9 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
You can create a PDB by plugging an unplugged PDB into a CDB.
This chapter contains the following topics:
- About Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
TheUSINGclause of theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement specifies a XML metadata file or a compressed archive file with a .pdb extension. - About Adopting a Non-CDB as a PDB
To generate an XML file that describes a non-CDB, use theDBMS_PDB.DESCRIBEprocedure. Afterward, plug in the non-CDB just as you plug in an unplugged PDB. - Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
Plug in a PDB with theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USINGstatement. - Adopting a Non-CDB as a PDB
You can adopt (move) a non-CDB into a PDB by using theDBMS_PDB.DESCRIBEprocedure. - After Plugging in an Unplugged PDB
Certain rules regarding users and tablespaces apply after plugging in an unplugged PDB. - Plugging in an Unplugged PDB: Examples
These examples plug in an unplugged PDB namedsalespdbusing the/disk1/usr/salespdb.xmlfile or the/disk1/usr/sales.pdbfile given different factors.
Parent topic: Creating and Removing PDBs and Application Containers
9.1 About Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
The USING clause of the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement specifies a XML metadata file or a compressed archive file with a .pdb extension.
This section contains the following topics:
- About the XML File and Archive File
An XML metadata file describes the unplugged PDB and the files associated with the PDB (such as the data files and wallet file). An archive file includes both the XML metadata file and the PDB files. - Source File Locations When Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
Use theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USINGstatement to plug an unplugged PDB into a CDB.
Parent topic: Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.1.1 About the XML File and Archive File
An XML metadata file describes the unplugged PDB and the files associated with the PDB (such as the data files and wallet file). An archive file includes both the XML metadata file and the PDB files.
When the XML metadata file is specified, the XML file includes the full paths of the PDB files. When the .pdb archive file is specified, the XML metadata file contains the relative file names only.
The following figure illustrates how to plug in an unplugged PDB.
Figure 9-1 Plugging an Unplugged PDB Into a CDB Root
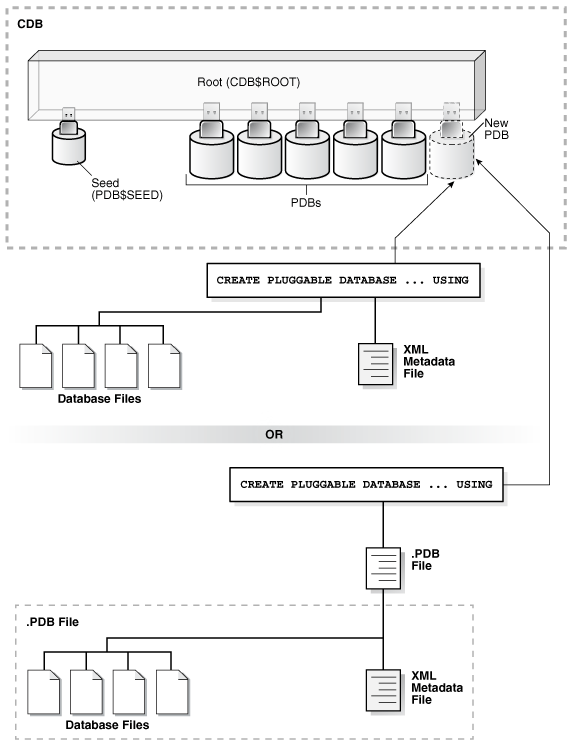
Description of "Figure 9-1 Plugging an Unplugged PDB Into a CDB Root"
The following figure illustrates how this technique creates a new application PDB in an application container.
