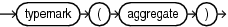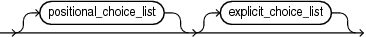13.31 Expression
An expression is an arbitrarily complex combination of operands (variables, constants, literals, operators, function invocations, and placeholders) and operators.
The simplest expression is a single variable.
The PL/SQL compiler determines the data type of an expression from the types of the operands and operators that comprise the expression. Every time the expression is evaluated, a single value of that type results.
Topics
Syntax
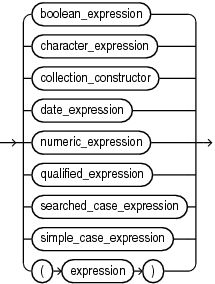
expression ::=
(boolean_expression ::=, character_expression ::=, collection_constructor ::=, date_expression ::=, numeric_expression ::=, qualified_expression ::= , searched_case_expression ::=, simple_case_expression ::=)
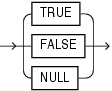
boolean_literal ::=
conditional_predicate ::=
other_boolean_form ::=
character_expression ::=
collection_constructor ::=
date_expression ::=
numeric_expression ::=
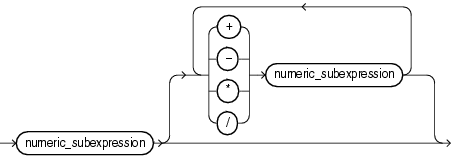
numeric_subexpression ::=
function_call ::=
qualified_expression ::=
typemark ::=
type_name ::=
aggregate ::=
positional_choice_list ::=
explicit_choice_list ::=
named_choice_list ::=
indexed_choice_list ::=
searched_case_expression ::=
simple_case_expression ::=
Semantics
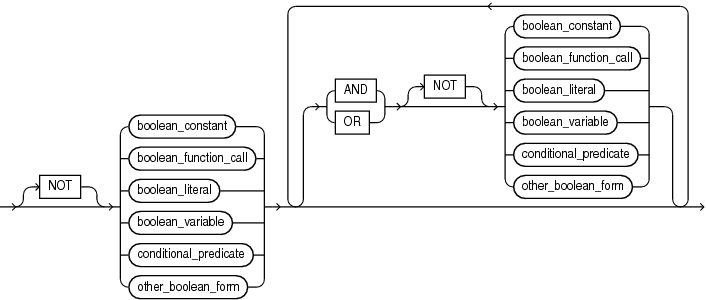
boolean_expression
Expression whose value is TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. For more information, see "BOOLEAN Expressions".
Restriction on boolean_expression
Because SQL has no data type equivalent to BOOLEAN, you cannot:
-
Assign a
BOOLEANvalue to a database table column -
Select or fetch the value of a database table column into a
BOOLEANvariable -
Use a
BOOLEANvalue in a SQL function(However, a SQL query can invoke a PL/SQL function that has a
BOOLEANparameter, as in Example 3-3.) -
Use a
BOOLEANexpression in a SQL statement, except as an argument to a PL/SQL function invoked in a SQL query, or in a PL/SQL anonymous block.Note:
An argument to a PL/SQL function invoked in a static SQL query cannot be a
BOOLEANliteral. The workaround is to assign the literal to a variable and then pass the variable to the function, as in Example 3-3.
NOT, AND, OR
See "Logical Operators".
boolean_constant
Name of a constant of type BOOLEAN.
boolean_function_call
Invocation of a previously defined function that returns a BOOLEAN value. For more semantic information, see "function_call".
boolean_variable
Name of a variable of type BOOLEAN.
conditional_predicate
See "Conditional Predicates for Detecting Triggering DML Statement".
other_boolean_form
collection
Name of a collection variable.
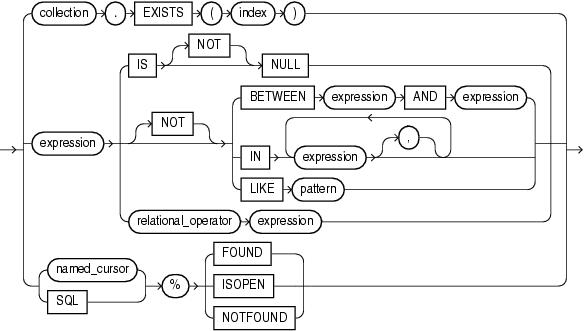
EXISTS
Collection method (function) that returns TRUE if the indexth element of collection exists and FALSE otherwise. For more information, see "EXISTS Collection Method".
