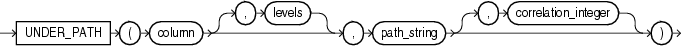24 Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Predefined public views RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW provide access to Oracle XML DB repository data. You can use Oracle SQL functions under_path and equals_path to query resources based on their path names, and functions path and depth to return resource path names and depths.
- Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Public viewsRESOURCE_VIEWandPATH_VIEWprovide a mechanism for using SQL to access data stored in Oracle XML DB Repository. You can use these views to access data stored in the repository using Internet protocols such as FTP and WebDAV or using application program interfaces (APIs). - Oracle SQL Functions That Use RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Oracle SQL functions used with public viewsRESOURCE_VIEWandPATH_VIEWincludeunder_path,equals_path,path, anddepth. - Accessing Repository Data Paths, Resources and Links: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to access Oracle XML DB Repository paths, resources, and link properties. - Deleting Repository Resources: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to delete Oracle XML DB Repository resources and paths. - Updating Repository Resources: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to update Oracle XML DB Repository resources and paths. - Working with Multiple Oracle XML DB Resources
To perform an operation on multiple Oracle XML DB resources, or to find one or more Oracle XML DB resources that meet a certain set of criteria, use SQL withRESOURCE_VIEWandPATH_VIEW. - Performance Guidelines for Oracle XML DB Repository Operations
Guidelines are presented for improving the performance of repository operations such as resource creation and querying. - Searching for Resources Using Oracle Text
TableXDB$RESOURCEin database schemaXDBstores the metadata and content of repository resources. You can search for resources that contain a specific keyword by using Oracle SQL functioncontainswithRESOURCE_VIEWorPATH_VIEW.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information about view
PATH_VIEW -
Oracle Database Reference for more information about view
RESOURCE_VIEW
Parent topic: Oracle XML DB Repository
24.1 Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Public views RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW provide a mechanism for using SQL to access data stored in Oracle XML DB Repository. You can use these views to access data stored in the repository using Internet protocols such as FTP and WebDAV or using application program interfaces (APIs).
Figure 24-1 illustrates this.
RESOURCE_VIEW consists of a resource, itself an XMLType instance, that contains the name of the resource, its ACLs, and its properties, static or extensible.
-
If the content of a resource is XML data stored somewhere in an
XMLTypetable or view then theRESOURCE_VIEWpoints to theXMLTyperow that stores the content. -
If the content of a resource is not XML data then the
RESOURCE_VIEWstores the content as a LOB.
Note:
As of Oracle Database Release 11.2.0.1.0, repository content stored in line as a LOB uses SecureFiles LOB storage. Prior to that, it used BasicFiles LOB storage.
Parent-child relationships between folders are maintained and traversed efficiently using the hierarchical repository index. Text indexes are available to search the properties of a resource, and internal B-tree indexes over names and ACLs speed up access to these attributes of the resource XMLType data.
RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW, along with PL/SQL package DBMS_XDB_REPOS, provide all query-based access to Oracle XML DB and DML functionality that is available through the API.
The base table for RESOURCE_VIEW is XDB.XDB$RESOURCE. Access this table only using RESOURCE_VIEW or PL/SQL package DBMS_XDB_REPOS.
Figure 24-1 Accessing Repository Resources Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
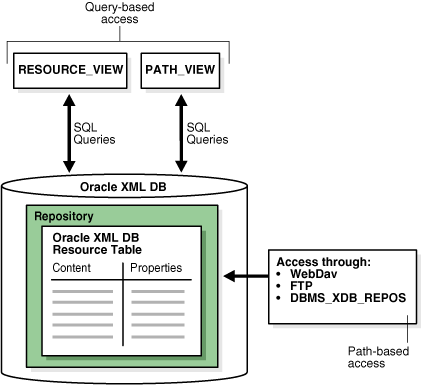
Description of "Figure 24-1 Accessing Repository Resources Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW"
Figure 24-2 illustrates the structure of RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW.
Figure 24-2 RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW Structure
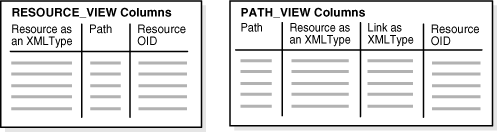
Description of "Figure 24-2 RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW Structure"
Note:
Neither RESOURCE_VIEW nor PATH_VIEW contains the root folder (/) resource. All other repository resources are included.