Figure 9-2 Plugging an Unplugged PDB Into an Application Root
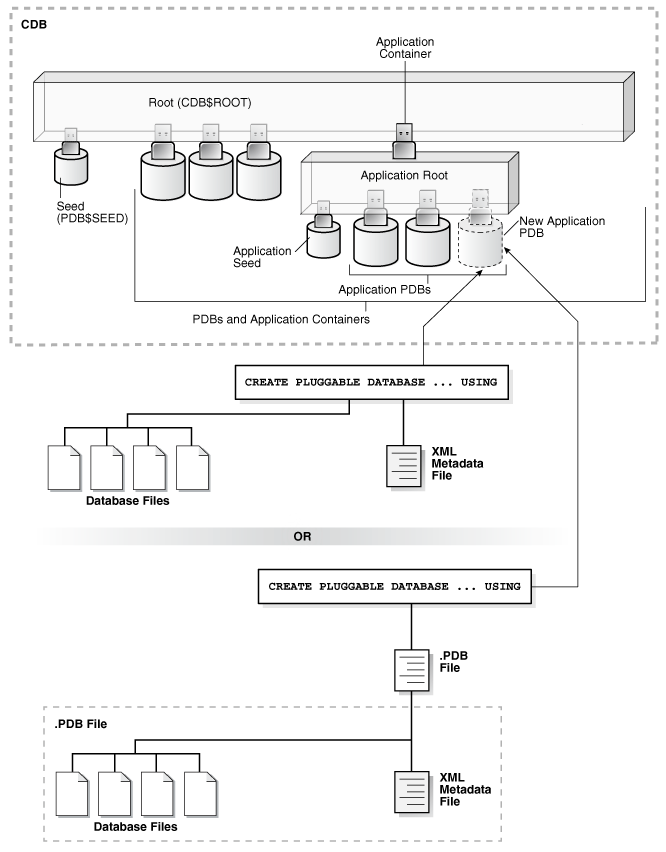
Description of "Figure 9-2 Plugging an Unplugged PDB Into an Application Root"
Note:
Automatic downgrade of a PDB is not supported. Therefore, you cannot plug in a PDB if the source CDB is a higher Oracle Database release than the target CDB.When you plug in an unplugged PDB, you must address the questions that apply to plugging in an unplugged PDB in Table 5-3. The table describes which CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE clauses you must specify based on different factors.
See Also:
Parent topic: About Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.1.2 Source File Locations When Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
Use the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USING statement to plug an unplugged PDB into a CDB.
When you use a .pdb archive file when plugging in a PDB, Oracle Database extracts this file when you plug in the PDB, and places the PDB files in the same directory as the .pdb archive file. Therefore, the clauses that specify the source file locations are not required when you use a .pdb archive file.
When you specify an XML metadata file when plugging in a PDB, this file describes the names and locations of an unplugged PDB source files. The XML file might not describe the locations of these files accurately if you transported the unplugged files from one storage system to a different one. The files are in a new location, but the file paths in the XML file still indicate the old location.
When plugging in an unplugged PDB using an XML metadata file (not a .pdb archive file), use either the SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause or the SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY clause. These clauses are mutually exclusive.
This section contains the following topics:
- SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT Clause
TheSOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause specifies how to locate PDB files when they reside in a location different from that specified in the XML file. - SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY Clause
TheSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause specifies the source directory of the files that will be used to create the new PDB.
Parent topic: About Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.1.2.1 SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT Clause
The SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause specifies how to locate PDB files when they reside in a location different from that specified in the XML file.
You can use this clause to specify one of the following options:
-
One or more file name patterns and replacement file name patterns, in the following form:
'string1' , 'string2' , 'string3' , 'string4' , ...
The string2 file name pattern replaces the string1 file name pattern, and the string4 file name pattern replaces the string3 file name pattern. You can use as many pairs of file name pattern and replacement file name pattern strings as required.
When you use this clause, ensure that the files you want to use for the PDB reside in the replacement file name patterns. Move or copy the files to these locations if necessary.
-
NONEwhen no file names need to be located because the PDB's XML file describes the file names accurately. Omitting theSOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is the same as specifyingNONE.
You can use the SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause only in a CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement with a USING clause that specifies an XML metadata file. Therefore, you can use this clause only when you are plugging in an unplugged PDB with an XML metadata file. You cannot use this clause when you are plugging in a PDB with a .pdb archive file.
Example 9-1 SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT Clause
This SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause uses the files in the /disk2/oracle/pdb7 directory instead of the /disk1/oracle/pdb7 directory. In this case, the XML file describing a PDB specifies the /disk1/oracle/pdb7 directory, but the PDB should use the files in the /disk2/oracle/pdb7 directory.