Restriction on EXISTS
You cannot use EXISTS if collection is an associative array.
index
Numeric expression whose data type either is PLS_INTEGER or can be implicitly converted to PLS_INTEGER (for information about the latter, see "Predefined PLS_INTEGER Subtypes").
IS [NOT] NULL
See "IS [NOT] NULL Operator".
BETWEEN expression AND expression
See "BETWEEN Operator".
IN expression [, expression ]...
See "IN Operator".
LIKE pattern
See "LIKE Operator".
relational_operator
See "Relational Operators".
SQL
Implicit cursor associated with the most recently run SELECT or DML statement. For more information, see "Implicit Cursors".
%FOUND, %ISOPEN, %NOTFOUND
Cursor attributes explained in "Implicit Cursor Attribute" and "Named Cursor Attribute".
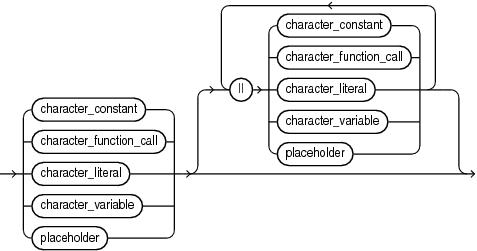
character_expression
Expression whose value has a character data type (that is, a data type in the CHAR family, described in "CHAR Data Type Family").
character_constant
Name of a constant that has a character data type.
character_function_call
Invocation of a previously defined function that returns a value that either has a character data type or can be implicitly converted to a character data type. For more semantic information, see "function_call".
character_literal
Literal of a character data type.
character_variable
Name of a variable that has a character data type.
||
Concatenation operator, which appends one string operand to another. For more information, see "Concatenation Operator".
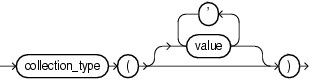
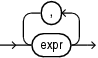
collection_constructor
Constructs a collection of the specified type with elements that have the specified values.
For more information, see "Collection Constructors".
collection_type
Name of a previously declared nested table type or VARRAY type (not an associative array type).
value
Valid value for an element of a collection of collection_type.
If collection_type is a varray type, then it has a maximum size, which the number of values cannot exceed. If collection_type is a nested table type, then it has no maximum size.
If you specify no values, then the constructed collection is empty but not null (for the difference between empty and null, see "Collection Types").
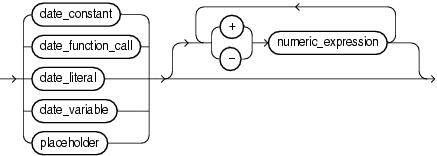
date_expression
Expression whose value has a date data type (that is, a data type in the DATE family, described in "DATE Data Type Family").
date_constant
Name of a constant that has a date data type.
date_function_call
Invocation of a previously defined function that returns a value that either has a date data type or can be implicitly converted to a date data type. For more semantic information, see "function_call".
date_literal
Literal whose value either has a date data type or can be implicitly converted to a date data type.
date_variable
Name of a variable that has a date data type.
+, -
Addition and subtraction operators.
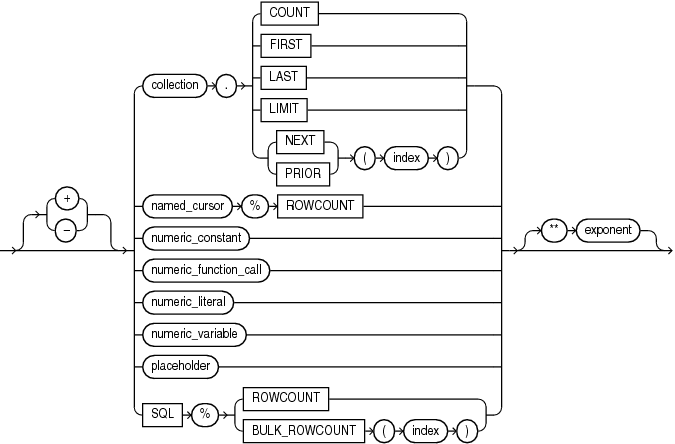
numeric_expression
Expression whose value has a date numeric type (that is, a data type in the DATE family, described in "NUMBER Data Type Family").
+, -, /, *, **
Addition, subtraction, division, multiplication, and exponentiation operators.
numeric_subexpression
collection
Name of a collection variable.
COUNT, FIRST, LAST, LIMIT, NEXT, PRIOR
Collection methods explained in "Collection Method Invocation".
named_cursor%ROWCOUNT
See "Named Cursor Attribute".
numeric_constant
Name of a constant that has a numeric data type.
numeric_function_call
Invocation of a previously defined function that returns a value that either has a numeric data type or can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type. For more semantic information, see "function_call".
numeric_literal
Literal of a numeric data type.
numeric_variable
Name of variable that has a numeric data type.
