
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
from matplotlib.patches import FancyBboxPatch
# Bbox object around which the fancy box will be drawn.
bb = mtransforms.Bbox([[0.3, 0.4], [0.7, 0.6]])
def draw_bbox(ax, bb):
# boxstyle=square with pad=0, i.e. bbox itself.
p_bbox = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="square,pad=0.",
ec="k", fc="none", zorder=10.,
)
ax.add_patch(p_bbox)
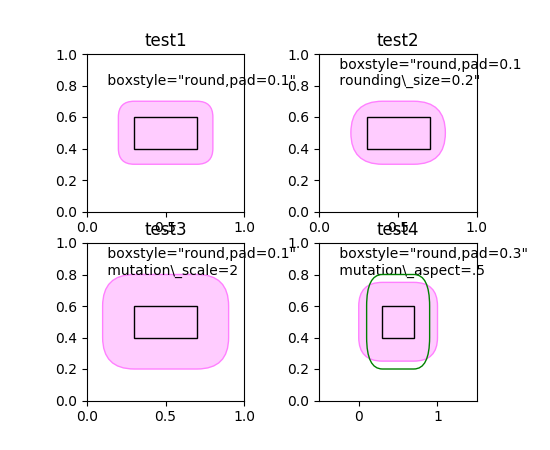
def test1(ax):
# a fancy box with round corners. pad=0.1
p_fancy = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="round,pad=0.1",
fc=(1., .8, 1.),
ec=(1., 0.5, 1.))
ax.add_patch(p_fancy)
ax.text(0.1, 0.8,
r' boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"',
size=10, transform=ax.transAxes)
# draws control points for the fancy box.
#l = p_fancy.get_path().vertices
#ax.plot(l[:,0], l[:,1], ".")
# draw the original bbox in black
draw_bbox(ax, bb)
def test2(ax):
# bbox=round has two optional argument. pad and rounding_size.
# They can be set during the initialization.
p_fancy = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="round,pad=0.1",
fc=(1., .8, 1.),
ec=(1., 0.5, 1.))
ax.add_patch(p_fancy)
# boxstyle and its argument can be later modified with
# set_boxstyle method. Note that the old attributes are simply
# forgotten even if the boxstyle name is same.
p_fancy.set_boxstyle("round,pad=0.1, rounding_size=0.2")
# or
#p_fancy.set_boxstyle("round", pad=0.1, rounding_size=0.2)
ax.text(0.1, 0.8,
' boxstyle="round,pad=0.1\n rounding\\_size=0.2"',
size=10, transform=ax.transAxes)
# draws control points for the fancy box.
#l = p_fancy.get_path().vertices
#ax.plot(l[:,0], l[:,1], ".")
draw_bbox(ax, bb)
def test3(ax):
# mutation_scale determine overall scale of the mutation,
# i.e. both pad and rounding_size is scaled according to this
# value.
p_fancy = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="round,pad=0.1",
mutation_scale=2.,
fc=(1., .8, 1.),
ec=(1., 0.5, 1.))
ax.add_patch(p_fancy)
ax.text(0.1, 0.8,
' boxstyle="round,pad=0.1"\n mutation\\_scale=2',
size=10, transform=ax.transAxes)
# draws control points for the fancy box.
#l = p_fancy.get_path().vertices
#ax.plot(l[:,0], l[:,1], ".")
draw_bbox(ax, bb)
def test4(ax):
# When the aspect ratio of the axes is not 1, the fancy box may
# not be what you expected (green)
p_fancy = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="round,pad=0.2",
fc="none",
ec=(0., .5, 0.), zorder=4)
ax.add_patch(p_fancy)
# You can compensate this by setting the mutation_aspect (pink).
p_fancy = FancyBboxPatch((bb.xmin, bb.ymin),
abs(bb.width), abs(bb.height),
boxstyle="round,pad=0.3",
mutation_aspect=.5,
fc=(1., 0.8, 1.),
ec=(1., 0.5, 1.))
ax.add_patch(p_fancy)
ax.text(0.1, 0.8,
' boxstyle="round,pad=0.3"\n mutation\\_aspect=.5',
size=10, transform=ax.transAxes)
draw_bbox(ax, bb)
def test_all():
plt.clf()
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
test1(ax)
ax.set_xlim(0., 1.)
ax.set_ylim(0., 1.)
ax.set_title("test1")
ax.set_aspect(1.)
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax.set_title("test2")
test2(ax)
ax.set_xlim(0., 1.)
ax.set_ylim(0., 1.)
ax.set_aspect(1.)
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.set_title("test3")
test3(ax)
ax.set_xlim(0., 1.)
ax.set_ylim(0., 1.)
ax.set_aspect(1)
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.set_title("test4")
test4(ax)
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, 1.5)
ax.set_ylim(0., 1.)
ax.set_aspect(2.)
plt.draw()
plt.show()
test_all()
Keywords: python, matplotlib, pylab, example, codex (see Search examples)