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/pdb7/', '/disk2/oracle/pdb7/')
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for the syntax of the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause
Parent topic: Source File Locations When Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.1.2.2 SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY Clause
The SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY clause specifies the source directory of the files that will be used to create the new PDB.
The clause specifies a directory that contains all of the files listed in the XML file. Using this clause is convenient when you have many data files and specifying a SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT pattern for each file is not feasible.
When you plug in a PDB, if the source files are all present in a single directory, then you can specify the directory name in this clause. The directory is scanned to find the appropriate files based on the unplugged PDB’s XML file.
You can use this clause to specify one of the following options:
-
The absolute path of the source file directory.
-
NONEwhen no files should be copied or moved during PDB creation. Omitting theSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is the same as specifyingNONE.
You can use the SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY clause only in a CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement with a USING clause that specifies an XML metadata file. Therefore, you can use this clause only when you are plugging in an unplugged PDB with an XML metadata file. You cannot use this clause when you are plugging in a PDB with a .pdb archive file.
You can specify this clause for configurations that use Oracle Managed Files and for configurations that do not use Oracle Managed Files.
Example 9-2 SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY Clause
This SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY clause generates file names for the new PDB by using the source files in the /oracle/pdb5/ directory.
SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY = '/oracle/pdb5/'
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for the syntax of the
SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause
Parent topic: Source File Locations When Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.2 About Adopting a Non-CDB as a PDB
To generate an XML file that describes a non-CDB, use the DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE procedure. Afterward, plug in the non-CDB just as you plug in an unplugged PDB.
Create the PDB with the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USING statement. When the non-CDB is plugged in to a CDB, it is a PDB.
Figure 9-3 Plug In a Non-CDB Using the DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE Procedure
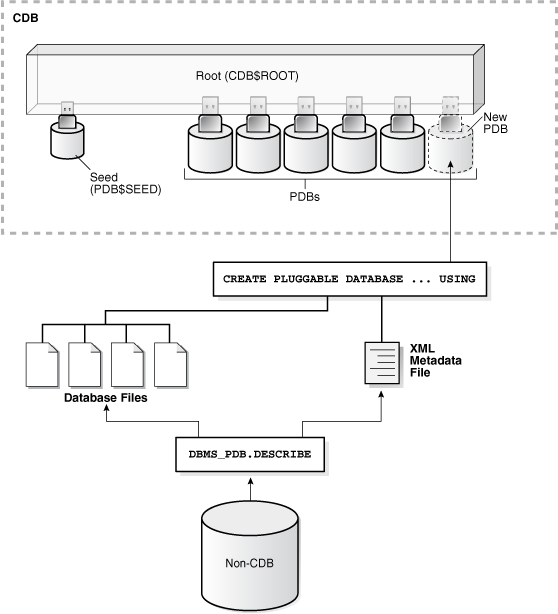
Description of "Figure 9-3 Plug In a Non-CDB Using the DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE Procedure"
You can use the same technique to create a new application PDB in an application container.
Note:
To use this technique, the non-CDB must be at release Oracle Database 12c or later.
See Also:
Parent topic: Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.3 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
Plug in a PDB with the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USING statement.
General Prerequisites
To plug in an unplugged PDB, the following prerequisites must be met:
-
Complete the prerequisites described in "General Prerequisites for PDB Creation".
-
Either the XML file that describes the PDB or the .pdb archive file must exist in a location that is accessible to the CDB.
The
USINGclause must specify the XML file or the .pdb archive file. If the PDB's XML file is unusable or cannot be located, then use theDBMS_PDB.RECOVERprocedure to generate an XML file using the PDB's data files. -
If an XML file (not a .pdb file) is specified in the
USINGclause, then the files associated with the PDB (such as the data files and wallet file) must exist in a location that is accessible to the CDB. -
If the target database for the plugin operation is the primary database in an Oracle Data Guard configuration, then ensure that the standby database can locate the files for the plugged-in PDB.
