.
Exclusion filters enable you to specify user sessions that will not be captured in the workload. This is useful if you want to filter out session types that do not need to captured in the workload, such as those that monitor the infrastructure—like Oracle Enterprise Manager (EM) or Statspack—or other such processes that are already running on the test system. For example, if the system where the workload will be replayed is running EM, replaying captured EM sessions on the system will result in duplication of workload. In this case, you may want to use exclusion filters to filter out EM sessions.
10.4 Workload Capture Restrictions
Certain types of user sessions and client requests may sometimes be captured in a workload, but they are not supported by Database Replay. Capturing these session and request types in a workload may result in errors during workload replay.
The following types of user sessions and client requests are not supported by Database Replay:
-
Direct path load of data from external files using utilities such as SQL*Loader
-
Non-PL/SQL based Advanced Queuing (AQ)
-
Flashback queries
-
Oracle Call Interface (OCI) based object navigations
-
Non SQL-based object access
-
Distributed transactions
Any distributed transactions that are captured will be replayed as local transactions.
-
XA transactions
XA transactions are not captured or replayed. All local transactions are captured.
-
JAVA_XAtransactionsIf the workload uses the
JAVA_XApackage,JAVA_XAfunction and procedure calls are captured as normal PL/SQL workload. To avoid problems during workload replay, consider dropping theJAVA_XApackage on the replay system to enable the replay to complete successfully. -
Database Resident Connection Pooling (DRCP)
-
Workloads using OUT binds
-
Multi-threaded Server (MTS) and shared server sessions with synchronization mode set to
OBJECT_ID -
Migrated sessions
The workload is captured for migrated sessions. However, user logins or session migration operations are not captured. Without a valid user login or session migration, the replay may cause errors because the workload may be replayed by a wrong user.
Typically, Database Replay refrains from capturing these types of non-supported user sessions and client requests. Even when they are captured, Database Replay will not replay them. Therefore, it is usually not necessary to manually filter out non-supported user sessions and client requests. In cases where they are captured and found to cause errors during replay, consider using workload capture filters to exclude them from the workload.
See Also:
-
"Using Filters with Workload Capture" for information about using workload capture filters
-
"Using Filters with Workload Replay" for information about using workload replay filters
10.5 Enabling and Disabling the Workload Capture Feature
PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter.
Note:
It is only necessary to enable the workload capture feature if you are capturing a database workload on a system running Oracle Database 10g Release 2.
If you are capturing a database workload on a system running Oracle Database 11g Release 1 or a later release, it is not necessary to enable the workload capture feature because it is enabled by default. Furthermore, the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter is only valid with Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2) and cannot be used with subsequent releases.
To enable the workload capture feature on a system running Oracle Database 10g Release 2, run the wrrenbl.sql script at the SQL prompt:
@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/wrrenbl.sql
The wrrenbl.sql script calls the ALTER SYSTEM SQL statement to set the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter to TRUE. If a server parameter file (spfile) is being used, the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter will be modified for the currently running instance and recorded in the spfile, so that the new setting will persist when the database is restarted. If a spfile is not being used, the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter will only be modified for the currently running instance, and the new setting will not persist when the database is restarted. To make the setting persistent without using a spfile, you will need to manually specify the parameter in the initialization parameter file (init.ora).
To disable workload capture, run the wrrdsbl.sql script at the SQL prompt:
@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/wrrdsbl.sql
The wrrdsbl.sql script calls the ALTER SYSTEM SQL statement to set the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter to FALSE. If a server parameter file (spfile) is being used, the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter will be modified for the currently running instance and also recorded in the spfile, so that the new setting will persist when the database is restarted. If a spfile is not being used, the PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter will only be modified for the currently running instance, and the new setting will not persist when the database is restarted. To make the setting persistent without using a spfile, you will need to manually specify the parameter in the initialization parameter file (init.ora).
Note:
The PRE_11G_ENABLE_CAPTURE initialization parameter can only be used with Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2). This parameter is not valid in subsequent releases. After upgrading the database, you will need to remove the parameter from the server parameter file (spfile) or the initialization parameter file (init.ora); otherwise, the database will fail to start up.
10.6 Enterprise Manager Privileges and Roles
The two security roles discussed in the following sections make it easier to grant or revoke privileges related to Database Replay entities.
10.6.1 Database Replay Viewer Role
The Database Replay Viewer role consists of the Database Replay Viewer (resource type) privilege.
10.6.2 Database Replay Operator Role
The Database Replay Operator role consists of the following privileges:
-
Database Replay Operator (resource type privilege)
-
Create new Named Credential (resource type privilege)
-
Create new job (resource type privilege)
-
Connect to any viewable target (target type privilege)
-
Execute Command Anywhere (target type privilege)
To capture or replay a workload on a database target, an Enterprise Manager user needs all the privileges granted by the Database Replay Operator role plus the target operator privilege for the database target.
