21 Managing Indexes
Indexes can provide faster data access. You can create, alter, monitor, and drop indexes.
- About Indexes
Indexes are optional structures associated with tables and clusters that allow SQL queries to execute more quickly against a table. - Guidelines for Managing Indexes
You can follow guidelines for managing indexes. - Creating Indexes
You can create several different types of indexes. You can create indexes explicitly, and you can create indexes associated with constraints. - Altering Indexes
You can alter an index by completing tasks such as changing its storage characteristics, rebuilding it, making it unusable, or making it visible or invisible. - Monitoring Space Use of Indexes
If key values in an index are inserted, updated, and deleted frequently, then the index can lose its acquired space efficiency over time. - Dropping Indexes
You can drop an index with theDROP INDEXstatement. - Managing Auto Indexes
You can use the automatic indexing feature to configure and use auto indexes in an Oracle database to improve database performance. - Indexes Data Dictionary Views
You can query a set of data dictionary views for information about indexes.
Parent topic: Schema Objects
21.1 About Indexes
Indexes are optional structures associated with tables and clusters that allow SQL queries to execute more quickly against a table.
Just as the index in this manual helps you locate information faster than if there were no index, an Oracle Database index provides a faster access path to table data. You can use indexes without rewriting any queries. Your results are the same, but you see them more quickly.
Oracle Database provides several indexing schemes that provide complementary performance functionality. These are:
-
B-tree indexes: the default and the most common
-
B-tree cluster indexes: defined specifically for cluster
-
Hash cluster indexes: defined specifically for a hash cluster
-
Global and local indexes: relate to partitioned tables and indexes
-
Reverse key indexes: most useful for Oracle Real Application Clusters applications
-
Bitmap indexes: compact; work best for columns with a small set of values
-
Function-based indexes: contain the precomputed value of a function/expression
-
Domain indexes: specific to an application or cartridge.
Indexes are logically and physically independent of the data in the associated table. Being independent structures, they require storage space. You can create or drop an index without affecting the base tables, database applications, or other indexes. The database automatically maintains indexes when you insert, update, and delete rows of the associated table. If you drop an index, all applications continue to work. However, access to previously indexed data might be slower.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for an overview of indexes
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.2 Guidelines for Managing Indexes
You can follow guidelines for managing indexes.
- Create Indexes After Inserting Table Data
Data is often inserted or loaded into a table using either the SQL*Loader or an import utility. It is more efficient to create an index for a table after inserting or loading the data. If you create one or more indexes before loading data, then the database must update every index as each row is inserted. - Index the Correct Tables and Columns
Follow guidelines about tables and columns that are suitable for indexing. - Order Index Columns for Performance
The order of columns in theCREATEINDEXstatement can affect query performance. In general, specify the most frequently used columns first. - Limit the Number of Indexes for Each Table
A table can have any number of indexes. However, the more indexes there are, the more overhead is incurred as the table is modified. - Drop Indexes That Are No Longer Required
It is best practice to drop indexes that are no longer required. - Indexes and Deferred Segment Creation
Index segment creation is deferred when the associated table defers segment creation. This is because index segment creation reflects the behavior of the table with which it is associated. - Estimate Index Size and Set Storage Parameters
Estimating the size of an index before creating one can facilitate better disk space planning and management. - Specify the Tablespace for Each Index
Indexes can be created in any tablespace. An index can be created in the same or different tablespace as the table it indexes. - Consider Parallelizing Index Creation
You can parallelize index creation, much the same as you can parallelize table creation. Because multiple processes work together to create the index, the database can create the index more quickly than if a single server process created the index sequentially. - Consider Creating Indexes with NOLOGGING
You can create an index and generate minimal redo log records by specifyingNOLOGGINGin theCREATE INDEXstatement. - Understand When to Use Unusable or Invisible Indexes
Use unusable or invisible indexes when you want to improve the performance of bulk loads, test the effects of removing an index before dropping it, or otherwise suspend the use of an index by the optimizer. - Understand When to Create Multiple Indexes on the Same Set of Columns
You can create multiple indexes on the same set of columns when the indexes are different in some way. For example, you can create a B-tree index and a bitmap index on the same set of columns. - Consider Costs and Benefits of Coalescing or Rebuilding Indexes
Improper sizing or increased growth can produce index fragmentation. To eliminate or reduce fragmentation, you can rebuild or coalesce the index. But before you perform either task weigh the costs and benefits of each option and choose the one that works best for your situation. - Consider Cost Before Disabling or Dropping Constraints
Because unique and primary keys have associated indexes, you should factor in the cost of dropping and creating indexes when considering whether to disable or drop aUNIQUEorPRIMARY KEYconstraint. - Consider Using the In-Memory Column Store to Reduce the Number of Indexes
The In-Memory Column Store is an optional portion of the system global area (SGA) that stores copies of tables, table partitions, and other database objects that is optimized for rapid scans. In the In-Memory Column Store, table data is stored by column rather than row in the SGA.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for conceptual information about indexes and indexing, including descriptions of the various indexing schemes offered by Oracle
-
Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide and Oracle Database Data Warehousing Guide for information about bitmap indexes
-
Oracle Database Data Cartridge Developer's Guide for information about defining domain-specific operators and indexing schemes and integrating them into the Oracle Database server
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.2.1 Create Indexes After Inserting Table Data
Data is often inserted or loaded into a table using either the SQL*Loader or an import utility. It is more efficient to create an index for a table after inserting or loading the data. If you create one or more indexes before loading data, then the database must update every index as each row is inserted.
Creating an index on a table that already has data requires sort space. Some sort space comes from memory allocated for the index creator. The amount for each user is determined by the initialization parameter SORT_AREA_SIZE. The database also swaps sort information to and from temporary segments that are only allocated during the index creation in the user's temporary tablespace.
Under certain conditions, data can be loaded into a table with SQL*Loader direct-path load, and an index can be created as data is loaded.
See Also:
Oracle Database Utilities for information about using SQL*Loader for direct-path load
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.2 Index the Correct Tables and Columns
Follow guidelines about tables and columns that are suitable for indexing.
Use the following guidelines for determining when to create an index:
-
Create an index if you frequently want to retrieve less than 15% of the rows in a large table. The percentage varies greatly according to the relative speed of a table scan and how the row data is distributed in relation to the index key. The faster the table scan, the lower the percentage; the more clustered the row data, the higher the percentage.
-
To improve performance on joins of multiple tables, index columns used for joins.
Note:
Primary and unique keys automatically have indexes, but you might want to create an index on a foreign key.
-
Small tables do not require indexes. If a query is taking too long, then the table might have grown from small to large.
Columns That Are Suitable for Indexing
Some columns are strong candidates for indexing. Columns with one or more of the following characteristics are candidates for indexing:
-
Values are relatively unique in the column.
-
There is a wide range of values (good for regular indexes).
-
There is a small range of values (good for bitmap indexes).
-
The column contains many nulls, but queries often select all rows having a value. In this case, use the following phrase:
WHERE COL_X > -9.99 * power(10,125)
Using the preceding phrase is preferable to:
WHERE COL_X IS NOT NULL
This is because the first uses an index on
COL_X(assuming thatCOL_Xis a numeric column).
Columns That Are Not Suitable for Indexing
Columns with the following characteristics are less suitable for indexing:
-
There are many nulls in the column, and you do not search on the not null values.
LONG and LONG RAW columns cannot be indexed.
Virtual Columns
See Also:
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.3 Order Index Columns for Performance
The order of columns in the CREATE INDEX statement can affect query performance. In general, specify the most frequently used columns first.