On the standby database, set the
STANDBY_PDB_SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYinitialization parameter to a location that contains the source data files for instantiating the PDB. If the files are not found, then the standby database tries to locate the files in the OMF location. If not found in the OMF location, then you must copy the data files to the OMF location on the standby database, and restart redo apply on the standby database. -
The source and target CDB platforms must meet the following requirements:
-
They must have the same endianness.
-
The database options installed on the source platform must be the same as, or a subset of, the database options installed on the target platform.
-
-
If you are creating an application PDB, then the application name and version of the unplugged PDB must match the application name and version of the application container into which the application PDB is being plugged.
Character Set Prerequisites
You must meet the following prerequisites for matching the character sets:
-
If the character set of the CDB into which the PDB is being plugged is not AL32UTF8, then the CDB that contained the unplugged PDB and the target CDB must have compatible character sets and national character sets. To be compatible, the character sets and national character sets must meet the requirements specified in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide.
If the character set of the CDB into which the PDB is being plugged is AL32UTF8, then this requirement does not apply.
-
If you are creating an application PDB, then the application PDB must have the same character set and national character set as the application container.
If the database character set of the CDB is AL32UTF8, then the character set and national character set of the application container can be different from the CDB. However, all application PDBs in an application container must have same character set and national character set, matching that of the application container.
To determine whether the preceding requirements are met, use the DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITY function. Step 2 in the following procedure describes using this function.
To plug in a PDB:
-
In SQL*Plus, ensure that the current container is the CDB root or application root of the target CDB.
When the current container is the CDB root, the PDB is created in the CDB. When the current container is an application root, the application PDB is created in the application container.
-
(Optional) Run the
DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITYfunction to determine whether the unplugged PDB is compatible with the CDB.-
If the PDB is not yet unplugged, then run the
DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBEprocedure to produce an XML file that describes the PDB.If the PDB is already unplugged, then proceed to Step 2b.
For example, to generate an XML file named
salespdb.xmlin the /disk1/oracle directory, run the following procedure:BEGIN DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE( pdb_descr_file => '/disk1/oracle/salespdb.xml', pdb_name => 'SALESPDB'); END; /If the PDB is in a remote CDB, then you can include
@database_link_namein thepdb_nameparameter, wheredatabase_link_nameis the name of a valid database link to the remote CDB or to the PDB. For example, if the database link name to the remote CDB isrcdb, then set thepdb_namevalue toSALESPDB@rcdb. -
Run the
DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITYfunction.When you run the function, set the following parameters:
-
pdb_descr_file- Set this parameter to the full path to the XML file. -
pdb_name- Specify the name of the new PDB. If this parameter is omitted, then the PDB name in the XML file is used.
For example, to determine whether a PDB described by the
/disk1/usr/salespdb.xmlfile is compatible with the current CDB, run the following PL/SQL block:SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE compatible CONSTANT VARCHAR2(3) := CASE DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITY( pdb_descr_file => '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml', pdb_name => 'SALESPDB') WHEN TRUE THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END; BEGIN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(compatible); END; /If the output is
YES, then the PDB is compatible, and you can continue with the next step. If the output isNO, then the PDB is not compatible: check thePDB_PLUG_IN_VIOLATIONSview to see why it is not compatible. -
Note:
You can specify a .pdb archive file in thepdb_descr_fileparameter. -
-
If the PDB is not unplugged, then unplug it.
-
Run the
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ... USINGstatement, specifying the XML file or the .pdb archive file in theUSINGclause. Specify other clauses when they are required.After you create the PDB, it is in mounted mode, and its status is
NEW. You can view the open mode of a PDB by querying theOPEN_MODEcolumn in theV$PDBSview. You can view the status of a PDB by querying theSTATUScolumn of theCDB_PDBSorDBA_PDBSview.A new default service is created for the PDB. The service has the same name as the PDB and can be used to access the PDB. Oracle Net Services must be configured properly for clients to access this service.
-
Open the new PDB in read/write mode.