10.7 Capturing a Database Workload Using Enterprise Manager
This section describes how to capture a database workload using Enterprise Manager. The primary tool for capturing database workloads is Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Tip:
If Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can capture database workloads using APIs, as described in "Capturing a Database Workload Using APIs".
To capture a database workload using Enterprise Manager:
Tip:
After capturing a workload on the production system, you need to preprocess the captured workload, as described in Preprocessing a Database Workload.
10.8 Capturing Workloads from Multiple Databases Concurrently
Concurrent capture refers to capturing the workload on multiple databases simultaneously.
To capture a concurrent database replay workload:
-
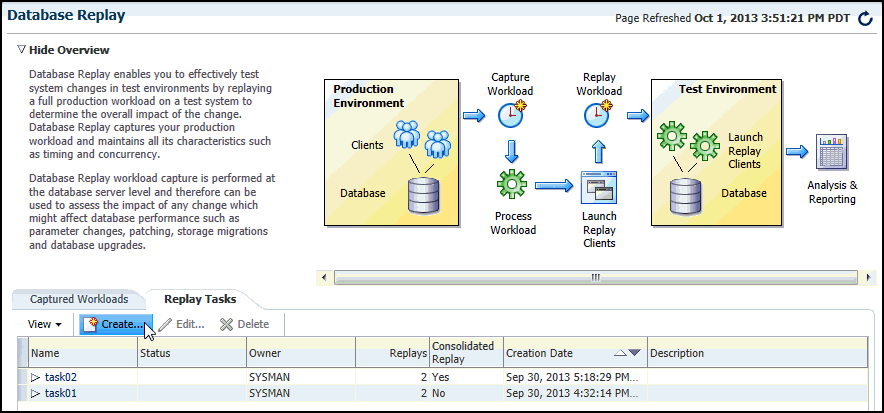
From the Enterprise menu of the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control console, select Quality Management, then Database Replay.
If the Database Login page appears, log in as a user with administrator privileges.
The Database Replay page appears.
-
From the Database Replay page, click the Captured Workloads tab, then click Create in the toolbar.
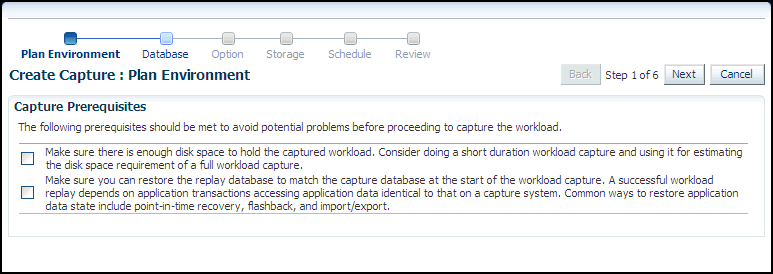
The Create Capture: Plan Environment page appears.
-
Make sure that you have met both prerequisites described on this page, then enable both checkboxes and click Next.
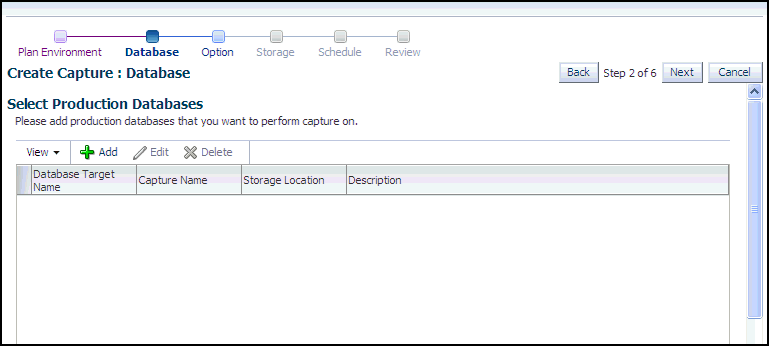
The Create Capture: Database page appears.
Tip:
For information about the prerequisites, see "Prerequisites for Capturing a Database Workload".
-
Click Add.
The Add pop-up appears.