SQL%ROWCOUNT
Cursor attribute explained in "Implicit Cursor Attribute".
SQL%BULK_ROWCOUNT]
Cursor attribute explained in "SQL%BULK_ROWCOUNT".
exponent
Numeric expression.
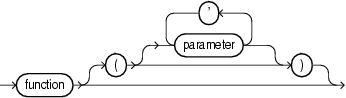
function_call
function
Name of a previously defined function.
parameter [, parameter ]...
List of actual parameters for the function being called. The data type of each actual parameter must be compatible with the data type of the corresponding formal parameter. The mode of the formal parameter determines what the actual parameter can be:
| Formal Parameter Mode | Actual Parameter |
|---|---|
|
|
Constant, initialized variable, literal, or expression |
|
|
Variable whose data type is not defined as |
|
|
Variable (typically, it is a string buffer or numeric accumulator) |
If the function specifies a default value for a parameter, you can omit that parameter from the parameter list. If the function has no parameters, or specifies a default value for every parameter, you can either omit the parameter list or specify an empty parameter list.
qualified_expression
Qualified expressions for RECORD types are allowed in any context where an expression of RECORD type is allowed.
Qualified expressions for associative array types are allowed in any context where an expression of associative array type is allowed.
typemark ( aggregate )
Specifies explicitly the type of the aggregate (qualified items).
typemark
type_name
Qualified expressions use an explicit type indication to provide the type of the qualified item. This explicit indication is known as a typemark.
identifier [ . ]
Indicates the type of the qualified item.
aggregate
A qualified expression combines expression elements to create values of aRECORD type, or associative array type.
positional_choice_list
expr [ , ]
Positional association is allowed for qualified expressions of RECORD type.
A positional association may not follow a named association in the same construct (and vice versa).
explicit_choice_list
named_choice_list | indexed_choice_list
Named choices must use names of fields from the qualifying structure type. Index key values must be compatible with the index type for the qualifying vector type.
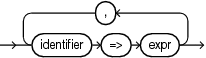
named_choice_list
A named choice applies only to structured types
identifier => expr [ , ]
Named association is allowed for qualified expressions of RECORD type.
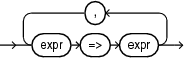
indexed_choice_list
An index choice applies only to vector types.
expr => expr [ , ]
Indexed choices (key-value pairs) is allowed for qualified expressions of associative array types. Both the key and the value may be expressions.
Using NULL as an index key value is not permitted with associative array type constructs.
searched_case_expression
WHEN boolean_expression THEN result
The boolean_expressions are evaluated sequentially. If a boolean_expression has the value TRUE, then the result associated with that boolean_expression is returned. Subsequent boolean_expressions are not evaluated.
ELSE result
The result is returned if and only if no boolean_expression has the value TRUE.
If you omit the ELSE clause, the searched case expression returns NULL.
See Also:
simple_case_expression
selector
An expression of any PL/SQL type except BLOB, BFILE, or a user-defined type. The selector is evaluated once.
WHEN selector_value THEN result
The selector_values are evaluated sequentially. If a selector_value is the value of selector, then the result associated with that selector_value is returned. Subsequent selector_values are not evaluated.
A selector_value can be of any PL/SQL type except BLOB, BFILE, an ADT, a PL/SQL record, an associative array, a varray, or a nested table.
ELSE result
The result is returned if and only if no selector_value has the same value as selector.
If you omit the ELSE clause, the simple case expression returns NULL.
Note:
If you specify the literal NULL for every result (including the result in the ELSE clause), then error PLS-00617 occurs.
See Also:
Examples
-
Example 2-28, "Concatenation Operator Examples"
-
Example 2-30, "Controlling Evaluation Order with Parentheses"
-
Example 2-31, "Expression with Nested Parentheses"
-
Example 2-32, "Improving Readability with Parentheses"
-
Example 2-33, "Operator Precedence"
-
Example 2-43, "Relational Operators in Expressions"
-
Example 2-44, "LIKE Operator in Expression"
-
Example 2-46, "BETWEEN Operator in Expressions"
-
Example 2-47, "IN Operator in Expressions"
-
Example 2-50, "Simple CASE Expression"
-
Example 2-52, "Searched CASE Expression"
-
Example 9-1, "Trigger Uses Conditional Predicates to Detect Triggering Statement"
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters:
-
"Qualified Expressions Overview" for more information and examples
-
"Literals"