You must open the new PDB in read/write mode for Oracle Database to complete the integration of the new PDB into the CDB. An error is returned if you attempt to open the PDB in read-only mode. After the PDB is opened in read/write mode, its status is
NORMAL. -
Back up the PDB.
A PDB cannot be recovered unless it is backed up.
Note:
If an error is returned during PDB creation, then the PDB being created might be in an UNUSABLE state. You can check a PDB's state by querying the CDB_PDBS or DBA_PDBS view, and you can learn more about PDB creation errors by checking the alert log. An unusable PDB can only be dropped, and it must be dropped before a PDB with the same name as the unusable PDB can be created.
See Also:
- "Modifying the Open Mode of One or More PDBs" for more information.
-
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User’s Guide for information about backing up a PDB.
-
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration to learn more about plugging in a PDB in an Oracle Data Guard environment
-
Oracle Database Reference for information about the
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter -
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about this procedure.
Parent topic: Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.4 Adopting a Non-CDB as a PDB
You can adopt (move) a non-CDB into a PDB by using the DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE procedure.
To adopt a non-CDB as a PDB using the DBMS_PDB package:
-
Create the CDB if it does not exist.
-
Ensure that the non-CDB is in a transactionally-consistent state.
-
Place the non-CDB in read-only mode.
-
Connect to the non-CDB, and run the
DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBEprocedure to construct an XML file that describes the non-CDB.The current user must have
SYSDBAadministrative privilege. The user must exercise the privilege usingAS SYSDBAat connect time.For example, to generate an XML file named
ncdb.xmlin the/disk1/oracledirectory, run the following procedure:BEGIN DBMS_PDB.DESCRIBE( pdb_descr_file => '/disk1/oracle/ncdb.xml'); END; /After the procedure completes successfully, you can use the XML file and the non-CDB database files to plug the non-CDB into a CDB.
-
Run the
DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITYfunction to determine whether the non-CDB is compatible with the CDB.When you run the function, set the following parameters:
-
pdb_descr_file- Set this parameter to the full path to the XML file. -
pdb_name- Specify the name of the new PDB. If this parameter is omitted, then the PDB name in the XML file is used.
For example, to determine whether a non-CDB described by the
/disk1/oracle/ncdb.xmlfile is compatible with the current CDB, run the following PL/SQL block:SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE compatible CONSTANT VARCHAR2(3) := CASE DBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITY( pdb_descr_file => '/disk1/oracle/ncdb.xml', pdb_name => 'NCDB') WHEN TRUE THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END; BEGIN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(compatible); END; /If the output is
YES, then the non-CDB is compatible, and you can continue with the next step. If the output isNO, then the non-CDB is not compatible, and you can check thePDB_PLUG_IN_VIOLATIONSview to see why it is not compatible. All violations must be corrected before you continue. For example, any version or patch mismatches should be resolved by running an upgrade or the datapatch utility. After correcting the violations, runDBMS_PDB.CHECK_PLUG_COMPATIBILITYagain to ensure that the non-CDB is compatible with the CDB. -
-
Shut down the non-CDB.
-
Plug in the non-CDB.
For example, the following SQL statement plugs in a non-CDB, copies its files to a new location, and includes only the
tbs3user tablespace from the non-CDB:CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE ncdb USING '/disk1/oracle/ncdb.xml' COPY FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/dbs/', '/disk2/oracle/ncdb/') USER_TABLESPACES=('tbs3');If there are no violations, then do not open the new PDB. You will open it in the following step.
The
USER_TABLESPACESclause enables you to separate data that was used for multiple tenants in a non-CDB into different PDBs. You can use multipleCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatements with this clause to create other PDBs that include the data from other tablespaces that existed in the non-CDB. -
Run the
ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/noncdb_to_pdb.sqlscript. This script must be run before the PDB can be opened for the first time.If the PDB was not a non-CDB, then running the
noncdb_to_pdb.sqlscript is not required. To run thenoncdb_to_pdb.sqlscript, complete the following steps:-
Access the PDB.