A path in the RESOURCE_VIEW is an arbitrary one of the paths that can be used to access the given resource. Oracle SQL function under_path lets applications search for resources that are contained (recursively) within a particular folder, get the resource depth, and so on. Each row in the PATH_VIEW and RESOURCE_VIEW columns is of data type XMLType. DML on repository views can be used to insert, rename, delete, and update resource properties and contents. Programmatic APIs must be used for some operations, such as creating links to existing resources.
Paths in the ANY_PATH column of the RESOURCE_VIEW and the PATH column in the PATH_VIEW are absolute paths: they start at the root.
Note:
Test resource paths for equality using Oracle SQL function equals_path: equals_path('/my/path') = 1. Do not test ANY_PATH for equality against an absolute path: ANY_PATH = '/my/path'.
Paths returned by the path function are relative paths under the path name specified by function under_path. For example, if there are two resources referenced by path names /a/b/c and /a/d, respectively, then a path expression that retrieves paths under folder /a returns relative paths b/c and d.
When there are multiple hard links to the same resource, only paths under the path name specified by function under_path are returned. If /a/b/c, /a/b/d, and /a/e are all links to the same resource, then a query on PATH_VIEW that retrieves all of the paths under /a/b returns only /a/b/c and /a/b/d, not /a/e.
- RESOURCE_VIEW Definition and Structure
Public viewRESOURCE_VIEWcontains one row for each resource in Oracle XML DB Repository (except for the root folder resource). - PATH_VIEW Definition and Structure
Public viewPATH_VIEWcontains one row for each unique path that accesses a resource in Oracle XML DB Repository (except for the root folder resource). Each resource can have multiple paths, also called links. - The Difference Between RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
PATH_VIEWincludes all the path names to a particular resource.RESOURCE_VIEWincludes one of the possible path names to the resource.PATH_VIEWalso includes the link properties. For better performance, useRESOURCE_VIEW, notPATH_VIEW, whenever possible. - Operations You Can Perform Using UNDER_PATH and EQUALS_PATH
You can use Oracle SQL functionsunder_pathandequals_pathto get a resource or its OID; create, delete, or update a resource; or list a directory that corresponds to a path name.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.1.1 RESOURCE_VIEW Definition and Structure
Public view RESOURCE_VIEW contains one row for each resource in Oracle XML DB Repository (except for the root folder resource).
Table 24-1 describes the structure of RESOURCE_VIEW.
Table 24-1 Structure of RESOURCE_VIEW
| Column | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
A resource in the repository (except for the root folder resource) |
|
|
|
An (absolute) path to the resource |
|
|
|
Resource OID, which is a unique handle to the resource |
Parent topic: Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.1.2 PATH_VIEW Definition and Structure
Public view PATH_VIEW contains one row for each unique path that accesses a resource in Oracle XML DB Repository (except for the root folder resource). Each resource can have multiple paths, also called links.
Table 24-2 describes the structure of PATH_VIEW.
Table 24-2 Structure of PATH_VIEW
| Column | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
An (absolute) path to repository resource |
|
|
|
The resource referred to by column |
|
|
|
Link property |
|
|
|
Resource OID |
Parent topic: Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.1.3 The Difference Between RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
PATH_VIEW includes all the path names to a particular resource. RESOURCE_VIEW includes one of the possible path names to the resource. PATH_VIEW also includes the link properties. For better performance, use RESOURCE_VIEW, not PATH_VIEW, whenever possible.
Figure 24-3 illustrates this difference.
Because many Internet applications need only one URL to access a resource, RESOURCE_VIEW is widely applicable.
PATH_VIEW contains both link properties and resource properties, whereas the RESOURCE_VIEW contains only resource properties.
Because it handles the information for multiple paths, PATH_VIEW access can be slower. If you use RESOURCE_VIEWthen the database can take advantage of the fact that only one path is needed; the index can do less work to determine all the possible paths.
Note:
When using RESOURCE_VIEW, if you specify a path using function under_path or equals_path, the function finds the resource regardless of whether or not the specified path is the arbitrary one chosen to normally appear with that resource using RESOURCE_VIEW.
