5 Using the XML Parser for C
An explanation is given of how to use the Extensible Markup Language (XML) parser for C.
Introduction to the XML Parser for C
Topics here include prerequisites and standards for the XML parser for C.
See Also:
Introduction to XML Parsing for Java for a generic introduction to XML parsing with Document Object Model (DOM) and Simple API for XML (SAX). Much of the information in the introduction is language-independent and applies equally to C.
Prerequisites for Using the XML Parser for C
The Oracle XML parser for C reads an XML document and uses DOM or SAX application programming interfaces (APIs) to provide programmatic access to its content and structure. You can use the parser in validating or nonvalidating mode. A pull parser is also available.
This chapter assumes that you are familiar with these technologies:
-
Document Object Model (DOM). DOM is an in-memory tree representation of the structure of an XML document.
-
Simple API for XML (SAX). SAX is a standard for event-based XML parsing.
-
Using the XML Pull Parser for C. Pull Parser uses XML events.
-
document type definition (DTD). An XML DTD defines the legal structure of an XML document.
-
XML Schema. Like a DTD, an XML schema defines the legal structure of an XML document.
-
XML Namespaces. Namespaces are a mechanism for differentiating element and attribute names.
If you require a general introduction to the preceding technologies, consult the XML resources listed in Related Documents.
Standards and Specifications for the XML Parser for C
The standards and specifications for the XDK XML parser are described.
-
XML 1.0 is a W3C Recommendation. The Oracle XML Developer's Kit (XDK) for C API provides full support for XML 1.0 (Second Edition).
-
The DOM Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 specifications are World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Recommendations. The XDK for C API provides full support for DOM Level 1 and 2, but no support for Level 3.
-
SAX is available in version 1.0, which is deprecated, and 2.0. SAX is not a W3C specification. The XDK for C API provides full support for both SAX 1.0 and 2.0.
-
XML Namespaces is a W3C Recommendation.
Related Topics
Using the XML Parser API for C
Oracle XML parser for C checks if an XML document is well-formed, and optionally validates it against a DTD. Your application can access the parsed data through the DOM or SAX APIs.
Overview of the Parser API for C
The core of the XML parsing API are the XML, DOM, and SAX APIs.
Table 5-1 describes the interfaces for these APIs. See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for the complete API documentation.
Table 5-1 Interfaces for XML, DOM, and SAX APIs
| Package | Interfaces | Function Name Convention |
|---|---|---|
|
XML |
This package implements a single
|
Function names begin with the string See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for API documentation. |
|
DOM |
This package provides programmatic access to parsed XML. The package implements these interfaces:
|
Function names begin with the string See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for API documentation. |
|
SAX |
This package provides programmatic access to parsed XML. The package implements the |
Function names begin with the string See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for API documentation. |
|
XML Pull Parser |
XML events is a representation of an XML document which is similar to SAX events in that the document is represented as a sequence of events like start tag, end tag, comment, and so on. The difference is that SAX events are driven by the parser (producer) and XML events are driven by the application (consumer). |
Function names begin with the string See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for API documentation. |
XML Parser for C Data Types
The data types used in the XML parser for C are described.
See Oracle Database XML C API Reference for the complete list of data types for XDK for C.
Table 5-2 Data Types Used in the XML Parser for C
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
String pointer |
|
|
Master XML context |
|
|
SAX callback structure (SAX only) |
|
|
32-bit (or larger) unsigned integer |
|
|
Native unsigned integer |
XML Parser for C Defaults
The defaults for the XML parser for C are described.
These are the defaults:
-
Character set encoding is 8-bit encoding of Unicode (UTF-8). If all your documents are ASCII, then setting the encoding to US-ASCII increases performance.
-
The parser prints messages to
stderrunless an error handler is provided. -
The parser checks inputs documents for well-formedness but not validity. You can set the property "validate" to validate the input.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you set the default encoding explicitly if using only single byte character sets (such as US-ASCII or any of the ISO-8859 character sets) for faster performance than is possible with multibyte character sets such as UTF-8.
-
The parser conforms with the XML 1.0 specification when processing white space, that is, the parser reports all white space to the application but indicates which white space can be ignored. However, some applications may prefer to set the property "discard-white space," which discards all white space between an end-element tag and this start-element tag.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database XML C API Reference for the DOM, SAX, pull parser, and callback APIs.
XML Parser for C Calling Sequence
The calling sequence for the XML parser for C is illustrated.