If you create a single index across columns to speed up queries that access, for example, col1, col2, and col3; then queries that access just col1, or that access just col1 and col2, are also speeded up. But a query that accessed just col2, just col3, or just col2 and col3 does not use the index.
Note:
In some cases, such as when the leading column has very low cardinality, the database may use a skip scan of this type of index. See Oracle Database Concepts for more information about index skip scan.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.4 Limit the Number of Indexes for Each Table
A table can have any number of indexes. However, the more indexes there are, the more overhead is incurred as the table is modified.
Specifically, when rows are inserted or deleted, all indexes on the table must be updated as well. Also, when a column is updated, all indexes that contain the column must be updated.
Thus, there is a trade-off between the speed of retrieving data from a table and the speed of updating the table. For example, if a table is primarily read-only, then having more indexes can be useful; but if a table is heavily updated, then having fewer indexes could be preferable.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.5 Drop Indexes That Are No Longer Required
It is best practice to drop indexes that are no longer required.
Consider dropping an index if:
-
It does not speed up queries. The table could be very small, or there could be many rows in the table but very few index entries.
-
The queries in your applications do not use the index.
-
The index must be dropped before being rebuilt.
See Also:
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.6 Indexes and Deferred Segment Creation
Index segment creation is deferred when the associated table defers segment creation. This is because index segment creation reflects the behavior of the table with which it is associated.
See Also:
"Understand Deferred Segment Creation" for further information
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.7 Estimate Index Size and Set Storage Parameters
Estimating the size of an index before creating one can facilitate better disk space planning and management.
You can use the combined estimated size of indexes, along with estimates for tables, the undo tablespace, and redo log files, to determine the amount of disk space that is required to hold an intended database. From these estimates, you can make correct hardware purchases and other decisions.
Use the estimated size of an individual index to better manage the disk space that the index uses. When an index is created, you can set appropriate storage parameters and improve I/O performance of applications that use the index. For example, assume that you estimate the maximum size of an index before creating it. If you then set the storage parameters when you create the index, then fewer extents are allocated for the table data segment, and all of the index data is stored in a relatively contiguous section of disk space. This decreases the time necessary for disk I/O operations involving this index.
The maximum size of a single index entry is dependent on the block size of the database.
Storage parameters of an index segment created for the index used to enforce a primary key or unique key constraint can be set in either of the following ways:
-
In the
ENABLE...USINGINDEXclause of theCREATETABLEorALTERTABLEstatement -
In the
STORAGEclause of theALTERINDEXstatement
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information about the limits related to index size
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about creating an index on an extended data type column
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.8 Specify the Tablespace for Each Index
Indexes can be created in any tablespace. An index can be created in the same or different tablespace as the table it indexes.
If you use the same tablespace for a table and its index, then it can be more convenient to perform database maintenance (such as tablespace or file backup) or to ensure application availability. All the related data is always online together.
Using different tablespaces (on different disks) for a table and its index produces better performance than storing the table and index in the same tablespace. Disk contention is reduced. But, if you use different tablespaces for a table and its index, and one tablespace is offline (containing either data or index), then the statements referencing that table are not guaranteed to work.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.9 Consider Parallelizing Index Creation
You can parallelize index creation, much the same as you can parallelize table creation. Because multiple processes work together to create the index, the database can create the index more quickly than if a single server process created the index sequentially.
When creating an index in parallel, storage parameters are used separately by each query server process. Therefore, an index created with an INITIAL value of 5M and a parallel degree of 12 consumes at least 60M of storage during index creation.
See Also:
Oracle Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide for information about using parallel execution
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.10 Consider Creating Indexes with NOLOGGING
You can create an index and generate minimal redo log records by specifying NOLOGGING in the CREATE INDEX statement.
Note:
Because indexes created using NOLOGGING are not archived, perform a backup after you create the index.
Creating an index with NOLOGGING has the following benefits:
-
Space is saved in the redo log files.
-
The time it takes to create the index is decreased.
-
Performance improves for parallel creation of large indexes.
In general, the relative performance improvement is greater for larger indexes created without LOGGING than for smaller ones. Creating small indexes without LOGGING has little effect on the time it takes to create an index. However, for larger indexes the performance improvement can be significant, especially when you are also parallelizing the index creation.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.11 Understand When to Use Unusable or Invisible Indexes
Use unusable or invisible indexes when you want to improve the performance of bulk loads, test the effects of removing an index before dropping it, or otherwise suspend the use of an index by the optimizer.
Unusable indexes
An unusable index is ignored by the optimizer and is not maintained by DML. One reason to make an index unusable is to improve bulk load performance. (Bulk loads go more quickly if the database does not need to maintain indexes when inserting rows.) Instead of dropping the index and later re-creating it, which requires you to recall the exact parameters of the CREATE INDEX statement, you can make the index unusable, and then rebuild it.
You can create an index in the unusable state, or you can mark an existing index or index partition unusable. In some cases the database may mark an index unusable, such as when a failure occurs while building the index. When one partition of a partitioned index is marked unusable, the other partitions of the index remain valid.
An unusable index or index partition must be rebuilt, or dropped and re-created, before it can be used. Truncating a table makes an unusable index valid.
When you make an existing index unusable, its index segment is dropped.
The functionality of unusable indexes depends on the setting of the SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES initialization parameter. When SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES is TRUE (the default), then:
-
DML statements against the table proceed, but unusable indexes are not maintained.
-
DML statements terminate with an error if there are any unusable indexes that are used to enforce the
UNIQUEconstraint. -
For nonpartitioned indexes, the optimizer does not consider any unusable indexes when creating an access plan for
SELECTstatements. The only exception is when an index is explicitly specified with theINDEX()hint. -
For a partitioned index where one or more of the partitions is unusable, the optimizer can use table expansion. With table expansion, the optimizer transforms the query into a
UNIONALLstatement, with some subqueries accessing indexed partitions and other subqueries accessing partitions with unusable indexes. The optimizer can choose the most efficient access method available for a partition. See Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide for more information about table expansion.
When SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES is FALSE, then:
-
If any unusable indexes or index partitions are present, then any DML statements that would cause those indexes or index partitions to be updated are terminated with an error.
-
For
SELECTstatements, if an unusable index or unusable index partition is present, but the optimizer does not choose to use it for the access plan, then the statement proceeds. However, if the optimizer does choose to use the unusable index or unusable index partition, then the statement terminates with an error.
Invisible Indexes
You can create invisible indexes or make an existing index invisible. An invisible index is ignored by the optimizer unless you explicitly set the OPTIMIZER_USE_INVISIBLE_INDEXES initialization parameter to TRUE at the session or system level. Unlike unusable indexes, an invisible index is maintained during DML statements. Although you can make a partitioned index invisible, you cannot make an individual index partition invisible while leaving the other partitions visible.
Using invisible indexes, you can do the following:
-
Test the removal of an index before dropping it.
-
Use temporary index structures for certain operations or modules of an application without affecting the overall application.
-
Add an index to a set of columns on which an index already exists.
See Also:
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.12 Understand When to Create Multiple Indexes on the Same Set of Columns
You can create multiple indexes on the same set of columns when the indexes are different in some way. For example, you can create a B-tree index and a bitmap index on the same set of columns.
When you have multiple indexes on the same set of columns, only one of these indexes can be visible at a time, and any other indexes must be invisible.
You might create different indexes on the same set of columns because they provide the flexibility to meet your requirements. You can also create multiple indexes on the same set of columns to perform application migrations without dropping an existing index and recreating it with different attributes.