-
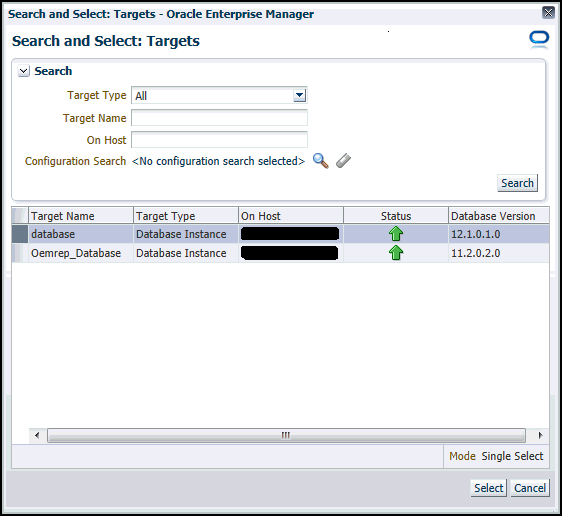
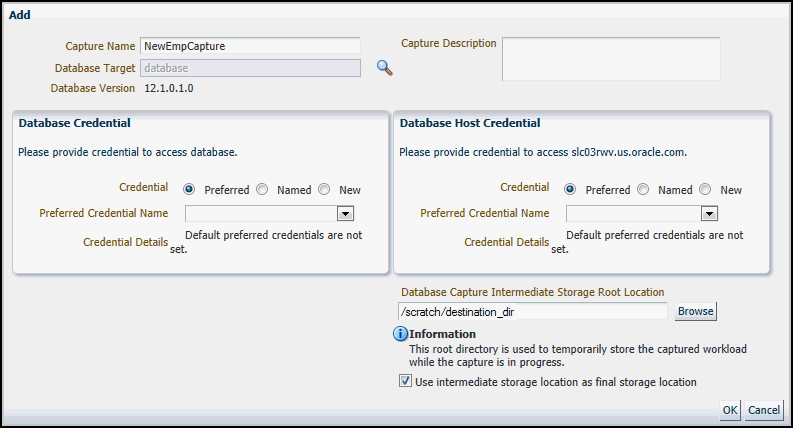
Provide a Capture name, provide an optional description, then click the Target Database search icon.
The Search and Select: Targets pop-up appears.
-
Choose a target database from the list, then click Select.
The Add pop-up reappears with added sections for Database Credential and Database Host Credential.
-
Provide database credentials, database host credentials, a Database Capture Intermediate Storage Location, then click OK.
-
After the Capture, the files are copied to the storage location, unless you use the intermediate storage location as the final storage location.
The selected target database now appears in the list of databases in the Select Production Databases table.
-
-
Add another database for concurrent capture:
-
Follow the instructions in steps 4 through 7.
The Create Capture: Database page reappears, and displays the additional database for capture along with the first database you specified in steps 4 through 7.
-
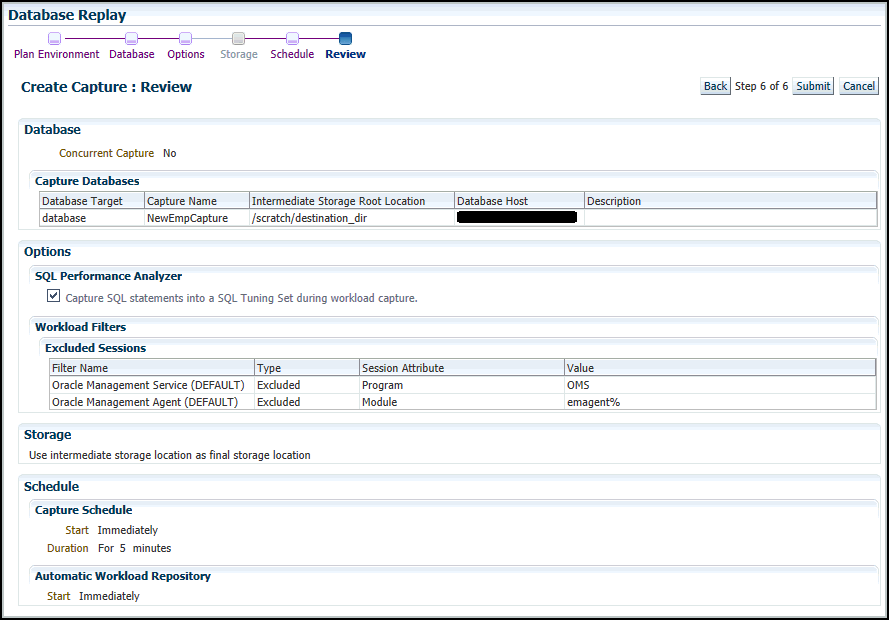
Provide a name and optional description for the concurrent capture, then click Next.
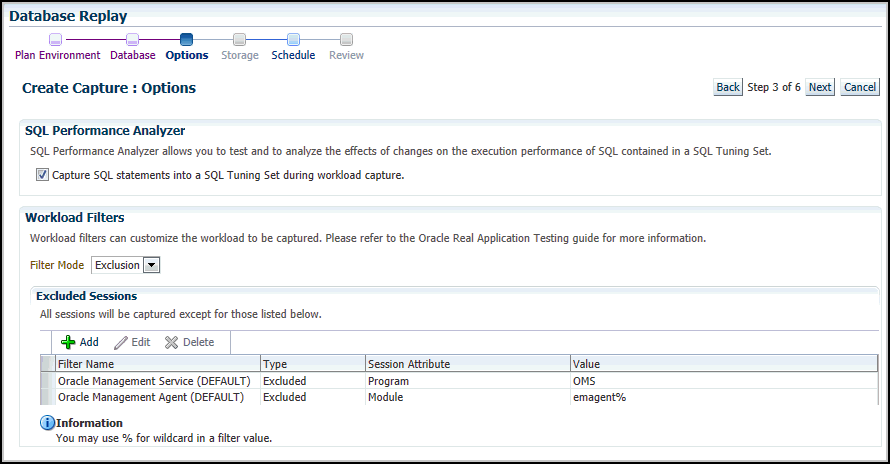
The Create Capture: Options page appears.