The current user must have
SYSDBAadministrative privilege, and the privilege must be either commonly granted or locally granted in the PDB. The user must exercise the privilege usingAS SYSDBAat connect time. -
Run the
noncdb_to_pdb.sqlscript:@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/noncdb_to_pdb.sql
The script opens the PDB, performs changes, and closes the PDB when the changes are complete.
-
-
Open the new PDB in read/write mode.
You must open the new PDB in read/write mode for Oracle Database to complete the integration of the new PDB into the CDB. An error is returned if you attempt to open the PDB in read-only mode. After the PDB is opened in read/write mode, its status is
NORMAL. -
Back up the PDB.
A PDB cannot be recovered unless it is backed up.
Note:
If an error is returned during PDB creation, then the PDB being created might be in an UNUSABLE state. You can check a PDB's state by querying the CDB_PDBS or DBA_PDBS view, and you can learn more about PDB creation errors by checking the alert log. An unusable PDB can only be dropped, and it must be dropped before a PDB with the same name as the unusable PDB can be created.
9.5 After Plugging in an Unplugged PDB
Certain rules regarding users and tablespaces apply after plugging in an unplugged PDB.
The following applies after plugging in an unplugged PDB:
-
User accounts in the PDB who used the default temporary tablespace of the source PDB use the default temporary tablespace of the target PDB. User accounts who used nondefault temporary tablespaces in the source PDB continue to use the same local temporary tablespaces in the target PDB.
-
Manually created common user accounts that existed in the source CDB but not in the target CDB do not have privileges granted commonly. However, if the target CDB has a common user with the same name as a common user in the PDB, then the latter is linked to the former and has the privileges granted to this common user in the target CDB.
If the cloned or plugged-in PDB has a common user account that does not exist in the target CDB, and if this user does not own objects in the PDB, then Oracle Database drops the user during the synchronization step; otherwise, the user account is locked in the target PDB. You have the following options regarding locked accounts:
-
Close the PDB, connect to the root, and create a common user account with the same name. When the PDB is opened in read/write mode, differences in roles and privileges granted commonly to the user account are resolved, and you can unlock the account. Privileges and roles granted locally to the user account remain unchanged during this process.
-
Create a new local user account in the PDB and use Data Pump to export/import the locked user's data into the new local user's schema.
-
Leave the user account locked.
-
Drop the user account.
-
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for information about common users and local users
-
Oracle Database Security Guide for information about creating common users and local users in a CDB
-
Oracle Database Utilities for information about using Oracle Data Pump with a CDB
Parent topic: Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
9.6 Plugging in an Unplugged PDB: Examples
These examples plug in an unplugged PDB named salespdb using the /disk1/usr/salespdb.xml file or the /disk1/usr/sales.pdb file given different factors.
In each example, the root to which the new PDB belongs depends on the current container when the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement is run:
-
When the current container is the CDB root, the new PDB is created in the CDB.
-
When the current container is an application root, the new application PDB is created in the application root’s application container.
Example 9-3 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using the NOCOPY Clause
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The XML file accurately describes the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is not required. -
The files are in the correct location. Therefore,
NOCOPYis included. -
Storage limits are not required for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is not required. -
A file with the same name as the temp file specified in the XML file exists in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
NOCOPY
TEMPFILE REUSE;
Example 9-4 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using the AS CLONE and NOCOPY Clauses
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is required. TheASCLONEclause ensures that the new PDB has unique identifiers. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The XML file accurately describes the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is not required. -
The files are in the correct location. Therefore,
NOCOPYis included. -
Storage limits are not required for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is not required. -
A file with the same name as the temp file specified in the XML file exists in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb AS CLONE USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
NOCOPY
TEMPFILE REUSE;
Example 9-5 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using the SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT, NOCOPY, and STORAGE Clauses
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The XML file does not accurately describe the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is required. In this example, the XML file indicates that the files are in /disk1/oracle/sales, but the files are in /disk2/oracle/sales, and theSOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is used. -
The files are in the correct location. Therefore,
NOCOPYis included. -