Different types of indexes are useful in different scenarios. For example, B-tree indexes are often used in online transaction processing (OLTP) systems with many concurrent transactions, while bitmap indexes are often used in data warehousing systems that are mostly used for queries. Similarly, locally and globally partitioned indexes are useful in different scenarios. Locally partitioned indexes are easy to manage because partition maintenance operations automatically apply to them. Globally partitioned indexes are useful when you want the partitioning scheme of an index to be different from its table's partitioning scheme.
You can create multiple indexes on the same set of columns when at least one of the following index characteristics is different:
-
The indexes are of different types.
See "About Indexes" and Oracle Database Concepts for information about the different types of indexes.
However, the following exceptions apply:
-
You cannot create a B-tree index and a B-tree cluster index on the same set of columns.
-
You cannot create a B-tree index and an index-organized table on the same set of columns.
-
-
The indexes use different partitioning.
Partitioning can be different in any of the following ways:
-
Indexes that are not partitioned and indexes that are partitioned
-
Indexes that are locally partitioned and indexes that are globally partitioned
-
Indexes that differ in partitioning type (range or hash)
-
-
The indexes have different uniqueness properties.
You can create both a unique and a non-unique index on the same set of columns.
21.2.13 Consider Costs and Benefits of Coalescing or Rebuilding Indexes
Improper sizing or increased growth can produce index fragmentation. To eliminate or reduce fragmentation, you can rebuild or coalesce the index. But before you perform either task weigh the costs and benefits of each option and choose the one that works best for your situation.
Table 21-1 is a comparison of the costs and benefits associated with rebuilding and coalescing indexes.
Table 21-1 Costs and Benefits of Coalescing or Rebuilding Indexes
| Rebuild Index | Coalesce Index |
|---|---|
|
Quickly moves index to another tablespace |
Cannot move index to another tablespace |
|
Higher costs: requires more disk space |
Lower costs: does not require more disk space |
|
Creates new tree, shrinks height if applicable |
Coalesces leaf blocks within same branch of tree |
|
Enables you to quickly change storage and tablespace parameters without having to drop the original index |
Quickly frees up index leaf blocks for use |
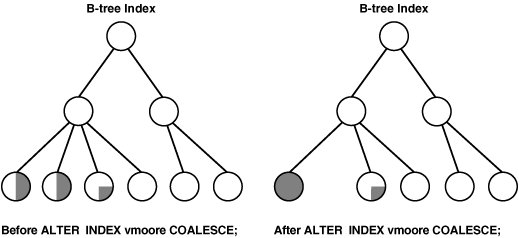
In situations where you have B-tree index leaf blocks that can be freed up for reuse, you can merge those leaf blocks using the following statement:
ALTER INDEX vmoore COALESCE;
Figure 21-1 illustrates the effect of an ALTER INDEX COALESCE on the index vmoore. Before performing the operation, the first two leaf blocks are 50% full. Therefore, you have an opportunity to reduce fragmentation and completely fill the first block, while freeing up the second.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.14 Consider Cost Before Disabling or Dropping Constraints
Because unique and primary keys have associated indexes, you should factor in the cost of dropping and creating indexes when considering whether to disable or drop a UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY constraint.
If the associated index for a UNIQUE key or PRIMARY KEY constraint is extremely large, then you can save time by leaving the constraint enabled rather than dropping and re-creating the large index. You also have the option of explicitly specifying that you want to keep or drop the index when dropping or disabling a UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY constraint.
See Also:
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.2.15 Consider Using the In-Memory Column Store to Reduce the Number of Indexes
The In-Memory Column Store is an optional portion of the system global area (SGA) that stores copies of tables, table partitions, and other database objects that is optimized for rapid scans. In the In-Memory Column Store, table data is stored by column rather than row in the SGA.
Note:
This feature is available starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1.0.2).
For tables used in OLTP or data warehousing environments, multiple indexes typically are created to improve the performance of analytic and reporting queries. These indexes can impede the performance of data manipulation language (DML) statements. When a table is stored in the In-Memory Column Store, indexes used for analytic or reporting queries can be greatly reduced or eliminated without affecting query performance. Eliminating these indexes can improve the performance of transactions and data loading operations.
Parent topic: Guidelines for Managing Indexes
21.3 Creating Indexes
You can create several different types of indexes. You can create indexes explicitly, and you can create indexes associated with constraints.
Live SQL:
To view and run examples related to creating indexes on Oracle Live SQL, go to Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
- Prerequisites for Creating Indexes
Prerequisites must be met before you can create indexes. - Creating an Index Explicitly
You can create indexes explicitly (outside of integrity constraints) using the SQL statementCREATE INDEX. - Creating a Unique Index Explicitly
Indexes can be unique or non-unique. Unique indexes guarantee that no two rows of a table have duplicate values in the key column (or columns). Non-unique indexes do not impose this restriction on the column values. - Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
You can create an index associated with a constraint when you issue theCREATE TABLEorALTER TABLESQL statement. - Creating a Large Index
When creating an extremely large index, consider allocating a larger temporary tablespace for the index creation. - Creating an Index Online
You can create and rebuild indexes online. Therefore, you can update base tables at the same time you are building or rebuilding indexes on that table. - Creating a Function-Based Index
Function-based indexes facilitate queries that qualify a value returned by a function or expression. The value of the function or expression is precomputed and stored in the index. - Creating a Compressed Index
As your database grows in size, consider using index compression to save disk space. - Creating an Unusable Index
When you create an index in theUNUSABLEstate, it is ignored by the optimizer and is not maintained by DML. An unusable index must be rebuilt, or dropped and re-created, before it can be used. - Creating an Invisible Index
An invisible index is an index that is ignored by the optimizer unless you explicitly set theOPTIMIZER_USE_INVISIBLE_INDEXESinitialization parameter toTRUEat the session or system level. - Creating Multiple Indexes on the Same Set of Columns
You can create multiple indexes on the same set of columns when the indexes are different in some way.
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.3.1 Prerequisites for Creating Indexes
Prerequisites must be met before you can create indexes.
To create an index in your own schema, at least one of the following prerequisites must be met:
-
The table or cluster to be indexed is in your own schema.
-
You have
INDEXprivilege on the table to be indexed. -
You have
CREATE ANY INDEXsystem privilege.
To create an index in another schema, all of the following prerequisites must be met:
-
You have
CREATE ANY INDEXsystem privilege. -
The owner of the other schema has a quota for the tablespaces to contain the index or index partitions, or
UNLIMITED TABLESPACEsystem privilege.
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.2 Creating an Index Explicitly
You can create indexes explicitly (outside of integrity constraints) using the SQL statement CREATE INDEX.
The following statement creates an index named emp_ename for the ename column of the emp table:
CREATE INDEX emp_ename ON emp(ename)
TABLESPACE users
STORAGE (INITIAL 20K
NEXT 20k);
Notice that several storage settings and a tablespace are explicitly specified for the index. If you do not specify storage options (such as INITIAL and NEXT) for an index, then the default storage options of the default or specified tablespace are automatically used.
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for syntax and restrictions on the use of the CREATE INDEX statement
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.3 Creating a Unique Index Explicitly
Indexes can be unique or non-unique. Unique indexes guarantee that no two rows of a table have duplicate values in the key column (or columns). Non-unique indexes do not impose this restriction on the column values.
