9 Managing Security for a Multitenant Environment in Enterprise Manager
You can manage common and local users and roles for a multitenant environment by using Oracle Enterprise Manager.
This section contains the following topics:
- About Managing Security for a Multitenant Environment in Enterprise Manager
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control supports the management of multitenant environment security. - Logging into a Multitenant Environment in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, you can log in to a CDB or a PDB, and switch from a PDB to a different PDB or to the root. - Managing Common and Local Users in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, Oracle Enterprise Manager enables you to create, edit, and drop common and local users. - Managing Common and Local Roles and Privileges in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, you can use Oracle Enterprise Manager to create, edit, drop, and revoke common and local roles.
Parent topic: Managing User Authentication and Authorization
About Managing Security for a Multitenant Environment in Enterprise Manager
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control supports the management of multitenant environment security.
In a multitenant environment, you can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to create, manage, and monitor common users and roles for both the root and the associated pluggable databases (PDBs).
Enterprise Manager enables you to switch easily between the root and a designated PDB.
Logging into a Multitenant Environment in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, you can log in to a CDB or a PDB, and switch from a PDB to a different PDB or to the root.
This section contains the following topics:
- Logging into a CDB or a PDB
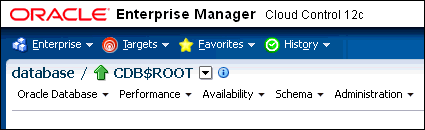
Different variations of the Enterprise Manager Database login page appear automatically based on the feature that you requested while logging in. - Switching to a Different PDB or to the Root
From Oracle Enterprise Manager, you can switch from one PDB to a different PDB, or to the root.
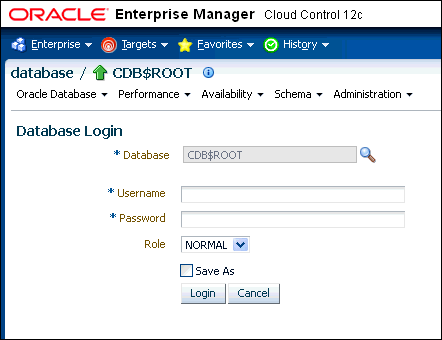
Logging into a CDB or a PDB
Different variations of the Enterprise Manager Database login page appear automatically based on the feature that you requested while logging in.
To log into a multitenant environment as a CDB administrator (an Enterprise Manager user who has the CONNECT privilege on the CDB target) to use a CDB-scoped feature:
Managing Common and Local Users in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, Oracle Enterprise Manager enables you to create, edit, and drop common and local users.
This section contains the following topics:
- Creating a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
A common user is a user that exists in the root and can access PDBs in the CDB. - Editing a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a common user account from the root. - Dropping a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can drop a common user from the CDB root. - Creating a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
A local user is a user that exists only in a specific PDB and does not have access to any other PDBs in the multitenant environment. - Editing a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a local user from the PDB in which the local user resides. - Dropping a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can drop a local user from the PDB in which the local user resides.
Creating a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
A common user is a user that exists in the root and can access PDBs in the CDB.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Managing Common and Local Users in Enterprise Manager
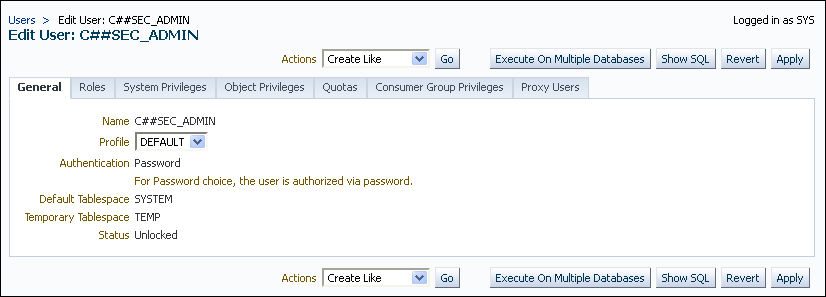
Editing a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a common user account from the root.
Dropping a Common User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can drop a common user from the CDB root.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Managing Common and Local Users in Enterprise Manager
Creating a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
A local user is a user that exists only in a specific PDB and does not have access to any other PDBs in the multitenant environment.
Editing a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a local user from the PDB in which the local user resides.
Dropping a Local User Account in Enterprise Manager
You can drop a local user from the PDB in which the local user resides.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Managing Common and Local Users in Enterprise Manager
Managing Common and Local Roles and Privileges in Enterprise Manager
In a multitenant environment, you can use Oracle Enterprise Manager to create, edit, drop, and revoke common and local roles.
This section contains the following topics:
- Creating a Common Role in Enterprise Manager
Common roles can be used to assign common privileges to common users. - Editing a Common Role in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a common role from the root. - Dropping a Common Role in Enterprise Manager
You can drop a common role from the root. - Revoking Common Privilege Grants in Enterprise Manager
You can revoke common privilege grants from the root. - Creating a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
A common role can be used to assign a local set of privileges to local users later. - Editing a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a local role in the PDB in which the local role resides. - Dropping a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
You can drop local role from the PDB in which the local role resides. - Revoking Local Privilege Grants in Enterprise Manager
You can revoke local privileges in the PDB in which the privileges are used.
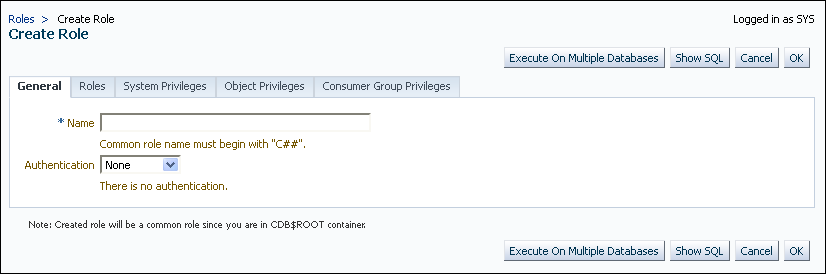
Creating a Common Role in Enterprise Manager
Common roles can be used to assign common privileges to common users.
Revoking Common Privilege Grants in Enterprise Manager
You can revoke common privilege grants from the root.
Creating a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
A common role can be used to assign a local set of privileges to local users later.
Editing a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
You can edit a local role in the PDB in which the local role resides.
Dropping a Local Role in Enterprise Manager
You can drop local role from the PDB in which the local role resides.