-
-
Select the workload capture options:
-
Under the SQL Performance Analyzer section, select whether to capture SQL statements into a SQL tuning set during workload capture.
While Database Replay provides an analysis of how a change affects your entire system, you can use a SQL tuning set in conjunction with the SQL Performance Analyzer to gain a more SQL-centric analysis of how the change affects SQL statements and execution plans.
By capturing a SQL tuning set during workload capture and another SQL tuning set during workload replay, you can use the SQL Performance Analyzer to compare these SQL tuning sets to each other without having to re-execute the SQL statements. This enables you to obtain a SQL Performance Analyzer report and compare the SQL performance, before and after changes, while running Database Replay.
Note:
Capturing SQL statements into a SQL tuning set is the default and recommended workload capture option.
-
Under the Workload Filters section, select whether to use exclusion filters by selecting Exclusion in the Filter Mode list, or inclusion filters by selecting Inclusion in the Filter Mode list.
To add filters, click Add and enter the filter name, session attribute, and value in the corresponding fields.
After selecting the desired workload capture options, click Next.
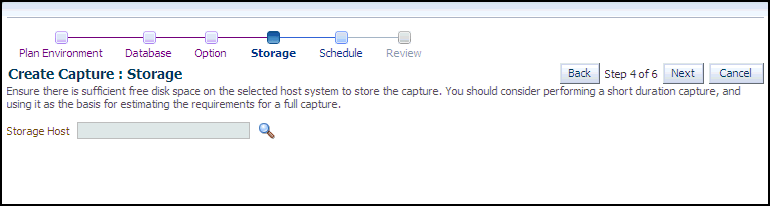
The Create Capture: Storage page appears.
-
-
Click the Storage Host icon, choose a target from the list, then click Select.
The Storage page now requests Host Credentials and a Storage Location.
-
Provide Host Credentials, click Browse to select a Storage Location, then click Next.
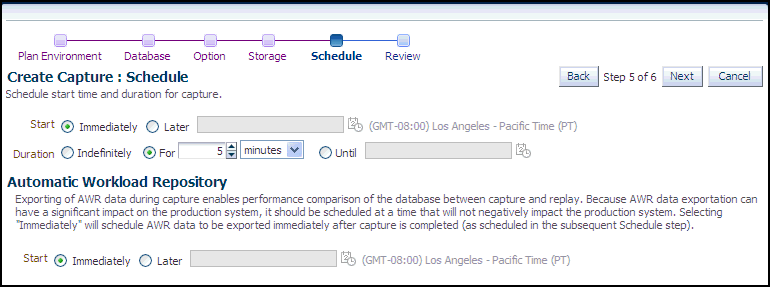
The Create Capture: Schedule page appears.
-
Schedule the starting time and duration for the capture, schedule the exporting of AWR data, then click Next.
-
The default capture duration is 5 minutes. Change the capture duration to capture representative activity over a time period of interest that needs to be tested.
The Create Capture: Review page appears.
-
-
If all of the parameters appear as you have intended, click Submit to start the Capture job.
-
The "Capture SQL statements into a SQL Tuning Set during workload capture" option is enabled by default. Uncheck this option if you do not want to compare SQL tuning sets at the end of the Replay.
The Database Replay page reappears, displays a message that the capture was created successfully, and displays the status of the capture in the Captures list, such as "Scheduled."
