The font-stretch property selects a normal, condensed, or expanded face from a font.
/* Keyword values */ font-stretch: ultra-condensed; font-stretch: extra-condensed; font-stretch: condensed; font-stretch: semi-condensed; font-stretch: normal; font-stretch: semi-expanded; font-stretch: expanded; font-stretch: extra-expanded; font-stretch: ultra-expanded; /* Global values */ font-stretch: inherit; font-stretch: initial; font-stretch: unset;
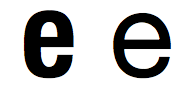
This property does not change the geometry of an arbitrary font by stretching or shrinking it. Like font-feature-settings or font-variant, it is merely a means to choose the most appropriate face of the font, if this one offers several of them.
Note: If the font provides several faces, the one fitting the best with the value of the font-stretch property is chosen. E.g. On OS X, in addition to the more common Bold, Regular, Italic, and BoldItalic faces, the "Helvetica Neue" font proposes a second set of faces with condensed, that is shrunk, characters: Condensed. Browsers supporting font-stretch will use the condensed faces for the value ultra-condensed to semi-condensed and the normal faces for the other (normal and all expanded values).

If the font has no condensed or expanded faces, like the default "Times New Roman" on Mac OS, font-stretch will not have any visible effect as the only suitable face will be used in all cases.:
| Initial value | normal |
|---|---|
| Applies to | all elements. It also applies to ::first-letter and ::first-line. |
| Inherited | yes |
| Media | visual |
| Computed value | as specified |
| Animation type | a font stretch |
| Canonical order | the unique non-ambiguous order defined by the formal grammar |
Syntax
Values
normal- Specifies a normal font face.
semi-condensed,condensed,extra-condensed,ultra-condensed- Specifies a font face more condensed than normal, with ultra-condensed as the most condensed.
semi-expanded,expanded,extra-expanded,ultra-expanded- Specifies a font face more expanded than normal, with ultra-expanded as the most expanded.
Interpolation
Font stretch values are interpolated in discrete steps. The interpolation happens as though the ordered values are equally spaced real numbers; the result is rounded to the nearest value, with values exactly halfway between two values rounded towards the later value, that is the most expanded one.
Formal syntax
normal | ultra-condensed | extra-condensed | condensed | semi-condensed | semi-expanded | expanded | extra-expanded | ultra-expanded
Example
HTML
<div class="ultra stretch"> This is text with the font extremely expanded</div> <div class="stretch"> This is text with the font stretched</div> <div class="normal"> This is text without font stretching</div> <div class="condensed"> This is text with the font condensed</div> <div class="ultra condensed"> This is text with the font extremely condensed</div>
CSS
.ultra.stretch{font-stretch: ultra-expanded;}
.stretch {font-stretch: expanded;}
.normal {font-stretch: normal;}
.condensed {font-stretch: condensed;}
.ultra.condensed {font-stretch: ultra-condensed;}
Result
Specifications
| Specification | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| CSS Fonts Module Level 3 The definition of 'font-stretch' in that specification. |
Candidate Recommendation | Initial definition |
The CSS property font-stretch was initially defined in CSS 2, but dropped in CSS 2.1 due to lack of implementation experience. It has been newly defined in CSS 3.
Browser compatibility
| Feature | Chrome | Edge | Firefox (Gecko) | Internet Explorer | Opera | Safari (WebKit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic support | 48.0 | (Yes) | 9.0 (9.0) | 9.0 | 35.0 | No support |
| Feature | Android | Edge | Firefox Mobile (Gecko) | IE Phone | Opera Mobile | Safari Mobile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic support | No support | (Yes) | 9.0 (9.0) | ? | No support | No support |