Figure 5-1 XML Parser for C Calling Sequence
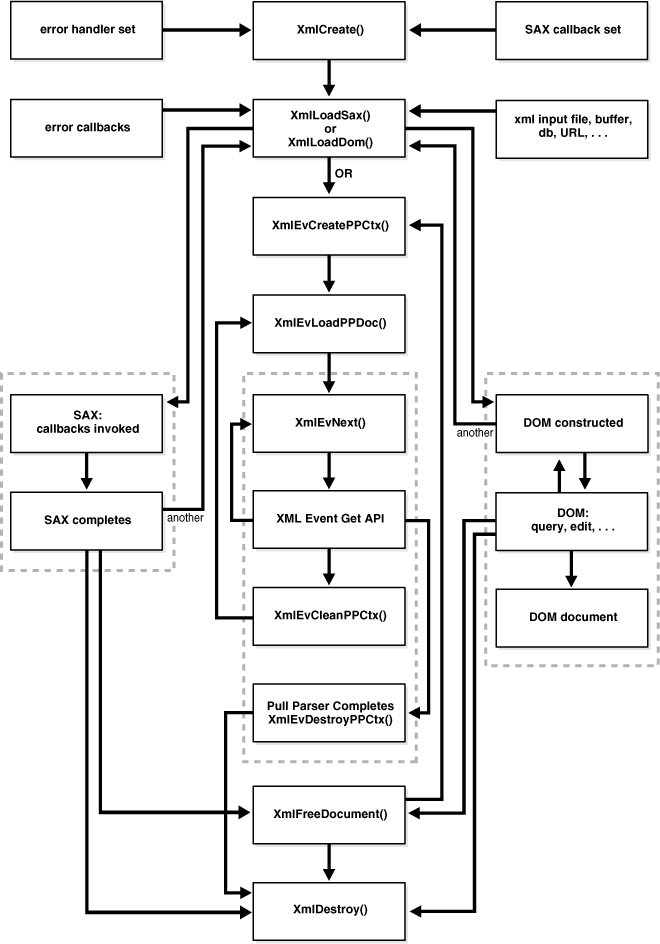
Description of "Figure 5-1 XML Parser for C Calling Sequence"
Using the XML Parser for C: Basic Process
The basic process for using the XML parser for C is described.
Perform these steps in your application:
You can use the memory callback functions XML_ALLOC_F and XML_FREE_F for your own memory allocation. If you do, then specify both functions.
Related Topics
Running the XML Parser for C Demo Programs
The $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/c/ (UNIX) and %ORACLE_HOME%\xdk\demo\c (Windows) directories include several XML applications that show how to use the XML parser for C with the DOM and SAX interfaces.
Table 5-3 describes the demos.
The make utility compiles the source file fileName.c to produce the demo program fileName and the output file fileName.out . The fileName.std is the expected output.
Table 5-3 C Parser Demos
| Directory | Contents | Demos |
|---|---|---|
|
|
DOMNamespace.c DOMSample.c FullDom.c FullDom.xml NSExample.xml Traverse.c XPointer.c class.xml cleo.xml pantry.xml |
The following demo programs use the DOM API:
|
|
|
NSExample.xml SAXNamespace.c SAXSample.c cleo.xml |
The following demo programs use the SAX APIs:
|
You can find documentation that describes how to compile and run the sample programs in the README in the same directory. The basic steps are:
-
Change into the
$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/cdirectory (UNIX) or%ORACLE_HOME%\xdk\demo\cdirectory (Windows). -
Make sure that your environment variables are set as described in Setting Up XDK for C Environment Variables on UNIX and Setting Up XDK for C Environment Variables on Windows.
-
Run
make(UNIX) orMake.bat(Windows) at the system prompt. Themakeutility changes into each demo subdirectory and runsmaketo do this:-
Compiles the C source files with the
ccutility. For example, theMakefilein the$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/c/domdirectory includes these line:$(CC) -o DOMSample $(INCLUDE) $@.c $(LIB)
-
Runs each demo program and redirects the output to a file. For example, the
Makefilein the$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/c/domdirectory includes this line:./DOMSample > DOMSample.out
-
-
Compare the
*.stdfiles to the*.outfiles for each program. The*.stdfile contains the expected output for each program. For example,DOMSample.stdcontains the expected output from runningDOMSample.
Using the C XML Parser Command-Line Utility
The xml utility, which is located in $ORACLE_HOME/bin (UNIX) or %ORACLE_HOME%\bin (Windows), is a command-line interface that parses XML documents. It checks for both well-formedness and validity.
To use xml ensure that your environment is set up as described in Setting Up XDK for C Environment Variables on UNIX and Setting Up XDK for C Environment Variables on Windows.
Use this syntax on the command line to invoke xml. Use xml.exe for Windows:
xml [options] [document URI] xml -f [options] [document filespec]
Table 5-4 describes the command-line options.