Use the CREATE UNIQUE INDEX statement to create a unique index. The following example creates a unique index:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX dept_unique_index ON dept (dname)
TABLESPACE indx;
Alternatively, you can define UNIQUE integrity constraints on the desired columns. The database enforces UNIQUE integrity constraints by automatically defining a unique index on the unique key. This is discussed in the following section. However, it is advisable that any index that exists for query performance, including unique indexes, be created explicitly.
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide for more information about creating an index for performance
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.4 Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
You can create an index associated with a constraint when you issue the CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE SQL statement.
- About Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
Oracle Database enforces aUNIQUEkey orPRIMARY KEYintegrity constraint on a table by creating a unique index on the unique key or primary key. - Specifying Storage Options for an Index Associated with a Constraint
You can set the storage options for the indexes associated withUNIQUEandPRIMARY KEYconstraints using theUSING INDEXclause. - Specifying the Index Associated with a Constraint
You can specify details about the indexes associated with constraints.
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.4.1 About Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
Oracle Database enforces a UNIQUE key or PRIMARY KEY integrity constraint on a table by creating a unique index on the unique key or primary key.
This index is automatically created by the database when the constraint is enabled. No action is required by you when you issue the CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statement to create the index, but you can optionally specify a USING INDEX clause to exercise control over its creation. This includes both when a constraint is defined and enabled, and when a defined but disabled constraint is enabled.
To enable a UNIQUE or PRIMARY KEY constraint, thus creating an associated index, the owner of the table must have a quota for the tablespace intended to contain the index, or the UNLIMITED TABLESPACE system privilege. The index associated with a constraint always takes the name of the constraint, unless you optionally specify otherwise.
Note:
An efficient procedure for enabling a constraint that can make use of parallelism is described in "Efficient Use of Integrity Constraints: A Procedure".
Parent topic: Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
21.3.4.2 Specifying Storage Options for an Index Associated with a Constraint
You can set the storage options for the indexes associated with UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints using the USING INDEX clause.
The following CREATE TABLE statement enables a PRIMARY KEY constraint and specifies the storage options of the associated index:
CREATE TABLE emp (
empno NUMBER(5) PRIMARY KEY, age INTEGER)
ENABLE PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX
TABLESPACE users;Parent topic: Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
21.3.4.3 Specifying the Index Associated with a Constraint
You can specify details about the indexes associated with constraints.
If you require more explicit control over the indexes associated with UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints, the database lets you:
-
Specify an existing index that the database is to use to enforce the constraint
-
Specify a
CREATEINDEXstatement that the database is to use to create the index and enforce the constraint
These options are specified using the USING INDEX clause. The following statements present some examples.
Example 1:
CREATE TABLE a (
a1 INT PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX (create index ai on a (a1)));
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
Example 2:
CREATE TABLE b(
b1 INT,
b2 INT,
CONSTRAINT bu1 UNIQUE (b1, b2)
USING INDEX (create unique index bi on b(b1, b2)),
CONSTRAINT bu2 UNIQUE (b2, b1) USING INDEX bi);
Example 3:
CREATE TABLE c(c1 INT, c2 INT); CREATE INDEX ci ON c (c1, c2); ALTER TABLE c ADD CONSTRAINT cpk PRIMARY KEY (c1) USING INDEX ci;
If a single statement creates an index with one constraint and also uses that index for another constraint, the system will attempt to rearrange the clauses to create the index before reusing it.
See Also:
Parent topic: Creating an Index Associated with a Constraint
21.3.5 Creating a Large Index
When creating an extremely large index, consider allocating a larger temporary tablespace for the index creation.
To do so, complete the following steps:
- Create a new temporary tablespace using the
CREATE TABLESPACEorCREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACEstatement. - Use the
TEMPORARY TABLESPACEoption of theALTER USERstatement to make this your new temporary tablespace. - Create the index using the
CREATE INDEXstatement. - Drop this tablespace using the
DROP TABLESPACEstatement. Then use theALTER USERstatement to reset your temporary tablespace to your original temporary tablespace.
Using this procedure can avoid the problem of expanding your usual, and usually shared, temporary tablespace to an unreasonably large size that might affect future performance.
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.6 Creating an Index Online
You can create and rebuild indexes online. Therefore, you can update base tables at the same time you are building or rebuilding indexes on that table.
You can perform DML operations while the index build is taking place, but DDL operations are not allowed. Parallel DML is not supported when creating or rebuilding an index online.
The following statements illustrate online index build operations:
CREATE INDEX emp_name ON emp (mgr, emp1, emp2, emp3) ONLINE;
Note:
Keep in mind that the time that it takes on online index build to complete is proportional to the size of the table and the number of concurrently executing DML statements. Therefore, it is best to start online index builds when DML activity is low.
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
See Also:
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.7 Creating a Function-Based Index
Function-based indexes facilitate queries that qualify a value returned by a function or expression. The value of the function or expression is precomputed and stored in the index.
In addition to the prerequisites for creating a conventional index, if the index is based on user-defined functions, then those functions must be marked DETERMINISTIC. Also, a function-based index is executed with the credentials of the owner of the function, so you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the function.
Note:
CREATE INDEX stores the timestamp of the most recent function used in the function-based index. This timestamp is updated when the index is validated. When performing tablespace point-in-time recovery of a function-based index, if the timestamp on the most recent function used in the index is newer than the timestamp stored in the index, then the index is marked invalid. You must use the ANALYZE INDEX...VALIDATE STRUCTURE statement to validate this index.
To illustrate a function-based index, consider the following statement that defines a function-based index (area_index) defined on the function area(geo):
CREATE INDEX area_index ON rivers (area(geo));
In the following SQL statement, when area(geo) is referenced in the WHERE clause, the optimizer considers using the index area_index.
SELECT id, geo, area(geo), desc
FROM rivers
WHERE Area(geo) >5000;
Because a function-based index depends upon any function it is using, it can be invalidated when a function changes. If the function is valid, then you can use an ALTER INDEX...ENABLE statement to enable a function-based index that has been disabled. The ALTER INDEX...DISABLE statement lets you disable the use of a function-based index. Consider doing this if you are working on the body of the function.
Note:
An alternative to creating a function-based index is to add a virtual column to the target table and index the virtual column. See "About Tables" for more information.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for more information about function-based indexes
-
Oracle Database Development Guide for information about using function-based indexes in applications and examples of their use
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.8 Creating a Compressed Index
As your database grows in size, consider using index compression to save disk space.
- Creating an Index Using Prefix Compression
Creating an index using prefix compression (also known as key compression) eliminates repeated occurrences of key column prefix values. Prefix compression is most useful for non-unique indexes with a large number of duplicates on the leading columns. - Creating an Index Using Advanced Index Compression
Advanced index compression works well on all supported indexes, including those that are not good candidates for prefix compression. Creating an index using advanced index compression can reduce the size of all unique and non-unique indexes and improves the compression ratio significantly, while still providing efficient access to the indexes.
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.8.1 Creating an Index Using Prefix Compression
Creating an index using prefix compression (also known as key compression) eliminates repeated occurrences of key column prefix values. Prefix compression is most useful for non-unique indexes with a large number of duplicates on the leading columns.
Prefix compression breaks an index key into a prefix and a suffix entry. Compression is achieved by sharing the prefix entries among all the suffix entries in an index block. This sharing can lead to substantial savings in space, allowing you to store more keys for each index block while improving performance.
Prefix compression can be useful in the following situations:
-
You have a non-unique index where
ROWIDis appended to make the key unique. If you use prefix compression here, then the duplicate key is stored as a prefix entry on the index block without theROWID. The remaining rows become suffix entries consisting of only theROWID. -
You have a unique multicolumn index.