-
-
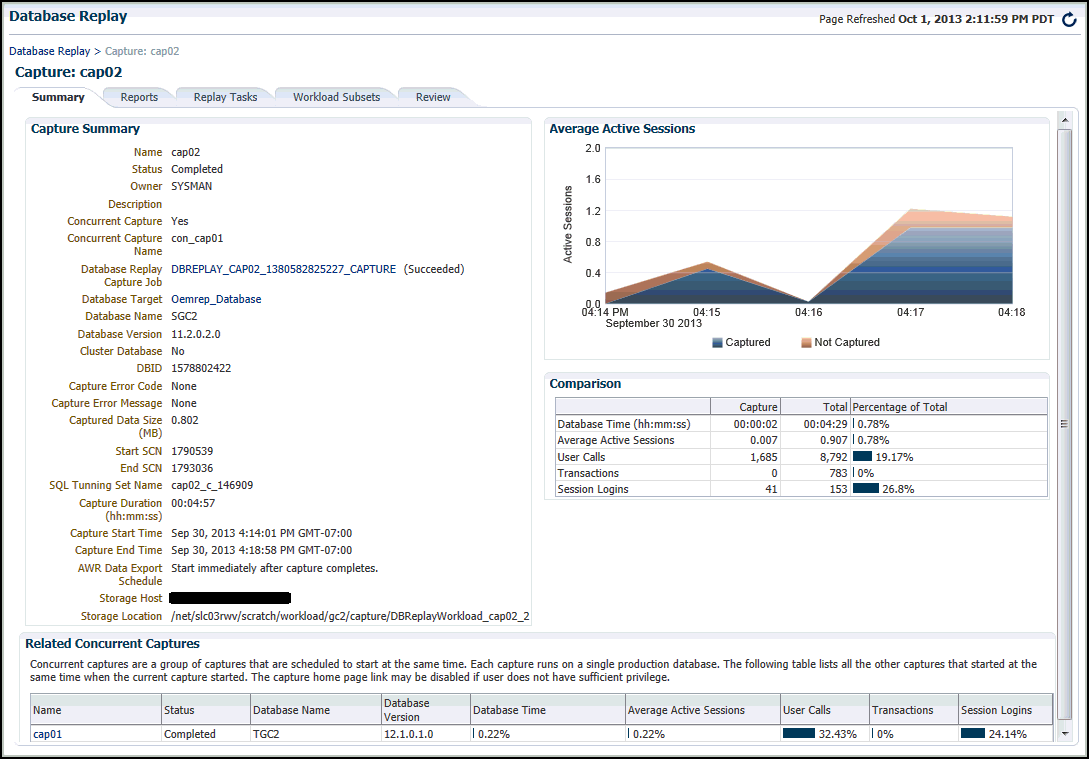
For detailed information about the capture, double-click the name of the capture.
The Capture Summary page appears, and displays several attributes, including the average active sessions, a workload comparison, and related concurrent captures.
10.9 Monitoring a Workload Capture Using Enterprise Manager
-
Monitor or stop an active workload capture
-
View a completed workload capture
Tip:
If Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can monitor workload capture using views, as described in "Monitoring Workload Capture Using Views".
This section contains the following topics:
10.9.1 Monitoring an Active Workload Capture
This section describes how to monitor an active workload capture using Enterprise Manager.
To monitor an active workload capture:
10.9.2 Stopping an Active Workload Capture
This section describes how to stop an active workload capture using Enterprise Manager.
To stop an active workload capture:
10.9.3 Viewing a Completed Workload Capture
This section describes how to manage a completed workload capture using Enterprise Manager.
To view a completed workload capture:
Tip:
See Analyzing Captured and Replayed Workloads for information about accessing workload capture reports.
10.10 Importing a Workload External to Enterprise Manager
This feature is available for Cloud Control Database plug-in 12.1.0.5 and later releases.
To import a database workload external to Enterprise Manager:
-
From the Database Replay page, click the Captured Workloads tab, then click Import in the toolbar.
The Import Workload: Source page appears.
-
Select one of the three choices available to import a captured workload, then click Next:
-
Import a completed captured workload from a directory in the file system
This option typically applies for a workload created using an API, in which you now want to import it to Enterprise Manager for subsequent processing. In this case, Enterprise Manager may not even be managing the Capture database.
-
Import a completed captured workload from a database target
In this case, Enterprise Manager is probably already managing the Capture database. The Capture could have been done on this database, or it could have been loaded in as would be the case for the option above.
-
Attach to a Capture running in a database target
This option is similar to the option above, except this a Capture that is still in progress, rather than one that has already completed.
The Import Workload: Database page appears.
-
-
Click the search icon next to the Database Target field and select a database from the pop-up that appears.
Note:
The target version of the database loading the workload must be at least as high as the one you used to capture the workload. For instance, if you captured using Oracle Database 12x, the database you select to read the Capture must be at least version 12x.
-
The system now requests database and host credentials.
-
In the previous step, if you chose to import a completed captured workload from a directory in the file system, the system also requires a workload location.
-
A consolidated Replay has a different directory structure in which there are at least two capture directories. Consequently, if the workload directory contains a consolidated Replay, you need to enable the check box so that Enterprise Manager can be aware of the consolidated Replay during the import operation.
-
-
Provide the requisite input for the step above, then click Next.
The Import Workload: Workload page appears.
-
If you chose "Import a completed captured workload from a directory in the file system" in step 2, this page provides a Load Workload button.
-
If you chose “Import a completed captured workload from a database target" or “Attach to a Capture running in a database target" in step 2, this page provides a Discover Workload button.
-
-
Click either Load Workload or Discover Workload, depending on which button is available in accordance with your selection in step 2.
The system displays workloads, if found, in the Discovered Workloads table.
-
Either click Next to load the workload, or select one of the workloads, then click Next to continue importing the workload.
The Import Workload: Replay page appears only under the following conditions:
-
You chose "Import a completed captured workload from a directory in the file system" in step 2.
-
The workload contains one or more Replays.
-
-
Optional: Select one or more Replays, if desired, provide a Replay Task Name, then click Next.
The Import Workload: Review page appears.