Figure 24-3 RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW Explained
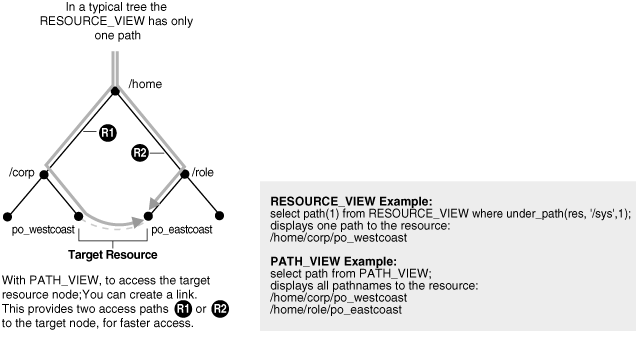
Description of "Figure 24-3 RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW Explained"
Parent topic: Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.1.4 Operations You Can Perform Using UNDER_PATH and EQUALS_PATH
You can use Oracle SQL functions under_path and equals_path to get a resource or its OID; create, delete, or update a resource; or list a directory that corresponds to a path name.
-
Given a path name, you can:
-
Get a resource or its OID
-
List the directory given by the path name
-
Create a resource
-
Delete a resource
-
Update a resource
-
-
Given a condition that uses
under_pathor other SQL functions, you can:-
Update resources
-
Delete resources
-
Get resources or their OID
-
Parent topic: Overview of Oracle XML DB RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.2 Oracle SQL Functions That Use RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Oracle SQL functions used with public views RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW include under_path, equals_path, path, and depth.
- UNDER_PATH SQL Function
Oracle SQL functionunder_pathuses the hierarchical index of Oracle XML DB Repository to return the paths to all hard links under a particular path. This index is designed to speed access when traversing a path (the most common usage). - EQUALS_PATH SQL Function
You use Oracle SQL functionequals_pathto find a resource that has a given path name. It is functionally equivalent tounder_pathwith a depth restriction of zero. - PATH SQL Function
Oracle SQL functionpathreturns the relative path name of the resource under a givenpathnameargument to functionunder_pathorequal_path. - DEPTH SQL Function
Oracle SQL functiondepthreturns the folder depth of the resource under the specified starting path.
Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.2.1 UNDER_PATH SQL Function
Oracle SQL function under_path uses the hierarchical index of Oracle XML DB Repository to return the paths to all hard links under a particular path. This index is designed to speed access when traversing a path (the most common usage).
If the other parts of a query predicate are very selective, however, then a functional implementation of under_path can be chosen that walks back up the repository. This can be more efficient, because fewer links must be traversed. Figure 24-4 shows the under_path syntax.
Table 24-3 details the signature of Oracle SQL function under_path.
Table 24-3 UNDER_PATH SQL Function Signature
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
under_path(resource_column, pathname); |
Determines whether a resource is under a specified path. Parameters:
|
under_path(resource_column, depth, pathname); |
Determines whether a resource is under a specified path, with a depth argument to restrict the number of levels to search. Parameters:
|
under_path(resource_column, pathname, correlation); |
Determines if a resource is under a specified path, with a correlation argument for related SQL functions. Parameters:
|
under_path(resource_column, depth, pathname, correlation); |
Determines if a resource is under a specified path with a depth argument to restrict the number of levels to search, and with a correlation argument for related SQL functions. Parameters:
For a resource to be returned, only one of the accessible paths to the resource must be under the |
Note:
Function under_path does not follow weak links, because such traversal could lead to cycles. A weak-link argument to under_path is resolved correctly, but weak links are not followed when traversing resources under that path.
24.2.2 EQUALS_PATH SQL Function
You use Oracle SQL function equals_path to find a resource that has a given path name. It is functionally equivalent to under_path with a depth restriction of zero.
equals_path(resource_column, pathname);
where:
-
resource_columnis the column name or column alias of theRESOURCEcolumn inPATH_VIEWorRESOURCE_VIEW. -
pathnameis the (absolute) path name to resolve. This can contain components that are hard or weak resource links.
Figure 24-5 illustrates the complete equals_path syntax.
Note:
-
Test resource paths for equality using Oracle SQL function
equals_path:equals_path('/my/path') = 1. Do not testANY_PATHfor equality against an absolute path:ANY_PATH = '/my/path'. -
Use bind variables, instead of hard-coded strings, with
equals_path.
24.2.3 PATH SQL Function
Oracle SQL function path returns the relative path name of the resource under a given pathname argument to function under_path or equal_path.
The path column in the RESOURCE_VIEW always contains the absolute path of the resource. The syntax of function path is:
path(correlation);
where:
-
correlationis an integer that can be used to correlatepathwith under_path orequals_path.
Figure 24-6 illustrates the syntax for function path.
24.3 Accessing Repository Data Paths, Resources and Links: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to access Oracle XML DB Repository paths, resources, and link properties.