You enable prefix compression using the COMPRESS clause. The prefix length (as the number of key columns) can also be specified to identify how the key columns are broken into a prefix and suffix entry. For example, the following statement compresses duplicate occurrences of a key in the index leaf block:
CREATE INDEX hr.emp_ename ON emp(ename) TABLESPACE users COMPRESS 1;
You can also specify the COMPRESS clause during rebuild. For example, during rebuild, you can disable compression as follows:
ALTER INDEX hr.emp_ename REBUILD NOCOMPRESS;
The COMPRESSION column in the ALL_INDEXES view and ALL_PART_INDEXES views shows whether an index is compressed, and, if it is compressed, the type of compression enabled for the index.
Live SQL:
View and run a related example on Oracle Live SQL at Oracle Live SQL: Creating Indexes.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for a more detailed discussion of prefix compression
Parent topic: Creating a Compressed Index
21.3.8.2 Creating an Index Using Advanced Index Compression
Advanced index compression works well on all supported indexes, including those that are not good candidates for prefix compression. Creating an index using advanced index compression can reduce the size of all unique and non-unique indexes and improves the compression ratio significantly, while still providing efficient access to the indexes.
For a partitioned index, you can specify the compression type on a partition by partition basis. You can also specify advanced index compression on index partitions even when the parent index is not compressed.
Advanced index compression works at the block level to provide the best compression for each block.
You can enable advanced index compression using the COMPRESS ADVANCED clause and can specify the following compression levels:
-
LOW: This level provides lower compression ratio at minimal CPU overhead. Before enablingCOMPRESS ADVANCED LOW, the database must be at 12.1.0 or higher compatibility level. -
HIGH: This level, the default, provides higher compression ratio at some CPU overhead. Before enablingCOMPRESS ADVANCED HIGH, the database must be at 12.2.0 or higher compatibility level.When a
CREATE INDEXDDL statement is executed, a block is filled with rows. At high compression level, when the block is full, it is compressed with advanced index compression if enough space is saved to insert the next row. When a block becomes full, the block might be recompressed using advanced index compression to avoid splitting the block if enough space is saved to insert the incoming key.
The COMPRESSION column in the ALL_INDEXES view shows whether an index is compressed, and, if it is compressed, the type of compression enabled for the index. The possible values for the COMPRESSION column are ADVANCED HIGH, ADVANCED LOW, DISABLED, or ENABLED. The COMPRESSION column in the ALL_IND_PARTITIONS and ALL_IND_SUBPARTITIONS views indicates whether index compression is ENABLED or DISABLED for the partition or subpartition.
Note:
-
Advanced index compression is not supported for bitmap indexes or index-organized tables.
-
When low level advanced index compression is enabled, advanced index compression cannot be specified on a single column unique index. This restriction does not apply when high level advanced index compression is enabled.
Example 21-1 Enabling Low Level Advanced Index Compression During Index Creation
For example, the following statement enables low level advanced index compression during the creation of the hr.emp_mndp_ix index:
CREATE INDEX hr.emp_mndp_ix ON hr.employees(manager_id, department_id) COMPRESS ADVANCED LOW;
Example 21-2 Enabling High Level Advanced Index Compression During Index Rebuild
You can also specify the COMPRESS ADVANCED clause during an index rebuild. For example, during rebuild, you can enable high level advanced index compression for the hr.emp_manager_ix index as follows:
ALTER INDEX hr.emp_manager_ix REBUILD COMPRESS ADVANCED HIGH;
Parent topic: Creating a Compressed Index
21.3.9 Creating an Unusable Index
When you create an index in the UNUSABLE state, it is ignored by the optimizer and is not maintained by DML. An unusable index must be rebuilt, or dropped and re-created, before it can be used.
If the index is partitioned, then all index partitions are marked UNUSABLE.
The database does not create an index segment when creating an unusable index.
The following procedure illustrates how to create unusable indexes and query the database for details about the index.
To create an unusable index:
-
If necessary, create the table to be indexed.
For example, create a hash-partitioned table called
hr.employees_partas follows:sh@PROD> CONNECT hr Enter password: ** Connected. hr@PROD> CREATE TABLE employees_part 2 PARTITION BY HASH (employee_id) PARTITIONS 2 3 AS SELECT * FROM employees; Table created. hr@PROD> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees_part; COUNT(*) ---------- 107 -
Create an index with the keyword
UNUSABLE.The following example creates a locally partitioned index on
employees_part, naming the index partitionsp1_i_emp_enameandp2_i_emp_ename, and makingp1_i_emp_enameunusable:hr@PROD> CREATE INDEX i_emp_ename ON employees_part (employee_id) 2 LOCAL (PARTITION p1_i_emp_ename UNUSABLE, PARTITION p2_i_emp_ename); Index created.
-
(Optional) Verify that the index is unusable by querying the data dictionary.
The following example queries the status of index
i_emp_enameand its two partitions, showing that only partitionp2_i_emp_enameis unusable:hr@PROD> SELECT INDEX_NAME AS "INDEX OR PARTITION NAME", STATUS 2 FROM USER_INDEXES 3 WHERE INDEX_NAME = 'I_EMP_ENAME' 4 UNION ALL 5 SELECT PARTITION_NAME AS "INDEX OR PARTITION NAME", STATUS 6 FROM USER_IND_PARTITIONS 7 WHERE PARTITION_NAME LIKE '%I_EMP_ENAME%'; INDEX OR PARTITION NAME STATUS ------------------------------ -------- I_EMP_ENAME N/A P1_I_EMP_ENAME UNUSABLE P2_I_EMP_ENAME USABLE
-
(Optional) Query the data dictionary to determine whether storage exists for the partitions.
For example, the following query shows that only index partition
p2_i_emp_enameoccupies a segment. Because you createdp1_i_emp_enameas unusable, the database did not allocate a segment for it.hr@PROD> COL PARTITION_NAME FORMAT a14 hr@PROD> COL SEG_CREATED FORMAT a11 hr@PROD> SELECT p.PARTITION_NAME, p.STATUS AS "PART_STATUS", 2 p.SEGMENT_CREATED AS "SEG_CREATED", 3 FROM USER_IND_PARTITIONS p, USER_SEGMENTS s 4 WHERE s.SEGMENT_NAME = 'I_EMP_ENAME'; PARTITION_NAME PART_STA SEG_CREATED -------------- -------- ----------- P2_I_EMP_ENAME USABLE YES P1_I_EMP_ENAME UNUSABLE NO
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information on creating unusable indexes, including restrictions.
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.10 Creating an Invisible Index
An invisible index is an index that is ignored by the optimizer unless you explicitly set the OPTIMIZER_USE_INVISIBLE_INDEXES initialization parameter to TRUE at the session or system level.
To create an invisible index:
-
Use the
CREATE INDEXstatement with theINVISIBLEkeyword.The following statement creates an invisible index named
emp_enamefor theenamecolumn of theemptable:CREATE INDEX emp_ename ON emp(ename) TABLESPACE users STORAGE (INITIAL 20K NEXT 20k) INVISIBLE;
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information on creating invisible indexes
Parent topic: Creating Indexes
21.3.11 Creating Multiple Indexes on the Same Set of Columns
You can create multiple indexes on the same set of columns when the indexes are different in some way.
To create multiple indexes on the same set of columns, the following prerequisites must be met:
-
The prerequisites for required privileges in "Creating Indexes".
-
Only one index on the same set of columns can be visible at any point in time.
If you are creating a visible index, then any existing indexes on the set of columns must be invisible..
Alternatively, you can create an invisible index on the set of columns.
