« CSS « Understanding CSS z-index
Stacking without z-index
When no element has a z-index, elements are stacked in this order (from bottom to top):
- Background and borders of the root element
- Descendant blocks in the normal flow, in order of appearance (in HTML)
- Descendant positioned elements, in order of appearance (in HTML)
In the following example, absolute and relatively positioned blocks are properly sized and positioned to illustrate the stacking rules.
Notes:
- Given a homogeneous group of elements without any z-index property, such as the positioned blocks (DIV #1 to #4) in the example, the element's stacking order is their order in the HTML hierarchy, regardless of their position.
-
Standard blocks (DIV #5) in the normal flow, without any positioning property, are always rendered before positioned elements, and appear below them, even if they come later in the HTML hierarchy.
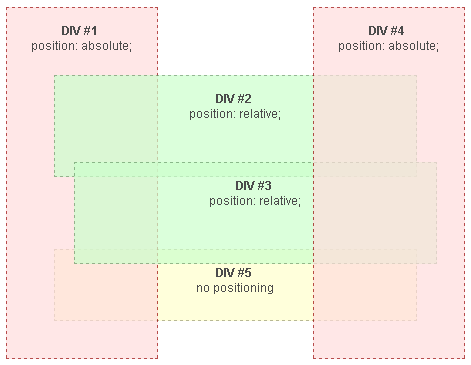
Example
HTML
<div id="absdiv1"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span> <br />position: absolute; </div> <div id="reldiv1"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span> <br />position: relative; </div> <div id="reldiv2"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span> <br />position: relative; </div> <div id="absdiv2"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span> <br />position: absolute; </div> <div id="normdiv"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #5</span> <br />no positioning </div>
CSS
.bold {
font-weight: bold;
font: 12px Arial;
}
#normdiv {
height: 70px;
border: 1px dashed #999966;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#reldiv1 {
opacity: 0.7;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 30px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#reldiv2 {
opacity: 0.7;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 20px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#absdiv1 {
opacity: 0.7;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
text-align: center;
}
#absdiv2 {
opacity: 0.7;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
text-align: center;
}
Result
(If the image does not display in CodePen, click the Tidy button in the CSS section)
See also
- Stacking and float : How floating elements are handled
- Adding z-index : Using z-index to change default stacking
- The stacking context : Notes on the stacking context
- Stacking context example 1 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the last level
- Stacking context example 2 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on all levels
- Stacking context example 3 : 3-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the second level
Original Document Information
- Author(s): Paolo Lombardi
- This article is the english translation of an article I wrote in italian for YappY. I grant the right to share all the content under Creative Commons: Attribution-Sharealike license
- Last Updated Date: November 3rd, 2014
Document Tags and Contributors
Tags:
Contributors to this page:
SphinxKnight,
ViktorPalansky,
javichito,
duncanmcdonald,
teoli,
xfq,
Jeremie,
Sheppy,
tregagnon,
azatazz,
deepakjoy,
Mgjbot,
Fredchat,
Nickolay,
Rod Whiteley,
bradipao
Last updated by:
SphinxKnight,