The first few examples use resources specified by the following paths:
/a/b/c
/a/b/c/d
/a/e/c
/a/e/c/d
Example 24-1 uses Oracle SQL function path to retrieve the relative paths under path /a/b.
Example 24-2 uses ANY_PATH to retrieve the absolute paths under path /a/b.
Example 24-3 is the same as Example 24-2, except that the test is not-equals (!=) instead of equals (=). The query in Example 24-3 finds all paths in the repository that are not under path /a/b.
Example 24-4 shows the relative paths that are under repository folders a/b and /a/e, respectively. The expression path(1) represents the paths that are under folder a/b, since it uses the same correlation number, 1, as the expression under_path(RES, '/a/b', 1), which specifies folder a/b. Similarly for path(2) and folder /a/e. Expression ANY_PATH returns the corresponding absolute paths.
Example 24-1 Determining Paths Under a Path: Relative
SELECT path(1) FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/a/b', 1) = 1;
PATH(1) ------- c c/d 2 rows selected.
Example 24-2 Determining Paths Under a Path: Absolute
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/a/b') = 1;
ANY_PATH -------- /a/b/c /a/b/c/d 2 rows selected.
Example 24-3 Determining Paths Not Under a Path
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/a/b') != 1
ANY_PATH
--------
/a
/a/b
/a/e
/a/e/c
/a/e/c/d
/home
/home/OE
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002/Apr
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002/Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002/Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336271PDT.xml
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002/Apr/EABEL-20021009123336251PDT.xml
. . .
/public
/sys
/sys/acls
/sys/acls/all_all_acl.xml
/sys/acls/all_owner_acl.xml
/sys/acls/bootstrap_acl.xml
/sys/acls/ro_all_acl.xml
/sys/apps
/sys/apps/plsql
/sys/apps/plsql/xs
/sys/apps/plsql/xs/netaclrc.xml
/sys/apps/plsql/xs/netaclsc.xml
/sys/databaseSummary.xml
/sys/log
/sys/schemas
/sys/schemas/OE
/sys/schemas/OE/localhost:8080
. . .
326 rows selected.
Example 24-4 Determining Paths Using Multiple Correlations
SELECT ANY_PATH, path(1), path(2)
FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, '/a/b', 1) = 1 OR under_path(RES, '/a/e', 2) = 1;
ANY_PATH PATH(1) PATH(2)
---------- -------- --------
/a/b/c c
/a/b/c/d c/d
/a/e/c c
/a/e/c/d c/d
4 rows selected.Example 24-5 Relative Path Names for Three Levels of Resources
SELECT path(1) FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, 3, '/sys', 1) = 1;
This produces a result similar to the following.
PATH(1)
-------
acls
acls/all_all_acl.xml
acls/all_owner_acl.xml
acls/bootstrap_acl.xml
acls/ro_all_acl.xml
apps
apps/plsql
apps/plsql/xs
databaseSummary.xml
log
schemas
schemas/OE
schemas/OE/localhost:8080
schemas/PUBLIC
schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org
schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com
93 rows selected.Example 24-6 Extracting Resource Metadata Using UNDER_PATH
SELECT ANY_PATH,
XMLQuery('declare namespace ns = "http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource' PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/sys') = 1;
This produces a result similar to the following:
ANY_PATH
--------
XMLQUERY('DECLARENAMESPACENS="HTTP://XMLNS.ORACLE.COM/XDB/XDBRESOURCE.XSD";(::)$
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sys/acls
<Resource xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd">
<CreationDate>2008-06-25T13:17:45.164662</CreationDate>
<ModificationDate>2008-06-25T13:17:47.865163</ModificationDate>
<DisplayName>acls</DisplayName>
<Language>en-US</Language>
<CharacterSet>UTF-8</CharacterSet>
<ContentType>application/octet-stream</ContentType>
<RefCount>1</RefCount>
</Resource>
/sys/acls/all_all_acl.xml
<Resource xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd">
<CreationDate>2008-06-25T13:17:47.759806</CreationDate>
<ModificationDate>2008-06-25T13:17:47.759806</ModificationDate>
<DisplayName>all_all_acl.xml</DisplayName>
<Language>en-US</Language>
<CharacterSet>UTF-8</CharacterSet>
<ContentType>text/xml</ContentType>
<RefCount>1</RefCount>
</Resource>
. . .