For example, the following steps create a B-tree index and a bitmap index on the same set of columns in the oe.orders table:
21.4 Altering Indexes
You can alter an index by completing tasks such as changing its storage characteristics, rebuilding it, making it unusable, or making it visible or invisible.
- About Altering Indexes
To alter an index, your schema must contain the index, or you must have theALTER ANY INDEXsystem privilege. - Altering Storage Characteristics of an Index
Alter the storage parameters of any index, including those created by the database to enforce primary and unique key integrity constraints, using theALTER INDEXstatement. - Rebuilding an Existing Index
When you rebuild an index, you use an existing index as the data source. Creating an index in this manner enables you to change storage characteristics or move to a new tablespace. Rebuilding an index based on an existing data source removes intra-block fragmentation. - Making an Index Unusable
When you make an index unusable, it is ignored by the optimizer and is not maintained by DML. When you make one partition of a partitioned index unusable, the other partitions of the index remain valid. - Making an Index Invisible or Visible
Making an index invisible is an alternative to making it unusable or dropping it. - Renaming an Index
You can rename an index using anALTER INDEXstatement with theRENAMEclause. - Monitoring Index Usage
Oracle Database provides a means of monitoring indexes to determine whether they are being used. If an index is not being used, then it can be dropped, eliminating unnecessary statement overhead.
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.4.1 About Altering Indexes
To alter an index, your schema must contain the index, or you must have the ALTER ANY INDEX system privilege.
With the ALTER INDEX statement, you can:
-
Rebuild or coalesce an existing index
-
Deallocate unused space or allocate a new extent
-
Specify parallel execution (or not) and alter the degree of parallelism
-
Alter storage parameters or physical attributes
-
Specify
LOGGINGorNOLOGGING -
Enable or disable prefix compression
-
Enable or disable advanced compression
-
Mark the index unusable
-
Make the index invisible
-
Rename the index
-
Start or stop the monitoring of index usage
You cannot alter index column structure.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for details on the
ALTERINDEXstatement
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.4.2 Altering Storage Characteristics of an Index
Alter the storage parameters of any index, including those created by the database to enforce primary and unique key integrity constraints, using the ALTER INDEX statement.
For example, the following statement alters the emp_ename index:
ALTER INDEX emp_ename
STORAGE (NEXT 40);
The parameters INITIAL and MINEXTENTS cannot be altered. All new settings for the other storage parameters affect only extents subsequently allocated for the index.
For indexes that implement integrity constraints, you can adjust storage parameters by issuing an ALTER TABLE statement that includes the USING INDEX subclause of the ENABLE clause. For example, the following statement changes the storage options of the index created on table emp to enforce the primary key constraint:
ALTER TABLE emp
ENABLE PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX;See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for syntax and restrictions on the use of the ALTER INDEX statement
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.4.3 Rebuilding an Existing Index
When you rebuild an index, you use an existing index as the data source. Creating an index in this manner enables you to change storage characteristics or move to a new tablespace. Rebuilding an index based on an existing data source removes intra-block fragmentation.
Compared to dropping the index and using the CREATE INDEX statement, rebuilding an existing index offers better performance. Before rebuilding an existing index, compare the costs and benefits associated with rebuilding to those associated with coalescing indexes as described in "Consider Costs and Benefits of Coalescing or Rebuilding Indexes".
The following statement rebuilds the existing index emp_name:
ALTER INDEX emp_name REBUILD;
The REBUILD clause must immediately follow the index name, and precede any other options. It cannot be used with the DEALLOCATE UNUSED clause.
You have the option of rebuilding the index online. Rebuilding online enables you to update base tables at the same time that you are rebuilding. The following statement rebuilds the emp_name index online:
ALTER INDEX emp_name REBUILD ONLINE;
To rebuild an index in a different user's schema online, the ALTER ANY INDEX system privileges is required.
Note:
Online index rebuilding has stricter limitations on the maximum key length that can be handled, compared to other methods of rebuilding an index. If an ORA-1450 (maximum key length exceeded) error occurs when rebuilding online, try rebuilding offline, coalescing, or dropping and recreating the index.
If you do not have the space required to rebuild an index, you can choose instead to coalesce the index. Coalescing an index is an online operation.
See Also:
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.4.4 Making an Index Unusable
When you make an index unusable, it is ignored by the optimizer and is not maintained by DML. When you make one partition of a partitioned index unusable, the other partitions of the index remain valid.
You must rebuild or drop and re-create an unusable index or index partition before using it.
The following procedure illustrates how to make an index and index partition unusable, and how to query the object status.
To make an index unusable:
-
Query the data dictionary to determine whether an existing index or index partition is usable or unusable.
For example, issue the following query (output truncated to save space):
hr@PROD> SELECT INDEX_NAME AS "INDEX OR PART NAME", STATUS, SEGMENT_CREATED 2 FROM USER_INDEXES 3 UNION ALL 4 SELECT PARTITION_NAME AS "INDEX OR PART NAME", STATUS, SEGMENT_CREATED 5 FROM USER_IND_PARTITIONS; INDEX OR PART NAME STATUS SEG ------------------------------ -------- --- I_EMP_ENAME N/A N/A JHIST_EMP_ID_ST_DATE_PK VALID YES JHIST_JOB_IX VALID YES JHIST_EMPLOYEE_IX VALID YES JHIST_DEPARTMENT_IX VALID YES EMP_EMAIL_UK VALID NO . . . COUNTRY_C_ID_PK VALID YES REG_ID_PK VALID YES P2_I_EMP_ENAME USABLE YES P1_I_EMP_ENAME UNUSABLE NO 22 rows selected.
The preceding output shows that only index partition
p1_i_emp_enameis unusable. -
Make an index or index partition unusable by specifying the
UNUSABLEkeyword.The following example makes index
emp_email_ukunusable:hr@PROD> ALTER INDEX emp_email_uk UNUSABLE; Index altered.
The following example makes index partition
p2_i_emp_enameunusable:hr@PROD> ALTER INDEX i_emp_ename MODIFY PARTITION p2_i_emp_ename UNUSABLE; Index altered.
-
(Optional) Query the data dictionary to verify the status change.
For example, issue the following query (output truncated to save space):
hr@PROD> SELECT INDEX_NAME AS "INDEX OR PARTITION NAME", STATUS, 2 SEGMENT_CREATED 3 FROM USER_INDEXES 4 UNION ALL 5 SELECT PARTITION_NAME AS "INDEX OR PARTITION NAME", STATUS, 6 SEGMENT_CREATED 7 FROM USER_IND_PARTITIONS; INDEX OR PARTITION NAME STATUS SEG ------------------------------ -------- --- I_EMP_ENAME N/A N/A JHIST_EMP_ID_ST_DATE_PK VALID YES JHIST_JOB_IX VALID YES JHIST_EMPLOYEE_IX VALID YES JHIST_DEPARTMENT_IX VALID YES EMP_EMAIL_UK UNUSABLE NO . . . COUNTRY_C_ID_PK VALID YES REG_ID_PK VALID YES P2_I_EMP_ENAME UNUSABLE NO P1_I_EMP_ENAME UNUSABLE NO 22 rows selected.
A query of space consumed by the
i_emp_enameandemp_email_uksegments shows that the segments no longer exist:hr@PROD> SELECT SEGMENT_NAME, BYTES 2 FROM USER_SEGMENTS 3 WHERE SEGMENT_NAME IN ('I_EMP_ENAME', 'EMP_EMAIL_UK'); no rows selected
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the
UNUSABLEkeyword, including restrictions
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.4.5 Making an Index Invisible or Visible
Making an index invisible is an alternative to making it unusable or dropping it.