Storage limits must be enforced for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is required. Specifically, all tablespaces that belong to the PDB must not exceed 2 gigabytes. -
A file with the same name as the temp file specified in the XML file exists in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/sales/', '/disk2/oracle/sales/')
NOCOPY
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G)
TEMPFILE REUSE;
Example 9-6 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB With the COPY, PATH_PREFIX, and FILE_NAME_CONVERT Clauses
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The path prefix must be added to the PDB's directory object paths. Therefore, the
PATH_PREFIXclause is required. In this example, the path prefix /disk2/oracle/sales/ is added to the PDB’s directory object paths. -
The XML file accurately describes the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is not required. -
The files are not in the correct location. Therefore,
COPYorMOVEmust be included. In this example, the files are copied.The
CREATE_FILE_DESTclause is not used, Oracle Managed Files is not enabled, and thePDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is not set. Therefore, theFILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is required. In this example, the files are copied from /disk1/oracle/sales to /disk2/oracle/sales. -
Storage limits are not required for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is not required. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
COPY
PATH_PREFIX = '/disk2/oracle/sales/'
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/sales/', '/disk2/oracle/sales/');
Example 9-7 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using the SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT, MOVE, FILE_NAME_CONVERT, and STORAGE Clauses
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The XML file does not accurately describe the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is required. In this example, the XML file indicates that the files are in /disk1/oracle/sales, but the files are in /disk2/oracle/sales, and theSOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is used. -
The files are not in the correct final location for the PDB. Therefore,
COPYorMOVEmust be included. In this example,MOVEis specified to move the files.The
CREATE_FILE_DESTclause is not used, Oracle Managed Files is not enabled, and thePDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is not set. Therefore, theFILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is required. In this example, the files are moved from /disk2/oracle/sales to /disk3/oracle/sales. -
Storage limits must be enforced for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is required. Specifically, all tablespaces that belong to the PDB must not exceed 2 gigabytes. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk1/oracle/sales/', '/disk2/oracle/sales/')
MOVE
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/sales/', '/disk3/oracle/sales/')
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G);
Example 9-8 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using the SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY, MOVE, FILE_NAME_CONVERT, and STORAGE Clauses
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
The XML file does not accurately describe the current locations of the files. Therefore, the
SOURCE_FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause orSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is required. In this example, the XML file indicates that the files are in /disk1/oracle/sales, but the files are in /disk2/oracle/sales, and theSOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORYclause is used. -
The files are not in the correct final location for the PDB. Therefore,
COPYorMOVEmust be included. In this example,MOVEis specified to move the files.The
CREATE_FILE_DESTclause is not used, Oracle Managed Files is not enabled, and thePDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter is not set. Therefore, theFILE_NAME_CONVERTclause is required. In this example, the files are moved from /disk2/oracle/sales to /disk3/oracle/sales. -
Storage limits must be enforced for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is required. Specifically, all tablespaces that belong to the PDB must not exceed 2 gigabytes. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB:
CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE salespdb USING '/disk1/usr/salespdb.xml'
SOURCE_FILE_DIRECTORY = '/disk2/oracle/sales/'
MOVE
FILE_NAME_CONVERT = ('/disk2/oracle/sales/', '/disk3/oracle/sales/')
STORAGE (MAXSIZE 2G);
Example 9-9 Plugging In an Unplugged PDB Using an Archive File
This example assumes the following factors:
-
The unplugged PDB is in a .pdb archive file named
sales.pdb. The archive file includes the XML metadata file and the PDB’s files (such as the data files and wallet file) in compressed form, and these files are extracted to the current directory of the .pdb archive file when theCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement is run. -
The new PDB is not based on the same unplugged PDB that was used to create an existing PDB in the CDB. Therefore, the
ASCLONEclause is not required. -
The
PATH_PREFIXclause is not required. -
Storage limits must be enforced for the PDB. Therefore, the
STORAGEclause is required. Specifically, all tablespaces that belong to the PDB must not exceed 2 gigabytes. -
There is no file with the same name as the new temp file that will be created in the target location. Therefore, the
TEMPFILE REUSEclause is not required.
Given the preceding factors, the following statement plugs in the PDB using an archive file:
iParent topic: Plugging In an Unplugged PDB