41 rows selected.Example 24-7 Using Functions PATH and DEPTH with PATH_VIEW
SELECT path(1) path, depth(1) depth FROM PATH_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, 3, '/sys', 1) = 1;
This produces a result similar to the following:
PATH DEPTH
---- -----
acls 1
acls/all_all_acl.xml 2
acls/all_owner_acl.xml 2
acls/bootstrap_acl.xml 2
acls/ro_all_acl.xml 2
apps 1
apps/plsql 2
apps/plsql/xs 3
databaseSummary.xml 1
log 1
schemas 1
schemas/OE 2
schemas/OE/localhost:8080 3
schemas/PUBLIC 2
schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org 3
schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com 3
. . .Example 24-8 Extracting Link and Resource Information from PATH_VIEW
SELECT PATH,
XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$l/ns:LINK/ns:Name' PASSING LINK AS "l" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(256)),
XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$l/ns:LINK/ns:ParentName' PASSING LINK AS "l" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(256)),
XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$l/ns:LINK/ns:ChildName' PASSING LINK AS "l" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(256)),
XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource/ns:DisplayName'
PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(128))
FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE PATH LIKE '/sys%';
This produces a result similar to the following:
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org/1999/xlink.xsd
xlink.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org/1999/xlink
xlink
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org/1999/csx.xlink.xsd
csx.xlink.xsd
. . .
118 rows selected.Example 24-9 All Repository Paths to a Certain Depth Under a Path
SELECT path(1) FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, 3, '/sys', 1) > 0;
This produces a result similar to the following:
PATH(1)
-------
acls
acls/all_all_acl.xml
acls/all_owner_acl.xml
acls/bootstrap_acl.xml
acls/ro_all_acl.xml
apps
apps/plsql
apps/plsql/xs
databaseSummary.xml
log
principals
principals/groups
principals/users
schemas
schemas/PUBLIC
schemas/PUBLIC/www.opengis.net
schemas/PUBLIC/www.w3.org
schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com
workspaces
. . .
43 rows selected.Example 24-10 Locating a Repository Path Using EQUALS_PATH
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE equals_path(RES, '/sys') > 0;
ANY_PATH
--------
/sys
1 row selected.Example 24-11 Retrieve RESID of a Given Resource
SELECT RESID FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource/ns:DisplayName'
PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(128))
= 'example';
This produces a result similar to the following:
RESID
--------------------------------
F301A10152470252E030578CB00B432B
1 row selected.Example 24-12 Obtaining the Path Name of a Resource from its RESID
DECLARE
resid_example RAW(16);
path VARCHAR2(4000);
BEGIN
SELECT RESID INTO resid_example FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE XMLCast(XMLQuery(
'declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource/ns:DisplayName'
PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(128))
= 'example';
SELECT ANY_PATH INTO path FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE RESID = resid_example;
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('The path is: ' || path);
END;
/
The path is: /public/example
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.Example 24-13 Folders Under a Given Path
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, 1, '/sys') = 1
AND XMLExists('declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource[@Container = xs:boolean("true")]'
PASSING RES AS "r");
This produces a result like the following:
ANY_PATH
--------
/sys/acls
/sys/apps
/sys/log
/sys/schemas
4 rows selected.Example 24-14 Joining RESOURCE_VIEW with an XMLType Table
SELECT ANY_PATH, XMLQuery('$p/PurchaseOrder/LineItems'
PASSING po.OBJECT_VALUE AS "p" RETURNING CONTENT)
FROM purchaseorder po, RESOURCE_VIEW rv
WHERE ref(po)
= XMLCast(XMLQuery('declare default element namespace
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
fn:data(/Resource/XMLRef)'
PASSING rv.RES RETURNING CONTENT)
AS REF XMLType)
AND ROWNUM < 2;
ANY_PATH
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
XMLQUERY('$P/PURCHASEORDER/LINEITEMS'PASSINGPO.OBJECT_VALUEAS"P"RETURNINGCONTENT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/home/OE/PurchaseOrders/2002/Apr/AMCEWEN-20021009123336171PDT.xml
<LineItems>
<LineItem ItemNumber="1">
<Description>Salesman</Description>
<Part Id="37429158920" UnitPrice="39.95" Quantity="2"/>
</LineItem>
<LineItem ItemNumber="2">
<Description>Big Deal on Madonna Street</Description>
<Part Id="37429155424" UnitPrice="29.95" Quantity="1"/>
</LineItem>
<LineItem ItemNumber="3">
<Description>Hearts and Minds</Description>
<Part Id="37429166321" UnitPrice="39.95" Quantity="1"/>
</LineItem>
. . .