Table 5-4 C XML Parser Command-Line Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Sets the base URI for the XSLT processor. The base URI of |
|
|
Checks well-formedness, but performs no validation. |
|
|
Specifies default input file encoding ("incoding"). |
|
|
Specifies DOM/SAX encoding ("outcoding"). |
|
|
Interprets the file as filespec, not URI. |
|
|
Evaluates |
|
|
Shows usage help and basic list of command-line options. |
|
|
Shows complete list command-line options. |
|
|
Specifies the number of times to iterate the |
|
|
Specifies the language for error reporting. |
|
|
Traverses the DOM and reports the number of elements, as shown in this sample output: ELEMENT 1
PCDATA 1
DOC 1
TOTAL 3 * 60 = 180 |
|
|
Specifies the output file of the |
|
|
Prints the document/DTD structures after the parse. For example, the root element +---ELEMENT greeting
+---PCDATA "hello" |
|
|
Prints the document from the root element. For example, the root element <greeting>hello</greeting> |
|
|
Prints from the root node (DOC) and includes the XML declaration. |
|
|
Specifies the encoding for |
|
|
Includes the XML declaration in the output. |
|
|
Specifies the |
|
|
Displays the XDK parser version, and then exits. |
|
|
Tests top-level variables in |
|
|
Preserves all white space. |
|
|
Stops parsing after a warning. |
|
|
Exercises the SAX interface and prints the document, as shown in this sample output: StartDocument
XMLDECL version='1.0' encoding=FALSE
<greeting>
"hello"
</greeting>
EndDocument |
Using the XML Parser Command-Line Utility: Example
You can test xml documents using the various XML files located in $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/c.
Example 5-1 displays the contents of NSExample.xml.
You can parse this file, count the number of elements, and display the DOM tree as shown in this example:
xml -np NSEample.xml > xml.out
Example 5-2shows the output.
Example 5-1 NSExample.xml
<!DOCTYPE doc [
<!ELEMENT doc (child*)>
<!ATTLIST doc xmlns:nsprefix CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST doc xmlns CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST doc nsprefix:a1 CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ELEMENT child (#PCDATA)>
]>
<doc nsprefix:a1 = "v1" xmlns="http://www.w3c.org"
xmlns:nsprefix="http://www.oracle.com">
<child>
This element inherits the default Namespace of doc.
</child>
</doc>
Example 5-2 xml.out
ELEMENT 2
PCDATA 1
DOC 1
DTD 1
ELEMDECL 2
ATTRDECL 3
TOTAL 10 * 112 = 1120
+---ELEMENT doc [nsprefix:a1='v1'*, xmlns='http://www.w3c.org'*, xmlns:nsprefix=
'http://www.oracle.com'*]
+---ELEMENT child
+---PCDATA "
This element inherits the default Namespace of doc.
"Using the DOM API for C
Topics here include controlling encoding for XML documents, using NULL-terminated and length-encoded functions, and handling errors.
Controlling the Data Encoding of XML Documents for the C API
XML data occurs in many encodings. You can control the XML encoding in various ways.
-
Specify a default encoding to assume for files that are not self-describing
-
Specify the presentation encoding for DOM or SAX
-
Re-encode when a DOM is serialized
Input XML data is always encoded. Some encodings are entirely self-describing, such as 16-bit encoding of Unicode (UTF-16), which requires a specific Byte Order Mark (BOM) before the start of the actual data. The XMLDecl or Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) header of the document can also specify an encoding. If the application cannot determine the specific encoding, then it applies the default input encoding. If you do not provide a default, then the application assumes UTF-8 on ASCII platforms and UTF-EBCDIC on EBCDIC platforms.
The API makes a provision for cases when the encoding data of the input document is corrupt. For example, suppose an ASCII document with an XMLDecl of encoding=ascii is blindly converted to EBCDIC. The new EBCDIC document contains (in EBCDIC) an XMLDecl that incorrectly claims the document is ASCII. The correct behavior for a program that is re-encoding XML data is to regenerate but not convert the XMLDecl. The XMLDecl is metadata, not data itself. This rule is often ignored, however, which causes corrupt documents. To work around this problem, the API provides an additional flag that enables you to forcibly set the input encoding, thereby overcoming an incorrect XMLDecl.
The precedence rules for determining input encoding are:
After the application has determined the input encoding, it can parse the document and present the data. You are allowed to choose the presentation encoding; the data is in that encoding regardless of the original input encoding.
When an application writes back a DOM in serialized form, it can choose at that time to re-encode the presentation data. Thus, you can place the serialized document in any encoding.
Using NULL-Terminated and Length-Encoded C API Functions
The native string representation in C is null-terminated. Thus, the primary DOM interface takes and returns null-terminated strings. When stored in table form, however, Oracle XML DB data is not null-terminated but length-encoded. Consequently, XDK provides an additional set of length-encoded APIs for the high-frequency cases to improve performance.
In particular, the DOM functions in Table 5-5 have dual APIs.
Table 5-5 NULL-Terminated and Length-Encoded C API Functions
| NULL-Terminated API | Length-Encoded API |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Handling Errors with the C API
The C API functions typically either return a numeric error code (0 for success, nonzero on failure), or pass back an error code through a variable. In all cases, the API stores error codes. Your application can retrieve the most recent error by invoking the XmlDomGetLastError() function.
By default, the functions output error messages to stderr. However, you can register an error message callback at initialization time. When an error occurs, the application invokes the registered callback and does not print an error.
Using orastream Functions
The orastream function API is an interface that enables you to stream large chunks of data out of a node instead of getting it all in one piece. Nodes of greater than 64 KB are thus accessible.