An invisible index is ignored by the optimizer unless you explicitly set the OPTIMIZER_USE_INVISIBLE_INDEXES initialization parameter to TRUE at the session or system level. You cannot make an individual index partition invisible. Attempting to do so produces an error.
To make an index invisible:
-
Submit the following SQL statement:
ALTER INDEX index INVISIBLE;
To make an invisible index visible again:
-
Submit the following SQL statement:
ALTER INDEX index VISIBLE;
Note:
If there are multiple indexes on the same set of columns, then only one of these indexes can be visible at any point in time. If you try to make an index on a set of columns visible, and another index on the same set of columns is visible, then an error is returned.
To determine whether an index is visible or invisible:
-
Query the dictionary views
USER_INDEXES,ALL_INDEXES, orDBA_INDEXES.For example, to determine if the index
ind1is invisible, issue the following query:SELECT INDEX_NAME, VISIBILITY FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE INDEX_NAME = 'IND1'; INDEX_NAME VISIBILITY ---------- ---------- IND1 VISIBLE
21.4.6 Renaming an Index
You can rename an index using an ALTER INDEX statement with the RENAME clause.
To rename an index, issue this statement:
ALTER INDEX index_name RENAME TO new_name;
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.4.7 Monitoring Index Usage
Oracle Database provides a means of monitoring indexes to determine whether they are being used. If an index is not being used, then it can be dropped, eliminating unnecessary statement overhead.
To start monitoring the usage of an index, issue this statement:
ALTER INDEX index MONITORING USAGE;
Later, issue the following statement to stop the monitoring:
ALTER INDEX index NOMONITORING USAGE;
The view USER_OBJECT_USAGE can be queried for the index being monitored to see if the index has been used. The view contains a USED column whose value is YES or NO, depending upon if the index has been used within the time period being monitored. The view also contains the start and stop times of the monitoring period, and a MONITORING column (YES/NO) to indicate if usage monitoring is currently active.
Each time that you specify MONITORING USAGE, the USER_OBJECT_USAGE view is reset for the specified index. The previous usage information is cleared or reset, and a new start time is recorded. When you specify NOMONITORING USAGE, no further monitoring is performed, and the end time is recorded for the monitoring period. Until the next ALTER INDEX...MONITORING USAGE statement is issued, the view information is left unchanged.
Parent topic: Altering Indexes
21.5 Monitoring Space Use of Indexes
If key values in an index are inserted, updated, and deleted frequently, then the index can lose its acquired space efficiency over time.
Monitor index efficiency of space usage at regular intervals by first analyzing the index structure, using the ANALYZE INDEX...VALIDATE STRUCTURE statement, and then querying the INDEX_STATS view:
SELECT PCT_USED FROM INDEX_STATS WHERE NAME = 'index';
The percentage of index space usage varies according to how often index keys are inserted, updated, or deleted. Develop a history of average efficiency of space usage for an index by performing the following sequence of operations several times:
-
Analyzing statistics
-
Validating the index
-
Checking
PCT_USED -
Dropping and rebuilding (or coalescing) the index
When you find that index space usage drops below its average, you can condense the index space by dropping the index and rebuilding it, or coalescing it.
See Also:
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.6 Dropping Indexes
You can drop an index with the DROP INDEX statement.
To drop an index, the index must be contained in your schema, or you must have the DROP ANY INDEX system privilege.
Some reasons for dropping an index include:
-
The index is no longer required.
-
The index is not providing anticipated performance improvements for queries issued against the associated table. For example, the table might be very small, or there might be many rows in the table but very few index entries.
-
Applications do not use the index to query the data.
-
The index has become invalid and must be dropped before being rebuilt.
-
The index has become too fragmented and must be dropped before being rebuilt.
When you drop an index, all extents of the index segment are returned to the containing tablespace and become available for other objects in the tablespace.
How you drop an index depends on whether you created the index explicitly with a CREATE INDEX statement, or implicitly by defining a key constraint on a table. If you created the index explicitly with the CREATE INDEX statement, then you can drop the index with the DROP INDEX statement. The following statement drops the emp_ename index:
DROP INDEX emp_ename;
You cannot drop only the index associated with an enabled UNIQUE key or PRIMARY KEY constraint. To drop a constraints associated index, you must disable or drop the constraint itself.
Note:
If a table is dropped, all associated indexes are dropped automatically.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for syntax and restrictions on the use of the
DROP INDEXstatement -
"Making an Index Invisible or Visible" for an alternative to dropping indexes
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.7 Managing Auto Indexes
You can use the automatic indexing feature to configure and use auto indexes in an Oracle database to improve database performance.
- About Automatic Indexing
The automatic indexing feature automates the index management tasks in an Oracle database. Automatic indexing automatically creates, rebuilds, and drops indexes in a database based on the changes in application workload, thus improving database performance. The automatically managed indexes are known as auto indexes. - How Automatic Indexing Works
This section describes how automatic indexing works. - Configuring Automatic Indexing in an Oracle Database
You can configure automatic indexing in an Oracle database using theDBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGUREprocedure. - Generating Automatic Indexing Reports
You can generate reports related to automatic indexing operations in an Oracle database using theREPORT_ACTIVITYandREPORT_LAST_ACTIVITYfunctions of theDBMS_AUTO_INDEXpackage. - Views Containing the Automatic Indexing Information
You can query a set of data dictionary views for getting information about the auto indexes in an Oracle database.
Parent topic: Managing Indexes
21.7.1 About Automatic Indexing
The automatic indexing feature automates the index management tasks in an Oracle database. Automatic indexing automatically creates, rebuilds, and drops indexes in a database based on the changes in application workload, thus improving database performance. The automatically managed indexes are known as auto indexes.
Index structures are an essential feature to database performance. Indexes are critical for OLTP applications, which use large data sets and run millions of SQL statements a day. Indexes are also critical for data warehousing applications, which typically query a relatively small amount of data from very large tables. If you do not update the indexes whenever there are changes in the application workload, the existing indexes can cause the database performance to deteriorate considerably.
Automatic indexing improves database performance by managing indexes automatically and dynamically in an Oracle database based on changes in the application workload.
Automatic indexing provides the following functionality:
-
Runs the automatic indexing process in the background periodically at a predefined time interval.
-
Analyzes application workload, and accordingly creates new indexes and drops the existing underperforming indexes to improve database performance.
-
Rebuilds the indexes that are marked unusable due to table partitioning maintenance operations, such as
ALTER TABLE MOVE. -
Provides PL/SQL APIs for configuring automatic indexing in a database and generating reports related to automatic indexing operations.
Note:
-
Auto indexes are local B-tree indexes.
-
Auto indexes can be created for partitioned as well as non-partitioned tables.
-
Auto indexes cannot be created for temporary tables.
Parent topic: Managing Auto Indexes
21.7.2 How Automatic Indexing Works
This section describes how automatic indexing works.
The automatic indexing process runs in the background every 15 minutes and performs the following operations:
-
Identifies auto index candidates
Auto index candidates are identified based on the usage of table columns in SQL statements.
-
Creates invisible auto indexes for the auto index candidates
The auto index candidates are created as invisible auto indexes, that is, these auto indexes cannot be used in SQL statements.
-
Verifies invisible auto indexes against SQL statements
The invisible auto indexes are validated against SQL statements.
If the performance of SQL statements is improved by using these indexes, then the indexes are configured as visible indexes, so that they can be used in SQL statements.