-
If everything appears as you have intended, click Submit.
The Database Replay page reappears and displays a message stating that the job was submitted successfully. The Status column for your loaded or imported workload in the Captured Workload table will show In Progress.
Tip:
You can check on the job's progress by clicking on the captured workload name that you just submitted in the Review step. A Capture Summary page appears, and you can click the Database Replay Import Job link to see the progress of the job execution steps.
10.11 Creating Subsets from an Existing Workload
For cases in which you have captured a large workload covering a long period of time, you may only want to replay a portion of it to accelerate testing. The Database Replay Workload Subsetting feature enables you to create new workloads by extracting portions of an existing captured workload.
Enterprise Manager provides a wizard to extract a subset of data from an existing workload that you can use for Replay on a test system. Each extracted subset is a legitimate workload that can be replayed on its own or with other workloads in a consolidated Replay.
To perform a Replay, you need to preprocess the workloads.
This feature is available for Cloud Control Database plug-in 12.1.0.5 and later releases.
To extract subsets from a workload:
-
From the Captured Workloads tab of the Database Replay page, select a workload for which you want to extract a subset, then click Subset.
The Subset Workload: Define page appears, showing an Active Sessions History chart for the workload.
-
Select a starting and ending time for the subset you want to extract from the workload:
-
Click Add above the Subsets table at the bottom of the page.
The Create Subset pop-up appears.
-
Select either snapshot or calendar times, provide start and end times, then click OK.
Note:
Snapshot time is the preferred choice, because not all performance data may be available for the calendar time you select.
Your selected time period now appears in the Active Sessions chart as a greyed-out segment.
-
Optional: Define one or more additional subsets with different time periods than those you selected in the step above.
-
Optional: In the Advanced Parameters section, indicate whether you want to include incomplete calls after the subset workload ends. The default is to include incomplete calls when the subset workload begins.
-
These parameters enable you to include the calls outside of your defined boundaries. For example, when you specify a starting and ending time as the boundaries for a transaction, the transaction may have started before your indicated start time, and may also have continued after your indicated end time.
-
-
-
Click Next.
The Subset Workload: Database page appears.
-
Click the search icon next to the Database Target field and select a database for subsetting from the Search and Select: Targets pop-up that appears.
The system now requests database and host credentials.
-
Provide the requisite input for the step above, then click Next.
The Subset Workload: Location page appears.
-
If the source host and staged database host are the same, the location is pre-populated, so you do not need to provide the location for the source workload files.
-
If the source host and staged database host are not the same, do the following:
-
Choose whether you want to access the workload files from the host name shown in the Host field, or whether you want to copy the files from the source host to the Destination Host shown.
Access Directly means that the database to be used to subset the workload can access the original workload directly using the specified file system location. This is typically the case when the original workload is stored at a network shared location.
Access Copy means that the two hosts are not in the shared network path. You need to provide the source host credentials so that Enterprise Manager can copy the original workload from its current location to the specified location on the subset database host.
-
Depending on your choice above, either provide the directory location containing the workload files, or provide the location for the destination host.
-
-
-
In the Subset field, specify the storage location for each subset, then click Next.
The Subset Workload: Schedule page appears.
-
Indicate when you want to start the subset job, then click Next.
The Subset Workload: Review page appears.
-
If everything appears as you have intended, click Submit.
The Database Replay page reappears and displays a message stating that the job was submitted successfully. The Status column for your subset in the Replay Tasks table will show In Progress.
Tip:
You can check on the job's progress by clicking on the subset name that you just submitted in the Review step. A Capture Summary page appears, and you can click the Database Replay Subset Job link to see the progress of the job execution steps.
10.12 Copying or Moving a Workload to a New Location
-
Duplicate the Capture files from the source to another host and location.
-
Move the Capture files to a new host and location, and delete the source files from the original location.
This feature is available for Cloud Control Database plug-in 12.1.0.5 and later releases.
To copy a workload to a new location:
-
From the Captured Workloads tab of the Database Replay page, select a workload you want to copy to a new location, then click Copy.
The Copy Workload page appears, and displays the current source location of the workload directory you selected.
-
Provide or change credentials for the storage host, if necessary. The system automatically picks up the previously defined credentials for the current storage host.
-
Leave the After Copy radio button enabled, which is "Keep original workload in the source location."
-
Select the Storage Host for the new location of the workload directory.
-
Provide credentials for the new storage host.
-
Select the directory for the new Destination Location for the workload.
-
Schedule the job, then click Submit.
The Database Replay page reappears and displays a message stating that the job was submitted and that the storage location has been updated successfully.
Tip:
You can check on the job's progress by going to the Job Activity page, searching for the job name that appeared in the submit message, then clicking its link to access the Job Run page.