The orastream API represents a generic input or output stream. This interface is available to XDK users through xml.h and is defined by the orastream data structure and a set of functions that implement the interface. The creator of the stream passes a list of stream function addresses, along with a stream context to OraStreamInit. This function returns an instance of an orastream structure.
Several stream properties are specified at the time of initialization. If read or write is provided, the stream operates in byte mode using OraStreamRead() and OraStreamWrite(). If "read_char" or "write_char" is provided, the stream operates in character mode using OraStreamReadChar() and OraStreamWriteChar(). In character mode only complete characters are read or written and are never split over buffer boundaries.
A stream context is used to represent the state of the orastream and it persists for the lifetime of a stream.
Just like the input or output streams in Java, a source or a sink for the data is always specified. Output streams store the address of the external stream or object where they must populate the data. Similarly, input streams store the address of the object that is read.
Here are the orastream functions:
struct orastream; typedef struct orastream orastream; typedef ub4 oraerr; /* Error code: zero is success, non-zero is failure */
/* Initialize (Create) & Destroy (Terminate) stream object */
orastream *OraStreamInit(void *sctx, void *sid, oraerr *err, ...);
oraerr OraStreamTerm(orastream *stream);
/* Set or Change SID (streamID) for stream (returns old stream ID through osid)*/
oraerr OraStreamSid(orastream *stream, void *sid, void **osid);
/* Is a stream readable or writable? */
boolean OraStreamReadable(orastream *stream);
boolean OraStreamWritable(orastream *stream);
/* Open & Close stream */
oraerr OraStreamOpen(orastream *stream, ubig_ora *length);
oraerr OraStreamClose(orastream *stream);
/* Read | Write byte stream */
oraerr OraStreamRead(orastream *stream, oratext *dest, ubig_ora size,
oratext **start, ubig_ora *nread, ub1 *eoi);
oraerr OraStreamWrite(orastream *stream, oratext *src, ubig_ora size,
ubig_ora *nwrote);
/* Read | Write char stream */
oraerr OraStreamReadChar(orastream *stream, oratext *dest, ubig_ora size,
oratext **start, ubig_ora *nread, ub1 *eoi);
oraerr OraStreamWriteChar(orastream *stream, oratext *src, ubig_ora size,
ubig_ora *nwrote);
/* Return handles for stream */
orastreamhdl *OraStreamHandle(orastream *stream);
/* Returns status: if the stream object is currently opened or not */
boolean OraStreamIsOpen(orastream *stream);
The stream error codes are:
#define ORASTREAM_ERR_NULL_POINTER 1 /* NULL pointer given */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_BAD_STREAM 2 /* invalid stream object */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_WRONG_DECTION 3 /* tried wrong-direction I/O */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_UNKNOWN_PROPERTY 4 /* unknown creation prop */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_NO_DIRECTION 5 /* neither read nor write? */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_BI_DIRECTION 6 /* both read any write? */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_NOT_OPEN 7 /* stream not open */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_WRONG_MODE 8 /* wrote byte/char mode */ /* --- Open errors --- */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_CANT_OPEN 10 /* can't open stream */ /* --- Close errors --- */ #define ORASTREAM_ERR_CANT_CLOSE 20 /* can't close stream */
See Also:
Oracle Database XML C API Reference for reference information such as parameter definitions in the orastream API
Example 5-3 Using orastream Functions
int test_read()
{
xmlctx *xctx = NULL;
oratext *barray, *docName = "NSExample.xml";
orastream* ostream = (orastream *) 0;
xmlerr ecode = 0;
ub4 wcount = 0;
ubig_ora destsize, nread;
oraerr oerr = 0;
ub1 eoi = 0;
nread = destsize = 1024;
if (!(xctx = XmlCreateNew(&ecode, (oratext *)"stream_xctx", NULL, wcount,
NULL)))
{
printf("Failed to create XML context, error %u\n", (unsigned)ecode);
return -1;
}
barray = XmlAlloc(xctx, sizeof(oratext) * destsize);
/* open function should be specified in order to read correctly. */
if (!(ostream = OraStreamInit(NULL,docName, (oraerr *)&ecode,
"open", fileopen,
"read", fileread,
NULL)))
{
printf("Failed to initialize OrsStream, error %u\n",(unsigned)ecode);
return -1;
}
/* check readable and writable */
if (OraStreamReadable(ostream))
printf("ostream is readable\n");
else
printf("ostream is not readable\n");
if (OraStreamWritable(ostream))
printf("ostream is writable\n");
else
printf("ostream is not writable\n");
if (oerr = OraStreamRead(ostream, barray, destsize, &barray, &nread, &eoi))
{
printf("Failed to read due to orastream was not open, error %u\n", oerr);
}
/* open orastream */
OraStreamOpen(ostream, NULL);
/* read document */
OraStreamRead(ostream, barray, destsize, &barray, &nread, &eoi);
OraStreamTerm(ostream);
XmlDestroy(xctx);
return 0;
}
ORASTREAM_OPEN_F(fileopen, sctx, sid, hdl, length)
{
FILE *fh = NULL;
printf("Opening orastream %s...\n", (oratext *)sid);
if (sid && ((fh= fopen(sid, "r")) != NULL))
{
printf("Opening orastream %s...\n", (oratext *)sid);
}
else
{
printf("Failed to open input file.\n");
return -1;
}
/* store file handle generically, NULL means stdout */
hdl->ptr_orastreamhdl = fh;
return XMLERR_OK;
}
ORASTREAM_READ_F(fileread, sctx, sid, hdl,
dest, size, start, nread, eoi)
{
FILE *fh = NULL;
int i =0;
printf("Reading orastream %s ...\n", (oratext *)sid);
// read data from file to dest
if ((fh = (FILE *) hdl->ptr_orastreamhdl) != NULL)
*nread = fread(dest, 1, size, fh);
printf("Read %d bytes from orastream...\n", (int) *nread);
*eoi = (*nread < size);
if (start)
*start = dest;
printf("printing document ...\n");
for(i =0; i < *nread; i++)
printf("%c", (char)dest[i]);
printf("\nend ...\n");
return ORAERR_OK;
}Using the SAX API for C
To use SAX, initialize an xmlsaxcb structure with function pointers and pass it to XmlLoadSax(). You can also include a pointer to a user-defined context structure, which you pass to each SAX function.