<LineItem ItemNumber="23">
<Description>Great Expectations</Description>
<Part Id="37429128022" UnitPrice="39.95" Quantity="4"/>
</LineItem>
</LineItems>
1 row selected.Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.4 Deleting Repository Resources: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to delete Oracle XML DB Repository resources and paths.
If you delete only leaf resources, then you can use DELETE FROM RESOURCE_VIEW, as in Example 24-15.
For multiple links to the same resource, deleting from RESOURCE_VIEW deletes the resource together with all of its links. Deleting from PATH_VIEW deletes only the link with the specified path.
Example 24-16 illustrates this.
Example 24-15 Deleting Resources
DELETE FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE equals_path(RES, '/public/myfile') = 1';
Example 24-16 Deleting Links to Resources
Suppose that '/home/myfile1' is a link to '/public/myfile':
CALL DBMS_XDB_REPOS.link('/public/myfile', '/home', 'myfile1');
The following SQL DML statement deletes everything in Oracle XML DB Repository that is found at path /home/myfile1 – both the link and the resource:
DELETE FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE equals_path(RES, '/home/myfile1') = 1;
The following DML statement deletes only the link with path /home/file1:
DELETE FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE equals_path(RES, '/home/file1') = 1;- Deleting Nonempty Folder Resources
TheDELETEDML operator is not allowed on a nonempty folder. If you try to delete a nonempty folder, you must first delete its contents and then delete the resulting empty folder. This rule must be applied recursively to any folders contained in the target folder.
Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.4.1 Deleting Nonempty Folder Resources
The DELETE DML operator is not allowed on a nonempty folder. If you try to delete a nonempty folder, you must first delete its contents and then delete the resulting empty folder. This rule must be applied recursively to any folders contained in the target folder.
However, the order of the paths returned from a WHERE clause is not guaranteed, and the DELETE operator does not allow an ORDER BY clause in its table-expression subclause. You cannot do the following:
DELETE FROM (SELECT 1 FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, '/public', 1) = 1
ORDER BY depth(1) DESCENDING);
Example 24-17 illustrates how to delete a nonempty folder: folder example is deleted, along with its subfolder example1.
Note:
As always, take care to avoid deadlocks with concurrent transactions when operating on multiple rows.
Example 24-17 Deleting a Nonempty Folder
SELECT PATH FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/home/US1') = 1;
PATH
--------------------------
/home/US1/example
/home/US1/example/example1
2 rows selected.
DECLARE
CURSOR c1 IS
SELECT ANY_PATH p FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, '/home/US1', 1) = 1
AND XMLExists('declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource[ns:Owner="US1"]' PASSING RES AS "r")
ORDER BY depth(1) DESC;
del_stmt VARCHAR2(500) :=
'DELETE FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE equals_path(RES, :1)=1';
BEGIN
FOR r1 IN c1 LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE del_stmt USING r1.p;
END LOOP;
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SELECT PATH FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/home/US1') = 1;
no rows selectedParent topic: Deleting Repository Resources: Examples
24.5 Updating Repository Resources: Examples
Examples here illustrate how to update Oracle XML DB Repository resources and paths.
Example 24-18 changes the resource at path /test/HR/example/paper.
See Also:
User-Defined Repository Metadata for additional examples of updating resource metadata
By default, the DisplayName element content, paper, was the same text as the last location step of the resource path, /test/HR/example/paper. This is only the default value, however. The DisplayName is independent of the resource path, so updating it does not change the path.
Element DisplayName is defined by the WebDAV standard, and it is recognized by WebDAV applications. Applications, such as an FTP client, that are not WebDAV-based do not recognize the DisplayName of a resource. An FTP client lists the resource as paper (using FTP command ls, for example) even after the UPDATE operation.
Example 24-19 changes the path for the resource from /test/HR/example/paper to /test/myexample. It is analogous to using the UNIX or Linux command mv /test/HR/example/paper /test/myexample.