10.13 Capturing a Database Workload Using APIs
Capturing a database workload using the DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE package involves:
See Also:
-
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about the
DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTUREpackage
10.13.1 Defining Workload Capture Filters
To add filters to a workload capture:
-
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.ADD_FILTER ( fname => 'user_ichan', fattribute => 'USER', fvalue => 'ICHAN'); END; /In this example, the
ADD_FILTERprocedure adds a filter named user_ichan, which can be used to filter out all sessions belonging to the user name ICHAN.The
ADD_FILTERprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
fnamerequired parameter specifies the name of the filter that will be added. -
The
fattributerequired parameter specifies the attribute on which the filter will be applied. Valid values include PROGRAM, MODULE, ACTION, SERVICE, INSTANCE_NUMBER, and USER. -
The
fvaluerequired parameter specifies the value for the corresponding attribute on which the filter will be applied. It is possible to use wildcards such as % with some of the attributes, such as modules and actions.
-
To remove filters from a workload capture:
-
Use the
DELETE_FILTERprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.DELETE_FILTER (fname => 'user_ichan'); END; /
In this example, the
DELETE_FILTERprocedure removes the filter named user_ichan from the workload capture.The
DELETE_FILTERprocedure in this example uses thefnamerequired parameter, which specifies the name of the filter to be removed. TheDELETE_FILTERprocedure will not remove filters that belong to completed captures; it only applies to filters of captures that have yet to start.
10.13.2 Starting a Workload Capture
It is important to have a well-defined starting point for the workload so that the replay system can be restored to that point before initiating a replay of the captured workload. To have a well-defined starting point for the workload capture, it is preferable not to have any active user sessions when starting a workload capture. If active sessions perform ongoing transactions, those transactions will not be replayed properly in subsequent database replays, since only that part of the transaction whose calls were executed after the workload capture is started will be replayed. To avoid this problem, consider restarting the database in restricted mode using STARTUP RESTRICT before starting the workload capture. Once the workload capture begins, the database will automatically switch to unrestricted mode and normal operations can continue while the workload is being captured. For more information about restarting the database before capturing a workload, see "Restarting the Database".
To start a workload capture:
-
Use the
START_CAPTUREprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.START_CAPTURE (name => 'dec10_peak', dir => 'dec10', duration => 600, capture_sts => TRUE, sts_cap_interval => 300, plsql_mode => 'extended' encryption => 'AES256'); END; /In this example, a workload named
dec10_peakwill be captured for 600 seconds and stored in the file system defined by the database directory object nameddec10. A SQL tuning set will also be captured in parallel with the workload capture.The
START_CAPTUREprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
namerequired parameter specifies the name of the workload that will be captured. -
The
dirrequired parameter specifies a directory object pointing to the directory where the captured workload will be stored. -
The
durationparameter specifies the number of seconds before the workload capture will end. If a value is not specified, the workload capture will continue until theFINISH_CAPTUREprocedure is called. -
The
capture_stsparameter specifies whether to capture a SQL tuning set in parallel with the workload capture. If this parameter is set toTRUE, you can capture a SQL tuning set during workload capture, then capture another SQL tuning set during workload replay, and use SQL Performance Analyzer to compare the SQL tuning sets without having to re-execute the SQL statements. This enables you to obtain a SQL Performance Analyzer report and compare the SQL performance—before and after the change—while running Database Replay. You can also export the resulting SQL tuning set with its AWR data using theEXPORT_AWRprocedure, as described in "Exporting AWR Data for Workload Capture".This feature is not supported for Oracle RAC. Workload capture filters that are defined using
DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTUREdo not apply to the SQL tuning set capture. The default value for this parameter isFALSE. -
The
sts_cap_intervalparameter specifies the duration of the SQL tuning set capture from the cursor cache in seconds. The default value is 300. Setting the value of this parameter below the default value may cause additional overhead with some workloads and is not recommended. -
The optional
plsql_modeparameter determines how PL/SQL is handled by DB Replay during capture and replays.These two values can be set for the
plsql_modeparameter:-
top_level: Only top-level PL/SQL calls are captured and replayed, which is how DB Replay handled PL/SQL prior to Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2.0.1). This is the default value. -
extended: Both top-level PL/SQL calls and SQL called from PL/SQL are captured. When the workload is replayed, the replay can be done at either top-level or extended level, but not both.
-
-
The
encryptionparameter specifies the algorithm used for encrypting capture files.The following encryption standards can be used for the
encryptionparameter:-
NULL - Capture files are not encrypted (the default value)
-
AES128- Capture files are encrypted using AES128 -
AES192- Capture files are encrypted using AES192 -
AES256- Capture files are encrypted using AES256
Note:
To run
START_CAPTUREwith encryption, you must set the password using theoracle.rat.database_replay.encryption(case-sensitive) identifier. The password is stored in a software keystore. For more information about creating a software keystore, see Oracle Database Advanced Security Guide. -
-
Example: Setting up a password-based software keystore:
The following statement creates a password-based software keystore:
ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT CREATE KEYSTORE 'MYKEYSTORE' IDENTIFIED BY password;The following statements open the password-based software keystore and create a backup of the password-based software keystore:
ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE OPEN IDENTIFIED BY password; ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEY IDENTIFIED BY password WITH BACKUP;
The following statement adds secret secret_key, with the tag DBREPLAY, for client 'oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption' to the password-based software keystore. It also creates a backup of the password-based software keystore before adding the secret:
ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT ADD SECRET secret_key FOR CLIENT 'oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption' USING TAG 'DBREPLAY' IDENTIFIED BY password WITH BACKUP;
The following statement closes the password-based software keystore:
ADMINISTER KEY MANAGEMENT SET KEYSTORE CLOSE IDENTIFIED BY password;Note:
The software keystore must be kept open before running database capture and database replay.