See Also:
Oracle Database XML C API Reference for the SAX callback structure
Using the XML Pull Parser for C
The XML Pull Parser is an implementation of the XML Events interface. The XML Pull Parser and the SAX parser are similar, but using the Pull Parser, the application (consumer) drives the events, while in SAX, the parser (producer) drives the events.
Both the XML Pull Parser and SAX represent the document as a sequence of events, with start tags, end tags, and comments. XML Pull Parser gives control to the application by exposing a simple set of APIs and an underlying set of events. Methods such as XmlEvNext allow an application to ask for (or pull) the next event, rather than handling the event in a callback, as in SAX. Thus, the application has more procedural control over XML processing. Also, the application can decide to stop further processing, unlike a SAX application, which parses the entire document.
Using Basic XML Pull Parsing Capabilities
The steps required to use the XML Pull Parser are described.
XML Event Context
The XML event context structure is shown.
Example 5-4 XML Event Context
typedef struct {
void *ctx_xmlevctx; /* implementation specific context */
xmlevdisp *disp_xmlevctx; /* dispatch table */
ub4 checkword_xmlevctx; /* checkword for integrity check */
ub4 flags_xmlevctx; /* mode; default: expand_entity */
struct xmlevctx *input_xmlevctx; /* input xmlevctx; chains the XML Event
context */
} xmlevctx;About the XML Event Context
Each XML Pull Parser is allowed to create its own context and implement its own API functions.
-
Dispatch Table
The dispatch table,
disp_xmlevctx, contains one pointer for each API function, except for theXmlEvCreatePPCtx,XmlEvCreatePPCtxVA,XmlEvDestoryPPCtx,XmlEvLoadPPDoc, andXmlEvCleanPPCtxfunctions.When the event context is created, the pointer
disp_xmlevctxis initialized with the address of that static table. -
Implementation-Specific Event Context
The field
ctx_xmlevctxmust be initialized with the address of the context specific to this invocation of the particular implementation. The implementation-specific event context is of type*void, so that it can differ for different applications. -
Input Event Context
Each Pull Parser can specify an input event context,
xmlevctx. This field enables the parser to chain multiple event producers. As a result, if a dispatch function is specified asNULLin a context, the application uses the next non-null dispatch function in the chain of input event contexts. The basexmlevctxmust ensure that all dispatch function pointers are non-null.
Parsing Multiple XML Documents
After creating and initializing the XML Event Context, an application can parse multiple documents using repeated invocations of XmlEvLoadPPDoc and XmlEvCleanPPCtx.
The properties defined by the application during the XML Event Context creation cannot be changed for each invocation of the XmlLoadPPDoc function. to change the properties, destroy the event context and then re-create it.
After XmlEvCleanPPCtx cleans up the internal structure of the current parser, the event context can be reused to parse another document.
ID Callback
You can provide a callback to convert text-based names to 8-byte identifiers (IDs).
Callback Function Signature
typedef sb8 (*xmlev_id_cb_funcp)( void *ctx , ub1 type, ub1 *token, ub4 tok_len,
sb8 nmspid, boolean isAttribute);Return Value
sb8: an 8-byte ID.
Arguments
-
*
ctx: The implementation context. -
type: The type, which is indicated by this enumeration:typedef enum { XML_EVENT_ID_URI, XML_EVENT_ID_QNAME, }xmlevidtype; -
*
tokenandtok_len: The actual text to be converted. -
nmspid: The namespace ID. -
isAttribute: A Boolean value indicating an attribute.