See Also:
Table 21-3 for additional examples that use SQL functions that apply to RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
Example 24-18 Updating a Resource
This is the complete resource before the update operation:
SELECT XMLSerialize(DOCUMENT r.RES AS CLOB)
FROM RESOURCE_VIEW r WHERE equals_path(r.RES, '/test/HR/example/paper') = 1;
XMLSERIALIZE(DOCUMENTR.RESASCLOB)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<Resource xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd" Hidden="false" Inv
alid="false" Container="false" CustomRslv="false" VersionHistory="false" StickyR
ef="true">
<CreationDate>2005-04-29T16:30:01.588835</CreationDate>
<ModificationDate>2005-04-29T16:30:01.588835</ModificationDate>
<DisplayName>paper</DisplayName>
<Language>en-US</Language>
<CharacterSet>UTF-8</CharacterSet>
<ContentType>application/octet-stream</ContentType>
<RefCount>1</RefCount>
<ACL>
<acl description="Public:All privileges to PUBLIC" xmlns="http://xmlns.oracl
e.com/xdb/acl.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:sch
emaLocation="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/acl.xsd http:
//xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/acl.xsd">
<ace>
<principal>PUBLIC</principal>
<grant>true</grant>
<privilege>
<all/>
</privilege>
</ace>
</acl>
</ACL>
<Owner>TESTUSER1</Owner>
<Creator>TESTUSER1</Creator>
<LastModifier>TESTUSER1</LastModifier>
<SchemaElement>http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBSchema.xsd#binary</SchemaElement
>
<Contents>
<binary>4F7261636C65206F7220554E4958</binary>
</Contents>
</Resource>
1 row selected.
All of the XML elements shown here are resource metadata elements, with the exception of Contents, which contains the resource content.
This UPDATE statement updates (only) the DisplayName metadata element.
UPDATE RESOURCE_VIEW r
SET r.RES =
XMLQuery('copy $i := $p1 modify
(for $j in $i/Resource/DisplayName
return replace value of node $j with $p2)
return $i'
PASSING r.RES AS "p1", 'My New Paper' AS "p2"
RETURNING CONTENT)
WHERE equals_path(r.RES, '/test/HR/example/paper') = 1;
1 row updated.
SELECT XMLSerialize(DOCUMENT r.RES AS CLOB)
FROM RESOURCE_VIEW r WHERE equals_path(r.RES, '/test/HR/example/paper') = 1;
XMLSERIALIZE(DOCUMENTR.RESASCLOB)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<Resource xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd" Hidden="false" Inv
alid="false" Container="false" CustomRslv="false" VersionHistory="false" StickyR
ef="true">
<CreationDate>2005-04-29T16:30:01.588835</CreationDate>
<ModificationDate>2005-04-29T16:30:01.883838</ModificationDate>
<DisplayName>My New Paper</DisplayName>
<Language>en-US</Language>
. . .
<Contents>
<binary>4F7261636C65206F7220554E4958</binary>
</Contents>
</Resource>
1 row selected.Example 24-19 Updating a Path in the PATH_VIEW
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/test') = 1;
ANY_PATH
--------
/test/HR
/test/HR/example
/test/HR/example/paper
3 rows selected.
UPDATE PATH_VIEW
SET PATH = '/test/myexample' WHERE PATH = '/test/HR/example/paper';
ANY_PATH
--------
/test/HR
/test/HR/example
/test/myexample
3 rows selected.Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.6 Working with Multiple Oracle XML DB Resources
To perform an operation on multiple Oracle XML DB resources, or to find one or more Oracle XML DB resources that meet a certain set of criteria, use SQL with RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW.
For example, you can perform the following operations:
-
Update resources based on attributes – see Example 24-20
-
Finding resources inside a folder – see Example 24-21
-
Copy a set of Oracle XML DB resources – see Example 24-22
The SQL DML statement in Example 24-22 copies all of the resources in folder public to folder newlocation. It is analogous to the UNIX or Linux command cp /public/* /newlocation. Target folder newlocation must exist before the copy.
Example 24-20 Updating Resources Based on Attributes
UPDATE RESOURCE_VIEW
SET RES =
XMLQuery('copy $i := $p1 modify
(for $j in $i/Resource/DisplayName
return replace value of node $j with $p2)
return $i'
PASSING RES AS "p1", 'My New Paper' AS "p2"
RETURNING CONTENT)
WHERE XMLCast(XMLQuery('declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource/ns:DisplayName'
PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(128))
= 'My Paper';
1 row updated.
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE XMLCast(XMLQuery('declare namespace ns =
"http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd"; (: :)
$r/ns:Resource/ns:DisplayName'
PASSING RES AS "r" RETURNING CONTENT)
AS VARCHAR2(128))
= 'My New Paper';
ANY_PATH
---------------
/test/myexample
1 row selected.Example 24-21 Finding Resources Inside a Folder
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE under_path(resource, '/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb') = 1;
ANY_PATH
--------------------------------------------------------------
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBSchema.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBStandard.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/acl.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/dav.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/log
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/log/xdblog.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/stats.xsd
/sys/schemas/PUBLIC/xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/xdbconfig.xsd
12 rows selected.
