See also
Android is designed to run efficiently on a wide array of devices, with very different hardware configurations. Some devices, like the T-Mobile G1, can change their hardware configuration at runtime. For instance, when you open the keyboard, the screen change from the portrait orientation to the landscape orientation.
Using the alternate resources framework
The platform's support for loading orientation-specific resources at run time is based on the alternate resources framework.
Providing orientation-specific resources is an important part of developing your app. If you are not familiar with resource directory qualifiers or how the platform uses them, please read Alternate Resources.
To make Android app development easier, the Android system automatically handles configuration change events and restarts the current activity with the new configuration. This is the default behavior that lets you declare resources like layouts and drawables based on the orientation, screen size, locale, etc.
While this behavior is really powerful, since your application adapts automatically to the device's configuration at runtime, it is sometimes confusing for new Android developers, who wonder why their activity is destroyed and recreated.
Facing this "issue," some developers choose to handle configuration changes themselves which is, in general, a short-term solution that will only complicate their lives later. On the other hand, the system's automatic resource handling is a very efficient and easy way to adapt an application's user interface to various devices and devices configurations. It sometimes comes at a price, though.
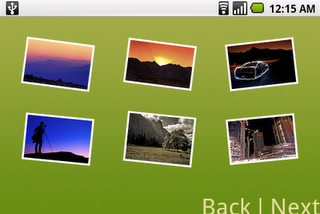
When your application displays a lot of data, or data that is expensive to fetch, the automatic destruction/creation of the activities can be lead to a painful user experience. Take the example of Photostream, a simple Flickr browsing application. After you launch the application and choose a Flickr account, the application downloads a set of 6 photos (on a T-Mobile G1) from the Flickr servers and displays them on screen. To improve the user experience, the application uses slightly different layouts and drawables in portrait and landscape modes and this is what the result looks like:
Photostream lets Android take care of the configuration change when the screen is rotated. However, can you imagine how painful it would be for the user to see all the images being downloaded again? The obvious solution to this problem is to temporarily cache the images. They could be cached on the SD card (if there's one), in the Application object, in a static field, etc. None of these techniques is adapted to the current situation: why should we bother caching the images when the screen is not rotated? Fortunately for us, Android offers a great API exactly for that purpose.
The Activity class has a special method called
onRetainNonConfigurationInstance(). This method
can be used to pass an arbitrary object to your future self and Android
is smart enough to call this method only when needed. In the case of Photostream,
the application used this method
to pass the downloaded images to the future activity on orientation change.
The implementation can be summarized like so:
@Override
public Object onRetainNonConfigurationInstance() {
final LoadedPhoto[] list = new LoadedPhoto[numberOfPhotos];
keepPhotos(list);
return list;
}
In the new activity, in onCreate(), all you have to do to
get your object back is to call getLastNonConfigurationInstance().
In Photostream, this method is invoked
and if the returned value is not null, the grid is loaded with the list of
photos from the previous activity:
private void loadPhotos() {
final Object data = getLastNonConfigurationInstance();
// The activity is starting for the first time, load the photos from Flickr
if (data == null) {
mTask = new GetPhotoListTask().execute(mCurrentPage);
} else {
// The activity was destroyed/created automatically, populate the grid
// of photos with the images loaded by the previous activity
final LoadedPhoto[] photos = (LoadedPhoto[]) data;
for (LoadedPhoto photo : photos) {
addPhoto(photo);
}
}
}
Be very careful with the object you pass through
onRetainNonConfigurationChange(), though. If the object you
pass is for some reason tied to the Activity/Context, you will leak
all the views and resources of the activity. This means you should
never pass a View, a Drawable, an Adapter, etc. Photostream for
instance extracts the bitmaps from the drawables and pass the bitmaps
only, not the drawables. Finally, remember that
onRetainNonConfigurationChange() should be used only to retain
data that is expensive to load. Otherwise, keep it simple and let Android
do everything.
Also read the guide to Handling Runtime Changes.