Internally, the XmlEvGetTagId and XmlEvGetAttrID APIs invoke this callback twice, once to fetch the namespace ID and once to fetch the actual ID of the tag or the attribute Qname.
The XmlEvGetTagUriID and XmlEvGetAttrUriID functions invoke this callback once to get the ID of the corresponding Universal Resource Identifier (URI).
If a callback is not supplied, an error XML_ERR_EVENT_NOIDCBK is returned when these APIs are used.
Error Handling for the XML Pull Parser
Error handling for the XML Pull Parser is described.
Parser Errors
Errors raised by the parser are described.
The XML Pull Parser returns the message XML_EVENT_FATAL_ERROR when it throws an error because the input document is malformed. Function XmlEvGetError is provided to get the error number and message.
During the XmlEvCreatePPCtx operation, any error handler supplied by the application during XmlCreate is overridden. The application must invoke the XmlErrSetHandler function after the XmlEvDestroyPPCtx operation to restore the original callback.
Programming Errors
To handle programmatic errors. XDK provides a callback that the application can supply when creating an event context. This callback is invoked when the application invokes an illegal API.
The callback signature is:
typedef void (* xmlev_err_cb_funcp)(xmlctx *xctx, xmlevctx *evctx,
xmlevtype cur_event);
An example of an illegal API invocation is:
XmlEvGetName cannot be called for the XML_EVENT_CHARACTERS event.
Sample Pull Parser Application
A sample pull parser application, a document to be parsed, and a list of the events that the application generates from the document are presented.
Example 5-5 shows the sample application code.
Example 5-6 shows the sample document to be parsed.
Example 5-7 shows the sequence of events generated when the attribute events property is FALSE and the expand entities properties is TRUE.
Example 5-5 Sample Pull Parser Application Example
# include "xml.h"
# include "xmlev.h"
...
xmlctx *xctx;
xmlevctx *evtcx;
if (!(xctx = XmlCreate(&xerr, (oratext *) "test")))
{
printf("Failed to create XML context, error %u\n", (unsigned) xerr);
return -1;
}
...
if(!(evctx = XmlEvCreatePPCtx(xctx, &xerr, NULL)))
{
printf("Failed to create EVENT context, error %u\n", (unsigned) xerr);
return -1;
}
for(i = 0; i < numDocs; i++)
{
if (xerr = XmlEvLoadPPDoc(xctx, evctx, "file", input_filenames[i], 0, NULL)
{
printf("Failed to load the document, error %u\n", (unsigned) xerr);
return -1;
}
...
for(;;)
{
xmlevtype cur_event;
cur_event = XmlEvNext(evctx);
switch(cur_event)
{
case XML_EVENT_FATAL_ERROR:
XmlEvGetError(evctx, (oratext **)&errmsg);
printf("Error %s\n", errmsg);
return;
case XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT:
printf("<%s>", XmlEvGetName0(evctx));
break;
case XML_EVENT_END_DOCUMENT:
printf("<%s>", XmlEvGetName0(evctx));
return;
}
}
XmlEvCleanPPCtx(xctx, evctx);
}
XmlEvDestroyPPCtx(xctx, evctx);
XmlDestroy(xctx);
Example 5-6 Sample Document to Parse
<!DOCTYPE doc [
<!ENTITY ent SYSTEM "file:attendees.txt">
<!ELEMENT doc ANY>
<!ELEMENT meeting (topic, date, publishAttendees)>
<!ELEMENT publishAttendees (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT topic (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT date (#PCDATA)>
]>
<!-- Begin Document -->
<doc>
<!-- Info about the meeting -->
<meeting>
<topic>Group meeting</topic>
<date>April 25, 2005</date>
<publishAttendees>&ent;</publishAttendees>
</meeting>
</doc>
<!-- End Document -->Example 5-7 Events Generated by Parsing a Sample Document
XML_EVENT_START_DOCUMENT XML_EVENT_START_DTD XML_EVENT_PE_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_ELEMENT_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_ELEMENT_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_ELEMENT_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_ELEMENT_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_ELEMENT_DECLARATION XML_EVENT_END_DTD XML_EVENT_COMMENT XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_SPACE XML_EVENT_COMMENT XML_EVENT_SPACE XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_CHARACTERS XML_EVENT_END_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_CHARACTERS XML_EVENT_END_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_START_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_START_ENTITY XML_EVENT_CHARACTERS XML_EVENT_END_ENTITY XML_EVENT_END_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_END_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_SPACE XML_EVENT_END_ELEMENT XML_EVENT_COMMENT XML_EVENT_END_DOCUMENT
Using OCI and the XDK for C API
This section describes accessing XDK for C functions from Oracle Call Interface (OCI).
Using XMLType Functions and Descriptions
You can use the C API for XML with XMLType columns in the database. An Oracle Call Interface (OCI) program can access XML data stored in a table by initializing the values of OCI handles.