10.13.3 Stopping a Workload Capture
This section describes how to stop a workload capture.
To stop a workload capture:
Tip:
After capturing a workload on the production system, you need to preprocess the captured workload, as described in Preprocessing a Database Workload.
10.13.4 Exporting AWR Data for Workload Capture
Exporting AWR data enables detailed analysis of the workload. This data is also required if you plan to run the Replay Compare Period report or the AWR Compare Period report on a pair of workload captures or replays.
To export AWR data:
-
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.EXPORT_AWR (capture_id => 2); END; /
In this example, the AWR snapshots that correspond to the workload capture with a capture ID of 2 are exported, along with any SQL tuning set that may have been captured during workload capture.
The
EXPORT_AWRprocedure uses thecapture_idrequired parameter, which specifies the ID of the capture whose AWR snapshots will be exported. The value of thecapture_idparameter is displayed in theIDcolumn of theDBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview.Note:
This procedure works only if the corresponding workload capture was performed in the current database and the AWR snapshots that correspond to the original capture time period are still available.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for information about the DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURES view
10.13.5 Importing AWR Data for Workload Capture
To import AWR data:
-
Use the
IMPORT_AWRfunction, as shown in the following example:CREATE USER capture_awr SELECT DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.IMPORT_AWR (capture_id => 2, staging_schema => 'capture_awr') FROM DUAL;In this example, the AWR snapshots that correspond to the workload capture with a capture ID of 2 are imported using a staging schema named
capture_awr.The
IMPORT_AWRprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
capture_idrequired parameter specifies the ID of the capture whose AWR snapshots will be import. The value of thecapture_idparameter is displayed in theIDcolumn of theDBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview. -
The
staging_schemarequired parameter specifies the name of a valid schema in the current database which can be used as a staging area while importing the AWR snapshots from the capture directory to theSYSAWRschema.
-
Note:
This function fails if the schema specified by the staging_schema parameter contains any tables with the same name as any of the AWR tables.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for information about the DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURES view
10.14 Encrypting and Decrypting an Existing Workload Capture Using APIs
This section describes how to encrypt and decrypt an existing workload capture using APIs.
During a workload capture, a variety of information such as connection strings, SQL text, and bind values are saved. This information can be encrypted if it contains sensitive data. You can enable encryption during workload capture as described in Starting a Workload Capture.
10.14.1 Encrypting an Existing Workload Capture
This section describes how to encrypt an existing workload capture.
To encrypt an existing workload capture:
-
Use the
ENCRYPT_CAPTUREprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.ENCRYPT_CAPTURE(src_dir => 'dec10', dst_dir => 'dec10_enc', encryption => 'AES128'); END; /The
ENCRYPT_CAPTUREprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
src_dirparameter points to the directory that contains the workload capture to be encrypted. -
The
dst_dirparameter points to the directory where the encrypted capture is saved after encryption. -
The
encryptionparameter specifies the algorithm used for encrypting the workload capture.
-
Note:
Before running DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.ENCRYPT_CAPTURE, you must store the oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption (case-sensitive) identifier in a software keystore.
10.14.2 Decrypting an Encrypted Workload Capture
This section describes how to decrypt an encrypted workload capture.
An encrypted workload capture can be decrypted by using the DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.DECRYPT_CAPTURE procedure.
To decrypt an encrypted workload capture:
-
Use the
DECRYPT_CAPTUREprocedure:BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.DECRYPT_CAPTURE(src_dir => 'dec10_enc', dst_dir => 'dec10'); END; /The
DECRYPT_CAPTUREprocedure in this example uses the following parameters:-
The
src_dirparameter points to the directory that contains the encrypted capture. -
The
dst_dirparameter points to the directory where the decrypted capture is saved after decryption.
-
Note:
Before running DBMS_WORKLOAD_CAPTURE.DECRYPT_CAPTURE, you must store the oracle.rat.database_replay.encryption (case-sensitive) identifier in a software keystore.
10.15 Monitoring Workload Capture Using Views
To access these views, you need DBA privileges:
-
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview lists all the workload captures that have been captured in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_FILTERSview lists all workload filters used for workload captures defined in the current database.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for information about the
DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview -
Oracle Database Reference for information about the
DBA_WORKLOAD_FILTERSview