If the performance of SQL statements is not improved by using these indexes, then the indexes are configured as unusable indexes and the SQL statements are blacklisted. The unusable indexes are later deleted by the automatic indexing process. The blacklisted SQL statements are not allowed to use auto indexes in future.
Note:
Auto indexes cannot be used by SQL statements that are running for the first time in a database.
-
Deletes the unused auto indexes
The auto indexes that are not used for a long period are deleted.
Note:
By default, the unused auto indexes are deleted after 373 days. The period for retaining the unused auto indexes in a database can be configured using the
DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGUREprocedure.
Parent topic: Managing Auto Indexes
21.7.3 Configuring Automatic Indexing in an Oracle Database
You can configure automatic indexing in an Oracle database using the DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE procedure.
The following examples describe some of the configuration settings that can be specified using the DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE procedure:
Enabling and disabling automatic indexing in a database
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_MODE configuration setting to enable or disable automatic indexing in a database.
The following statement enables automatic indexing in a database and creates any new auto indexes as visible indexes, so that they can be used in SQL statements:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_MODE','IMPLEMENT');The following statement enables automatic indexing in a database, but creates any new auto indexes as invisible indexes, so that they cannot be used in SQL statements:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_MODE','REPORT ONLY');The following statement disables automatic indexing in a database, so that no new auto indexes are created, and the existing auto indexes are disabled:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_MODE','OFF');Specifying schemas that can use auto indexes
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_SCHEMA configuration setting to specify schemas that can use auto indexes.
Note:
When automatic indexing is enabled in a database, all the schemas in the database can use auto indexes by default.The following statements add the SH and HR schemas to the exclusion list, so that the SH and HR schemas cannot use auto indexes.:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_SCHEMA', 'SH', FALSE);
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_SCHEMA', 'HR', FALSE);The following statement removes the HR schema from the exclusion list, so that the HR schema can use auto indexes:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_SCHEMA', 'HR', NULL);The following statement removes all the schema from the exclusion list, so that all the schemas in the database can use auto indexes:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_SCHEMA', NULL, TRUE);Specifying a retention period for unused auto indexes
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_AUTO configuration setting to specify a period for retaining unused auto indexes in a database. The unused auto indexes are deleted after the specified retention period.
Note:
By default, the unused auto indexes are deleted after 373 days.The following statement sets the retention period for unused auto indexes to 90 days.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_AUTO', '90');The following statement resets the retention period for auto indexes to the default value of 373 days.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_AUTO', NULL);Specifying a retention period for unused non-auto indexes
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_MANUAL configuration setting to specify a period for retaining unused non-auto indexes (manually created indexes) in a database. The unused non-auto indexes are deleted after the specified retention period.
Note:
By default, the unused non-auto indexes are never deleted by the automatic indexing process.The following statement sets the retention period for unused non-auto indexes to 60 days.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_MANUAL', '60');The following statement sets the retention period for unused non-auto indexes to NULL so that they are never deleted by the automatic indexing process.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_RETENTION_FOR_AUTO', NULL);Specifying a retention period for automatic indexing logs
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_REPORT_RETENTION configuration setting to specify a period for retaining automatic indexing logs in a database. The automatic indexing logs are deleted after the specified retention period.
Note:
By default, the automatic indexing logs are deleted after 31 days.The following statement sets the retention period for automatic indexing logs to 60 days.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_REPORT_RETENTION', '60');The following statement resets the retention period for automatic indexing logs to the default value 31 days.
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_REPORT_RETENTION', NULL);Note:
Automatic indexing reports are generated based on the automatic indexing logs. Therefore, automatic indexing reports cannot be generated for a period that is more than the retention period of the automatic indexing logs specified using theAUTO_INDEX_REPORT_RETENTION configuration setting.
Specifying a tablespace to store auto indexes
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_DEFAULT_TABLESPACE configuration setting to specify a tablespace to store auto indexes.
Note:
By default, the permanent tablespace specified during the database creation is used for storing auto indexes.The following statement specifies the tablespace of TBS_AUTO to store auto indexes:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_DEFAULT_TABLESPACE', 'TBS_AUTO');Specifying percentage of tablespace to allocate for auto indexes
You can use the AUTO_INDEX_SPACE_BUDGET configuration setting to specify percentage of tablespace to allocate for auto indexes. You can specify this configuration setting only when the tablespace used for storing auto indexes is the default permanent tablespace specified during the database creation, that is, when no value is specified for the AUTO_INDEX_DEFAULT_TABLESPACE configuration setting.
The following statement allocates 5 percent of the tablespace for auto indexes:
EXEC DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE('AUTO_INDEX_SPACE_BUDGET', '5');See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for a complete list of configuration settings related to automatic indexing that can be specified using the DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.CONFIGURE procedure
Parent topic: Managing Auto Indexes
21.7.4 Generating Automatic Indexing Reports
You can generate reports related to automatic indexing operations in an Oracle database using the REPORT_ACTIVITY and REPORT_LAST_ACTIVITY functions of the DBMS_AUTO_INDEX package.
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for the syntax of the REPORT_ACTIVITY and REPORT_LAST_ACTIVITY functions of the DBMS_AUTO_INDEX package.
Generating a report of automatic indexing operations for a specific period
The following example generates a report containing typical information about the automatic indexing operations for the last 24 hours. The report is generated in the plain text format by default.
declare
report clob := null;
begin
report := DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.REPORT_ACTIVITY();
end;The following example generates a report containing basic information about the automatic indexing operations for the month of November 2018. The report is generated in the HTML format and includes only the summary of automatic indexing operations.
declare
report clob := null;
begin
report := DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.REPORT_ACTIVITY(
activity_start => TO_TIMESTAMP('2018-11-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD'),
activity_end => TO_TIMESTAMP('2018-12-01', 'YYYY-MM-DD'),
type => 'HTML',
section => 'SUMMARY',
level => 'BASIC');
end;Generating a report of the last automatic indexing operation
The following example generates a report containing typical information about the last automatic indexing operation. The report is generated in the plain text format by default.
declare
report clob := null;
begin
report := DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.REPORT_LAST_ACTIVITY();
end;The following example generates a report containing basic information about the last automatic indexing operation. The report includes the summary, index details, and error information of the last automatic indexing operation. The report is generated in the HTML format.
declare
report clob := null;
begin
report := DBMS_AUTO_INDEX.REPORT_LAST_ACTIVITY(
type => 'HTML',
section => 'SUMMARY +INDEX_DETAILS +ERRORS',
level => 'BASIC');
end;Parent topic: Managing Auto Indexes
21.7.5 Views Containing the Automatic Indexing Information
You can query a set of data dictionary views for getting information about the auto indexes in an Oracle database.
The following views show information about the automatic indexing configuration settings and the auto indexes created in an Oracle database:
| View | Description |
|---|---|
|
Shows the current configuration settings for automatic indexing. |
|
The |
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for complete descriptions of these views
Parent topic: Managing Auto Indexes
21.8 Indexes Data Dictionary Views
You can query a set of data dictionary views for information about indexes.
The following views show information about indexes:
| View | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
These views show information about the columns of indexes on tables. Some columns in these views contain statistics that are generated by the |
|
These views show the following information about each index partition: the partitioning details, the storage parameters for the partition, and various partition statistics generated by the |
|
These views show information about the expressions of function-based indexes on tables. |
|
These views show information about the optimizer statistics for indexes. |
|
These views show the information about the last |
|
This view shows the index usage information produced by the |
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for the complete descriptions of these views
Parent topic: Managing Indexes