This applies to handles such as these:
-
Environment handle
-
Service handle
-
Error handle
-
Optional parameters
The program can pass these input values to the function OCIXmlDbInitXmlCtx(), which returns an XML context. After the program invokes the C API, the function OCIXmlDbFreeXmlCtx() frees the context.
Table 5-6 XMLType Functions
| Function Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Create empty |
|
|
Create from a source buffer |
|
|
Extract an |
|
|
Transform using an Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT) stylesheet |
|
|
Check if an |
|
|
Is document schema-based? |
|
|
Get schema information |
|
|
Get document namespace |
|
|
Validate using schema |
|
Cast |
Get DOM from |
|
Cast |
Get |
Initializing an XML Context for Oracle XML DB
An XML context is a required parameter in each C DOM API function. This opaque context encapsulates information pertaining to data encoding, error message language, and so on. The contents of this XML context are different for XDK applications and for Oracle XML DB applications.
Note:
Do not use an XML context for XDK in an Oracle XML DB application, or an XML context for Oracle XML DB in an XDK application.
For Oracle XML DB, the two OCI functions that initialize and free an XML context have these prototypes:
xmlctx *OCIXmlDbInitXmlCtx (OCIEnv *envhp, OCISvcCtx *svchp, OCIError *errhp,
ocixmldbparam *params, ub4 num_params);
void OCIXmlDbFreeXmlCtx (xmlctx *xctx);
See Also:
-
Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for reference material on the functions
-
Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for a discussion about OCI support for XML
-
Oracle Database XML C API Reference for reference information on the DOM APIs
Creating XMLType Instances on the Client
You can construct new XMLType instances on the client by using the XmlLoadDom() invocations.
Follow these basic steps:
You can construct empty XMLType instances by invoking XmlCreateDocument(). This function would be equivalent to an OCIObjectNew() for other types. You can operate on the (xmldocnode *) returned by the preceding invocation and finally cast it to a (void *) if it must be provided as a bind value.
Operating on XML Data in the Database Server
You can operate on XML data in Oracle Database using OCI statements. You can bind and define XMLType values using xmldocnode and use OCI statements to extract XML data from the database. You can use this data directly in C DOM functions or bind values directly to SQL statements.
Using OCI and the XDK for C API: Examples
Examples show how to use the DOM API to construct and save an XML schema-based document and to modify a database document.
Example 5-8 shows how to construct a schema-based document with the DOM API and save it to the database. You must include the header files xml.h and ocixmldb.h.
Example 5-9 shows how to get a document from the database and modify it with the DOM API.
Example 5-8 Constructing a Schema-Based Document with the DOM API
#include <xml.h>
#include <ocixmldb.h>
static oratext tlpxml_test_sch[] = "<TOP xmlns='example1.xsd'\n\
xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' \n\
xsi:schemaLocation='example1.xsd example1.xsd'/>";
void example1()
{
OCIEnv *envhp;
OCIError *errhp;
OCISvcCtx *svchp;
OCIStmt *stmthp;
OCIDuration dur;
OCIType *xmltdo;
xmldocnode *doc;
ocixmldbparam params[1];
xmlnode *quux, *foo, *foo_data;
xmlerr err;
/* Initialize envhp, svchp, errhp, dur, stmthp */
/* ........ */
/* Get an xml context */
params[0].name_ocixmldbparam = XCTXINIT_OCIDUR;
params[0].value_ocixmldbparam = &dur;
xctx = OCIXmlDbInitXmlCtx(envhp, svchp, errhp, params, 1);
/* Start processing */
printf("Supports XML 1.0: %s\n",
XmlHasFeature(xctx, (oratext *) "xml", (oratext *) "1.0") ? "YES" : "NO");
/* Parsing a schema-based document */
if (!(doc = XmlLoadDom(xctx, &err, "buffer", tlpxml_test_sch,
"buffer_length", sizeof(tlpxml_test_sch)-1,
"validate", TRUE, NULL)))
{
printf("Parse failed, code %d\n");
return;
}
/* Create some elements and add them to the document */
top = XmlDomGetDocElem(xctx, doc);
quux = (xmlnode *) XmlDomCreateElem(xctx ,doc, (oratext *) "QUUX");
foo = (xmlnode *) XmlDomCreateElem(xctx, doc, (oratext *) "FOO");