Example 24-22 Copying Resources
SELECT PATH FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/test') = 1;
PATH
-----------------
/test/HR
/test/HR/example
/test/myexample
3 rows selected.
INSERT INTO PATH_VIEW
SELECT '/newlocation/' || path(1), RES, LINK, NULL FROM PATH_VIEW
WHERE under_path(RES, '/test', 1) = 1
ORDER BY depth(1);
3 rows created.
SELECT PATH FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE under_path(RES, '/newlocation') = 1;
PATH
------------------------
/newlocation/HR
/newlocation/HR/example
/newlocation/myexample
3 rows selected.Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.7 Performance Guidelines for Oracle XML DB Repository Operations
Guidelines are presented for improving the performance of repository operations such as resource creation and querying.
Folders that contain a large number of resources can negatively affect concurrency, particularly when many resources are created or deleted. As a rule of thumb, do not have folders that contain more than 10,000 resources. This empirical limit is based on the database block size and the average filename length.
If you create resources in bulk, perform a COMMIT operation at least every 1,000 resources. Performance can be negatively impacted if you commit very often or you commit less often than every 1,000 resource creations.
When creating a file resource that is an XML Schema-based document for which the XML schema is known, specify the XML schema URL as a parameter to PL/SQL function DBMS_XDB_REPOS.createResource. This saves preparsing the document to determine the XML schema.
Oracle XML DB uses configuration file xdbconfig.xml for configuring the system and protocol environment. This file includes an element parameter, resource-view-cache-size, that defines the size in dynamic memory of the RESOURCE_VIEW cache. The default value is 1048576.
The performance of some queries on RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW can be improved by tuning resource-view-cache-size. In general, the bigger the cache size, the faster the query. The default resource-view-cache-size is appropriate for most cases, but you may want to enlarge your resource-view-cache-size element when querying a sizable RESOURCE_VIEW.
The default limits for the following elements are soft limits. The system automatically adapts when these limits are exceeded.
-
xdbcore-loadableunit-size– This element indicates the maximum size to which a loadable unit (partition) can grow in Kilobytes. When a partition is read into memory or a partition is built while consuming a new document, the partition is built until it reaches the maximum size. The default value is 16 KB. -
xdbcore-xobmem-bound– This element indicates the maximum memory in kilobytes that a document is allowed to occupy. The default value is 1024 KB. Once the document exceeds this number, some loadable units (partitions) are swapped out.
Related Topics
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about PL/SQL function DBMS_XDB_REPOS.createResource
Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW
24.8 Searching for Resources Using Oracle Text
Table XDB$RESOURCE in database schema XDB stores the metadata and content of repository resources. You can search for resources that contain a specific keyword by using Oracle SQL function contains with RESOURCE_VIEW or PATH_VIEW.
To evaluate such queries, you must first create a context index on the XDB$RESOURCE table. Depending on the type of documents stored in Oracle XML DB, choose one of the following options for creating your context index:
-
If Oracle XML DB contains only XML documents, that is, no binary data, then a regular Context Index can be created on the
XDB$RESOURCEtable. This is the case for Example 24-24.CREATE INDEX xdb$resource_ctx_i ON XDB.XDB$RESOURCE(OBJECT_VALUE) INDEXTYPE IS CTXSYS.CONTEXT; -
If Oracle XML DB contains binary data such as Microsoft Word documents, then a user filter is required to filter such documents prior to indexing. Use package
DBMS_XDBT(dbmsxdbt.sql) to create and configure the Context Index.-- Install the package - connected as SYS @dbmsxdbt -- Create the preferences EXEC DBMS_XDBT.createPreferences; -- Create the index EXEC DBMS_XDBT.createIndex;
Package DBMS_XDBT also includes procedures to synchronize and optimize the index. You can use procedure configureAutoSync() to automatically sync the index by using job queues.
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about installing and using DBMS_XDBT.
Example 24-23 Find All Resources Containing "Paper"
SELECT PATH FROM PATH_VIEW WHERE contains(RES, 'Paper') > 0;
PATH
-----------------------
/newlocation/myexample
/test/myexample
2 rows selected.Example 24-24 Find All Resources Containing "Paper" that are Under a Specified Path
SELECT ANY_PATH FROM RESOURCE_VIEW
WHERE contains(RES, 'Paper') > 0 AND under_path(RES, '/test') > 0;
ANY_PATH
----------------
/test/myexample
1 row selected.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Repository Access Using RESOURCE_VIEW and PATH_VIEW