foo_data = (xmlnode *) XmlDomCreateText(xctx, doc, (oratext *)"foo's data");
foo_data = XmlDomAppendChild(xctx, (xmlnode *) foo, (xmlnode *) foo_data);
foo = XmlDomAppendChild(xctx, quux, foo);
quux = XmlDomAppendChild(xctx, top, quux);
XmlSaveDom(xctx, &err, top, "stdio", stdout, NULL);
XmlSaveDom(xctx, &err, doc, "stdio", stdout, NULL);
/* Insert the document to my_table */
ins_stmt = "insert into my_table values (:1)";
status = OCITypeByName(envhp, errhp, svchp, (const text *) "SYS",
(ub4) strlen((char *)"SYS"), (const text *) "XMLTYPE",
(ub4) strlen((char *)"XMLTYPE"), (CONST text *) 0,
(ub4) 0, dur, OCI_TYPEGET_HEADER,
(OCIType **) &xmltdo)) ;
if (status == OCI_SUCCESS)
{
exec_bind_xml(svchp, errhp, stmthp, (void *)doc, xmltdo, ins_stmt));
}
/* free xml ctx */
OCIXmlDbFreeXmlCtx(xctx);
}
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* execute a sql statement which binds xml data */
/*--------------------------------------------------------*/
sword exec_bind_xml(svchp, errhp, stmthp, xml, xmltdo, sqlstmt)
OCISvcCtx *svchp;
OCIError *errhp;
OCIStmt *stmthp;
void *xml;
OCIType *xmltdo;
OraText *sqlstmt;
{
OCIBind *bndhp1 = (OCIBind *) 0;
OCIBind *bndhp2 = (OCIBind *) 0;
sword status = 0;
OCIInd ind = OCI_IND_NOTNULL;
OCIInd *indp = &ind;
if(status = OCIStmtPrepare(stmthp, errhp, (OraText *)sqlstmt,
(ub4)strlen((char *)sqlstmt),
(ub4) OCI_NTV_SYNTAX, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIBindByPos(stmthp, &bndhp1, errhp, (ub4) 1, (dvoid *) 0,
(sb4) 0, SQLT_NTY, (dvoid *) 0, (ub2 *)0,
(ub2 *)0, (ub4) 0, (ub4 *) 0, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIBindObject(bndhp1, errhp, (CONST OCIType *) xmltdo,
(dvoid **) &xml, (ub4 *) 0, (dvoid **) &indp, (ub4 *) 0)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIStmtExecute(svchp, stmthp, errhp, (ub4) 1, (ub4) 0,
(CONST OCISnapshot*) 0, (OCISnapshot*) 0, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
return OCI_SUCCESS;
}
Example 5-9 Modifying a Database Document with the DOM API
#include <xml.h>
#include <ocixmldb.h>
sword example2()
{
OCIEnv *envhp;
OCIError *errhp;
OCISvcCtx *svchp;
OCIStmt *stmthp;
OCIDuration dur;
OCIType *xmltdo;
xmldocnode *doc;
xmlnodelist *item_list; ub4 ilist_l;
ocixmldbparam params[1];
text *sel_xml_stmt = (text *)"SELECT xml_col FROM my_table";
ub4 xmlsize = 0;
sword status = 0;
OCIDefine *defnp = (OCIDefine *) 0;
/* Initialize envhp, svchp, errhp, dur, stmthp */
/* ... */
/* Get an xml context */
params[0].name_ocixmldbparam = XCTXINIT_OCIDUR;
params[0].value_ocixmldbparam = &dur;
xctx = OCIXmlDbInitXmlCtx(envhp, svchp, errhp, params, 1);
/* Start processing */
if(status = OCITypeByName(envhp, errhp, svchp, (const text *) "SYS",
(ub4) strlen((char *)"SYS"), (const text *) "XMLTYPE",
(ub4) strlen((char *)"XMLTYPE"), (CONST text *) 0,
(ub4) 0, dur, OCI_TYPEGET_HEADER,
(OCIType **) xmltdo_p)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(!(*xmltdo_p)) {
printf("NULL tdo returned\n");
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIStmtPrepare(stmthp, errhp, (OraText *)selstmt,
(ub4)strlen((char *)selstmt),
(ub4) OCI_NTV_SYNTAX, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIDefineByPos(stmthp, &defnp, errhp, (ub4) 1, (dvoid *) 0,
(sb4) 0, SQLT_NTY, (dvoid *) 0, (ub2 *)0,
(ub2 *)0, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIDefineObject(defnp, errhp, (OCIType *) *xmltdo_p,
(dvoid **) &doc,
&xmlsize, (dvoid **) 0, (ub4 *) 0)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
if(status = OCIStmtExecute(svchp, stmthp, errhp, (ub4) 1, (ub4) 0,
(CONST OCISnapshot*) 0, (OCISnapshot*) 0, (ub4) OCI_DEFAULT)) {
return OCI_ERROR;
}
/* We have the doc. Now we can operate on it */
printf("Getting Item list...\n");
item_list = XmlDomGetElemsByTag(xctx,(xmlelemnode *) elem,(oratext *)"Item");
ilist_l = XmlDomGetNodeListLength(xctx, item_list);
printf(" Item list length = %d \n", ilist_l);
for (i = 0; i < ilist_l; i++)
{
elem = XmlDomGetNodeListItem(xctx, item_list, i);
printf("Elem Name:%s\n", XmlDomGetNodeName(xctx, fragelem));
XmlDomRemoveChild(xctx, fragelem);
}
XmlSaveDom(xctx, &err, doc, "stdio", stdout, NULL);
/* free xml ctx */
OCIXmlDbFreeXmlCtx(xctx);
return OCI_SUCCESS;
}