10 Sharded Database Administration
Oracle Sharding provides tools and some automation for the administration of a sharded database.
The following topics describe sharded database administration in detail:
- Managing the Sharding-Enabled Stack
- Managing Oracle Sharding Database Users
- Monitoring a Sharded Database
Sharded databases can be monitored using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control or GDSCTL. - Backing Up and Recovering a Sharded Database
Because shards are hosted on individual Oracle databases, you can use Oracle Maximum Availability best practices to back up and restore shards individually. - Modifying a Sharded Database Schema
When making changes to duplicated tables or sharded tables in a sharded database, these changes should be done from the shard catalog database. - Propagation of Parameter Settings Across Shards
When you configure system parameter settings at the shard catalog, they are automatically propagated to all shards of the sharded database. - Managing Sharded Database Software Versions
- Shard Management
You can manage shards in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and GDSCTL. - Chunk Management
You can manage chunks in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and GDSCTL. - Shard Director Management
You can add, edit, and remove shard directors in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Region Management
You can add, edit, and remove regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Shardspace Management
You can add, edit, and remove shardspaces in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Shardgroup Management
You can add, edit, and remove shardgroups in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Services Management
You can manage services in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
10.1 Managing the Sharding-Enabled Stack
This section describes the startup and shutdown of components in the sharded database configuration. It contains the following topics:
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.1.1 Starting Up the Sharding-Enabled Stack
The following is the recommended startup sequence of the sharding-enabled stack:
-
Start the shard catalog database and local listener.
-
Start the shard directors (GSMs).
-
Start up the shard databases and local listeners.
-
Start the global services.
-
Start the connection pools and clients.
Parent topic: Managing the Sharding-Enabled Stack
10.1.2 Shutting Down the Sharding-Enabled Stack
The following is the recommended shutdown sequence of the sharding-enabled stack:
-
Shut down the connection pools and clients.
-
Stop the global services.
-
Shut down the shard databases and local listeners.
-
Stop the shard directors (GSMs).
-
Stop the shard catalog database and local listener.
Parent topic: Managing the Sharding-Enabled Stack
10.2 Managing Oracle Sharding Database Users
This section describes the database users specific to Oracle Sharding. It contains the following topics:
- About the GSMUSER Account
TheGSMUSERaccount is used by GDSCTL and global service managers to connect to databases in a GDS configuration. - About the GSMROOTUSER Account
GSMROOTUSERis a database account specific to Oracle Sharding that is only used when pluggable database (PDB) shards are present. The account is used by GDSCTL and global service managers to connect to the root container of container databases (CDBs) to perform administrative tasks.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.2.1 About the GSMUSER Account
The GSMUSER account is used by GDSCTL and global service managers to connect to databases in a GDS configuration.
GSMUSER exists by default on any Oracle database. In an Oracle Sharding configuration, the account is used to connect to shards instead of pool databases, and it must be granted both the SYSDG and SYSBACKUP system privileges after the account has been unlocked.
The password given to the GSMUSER account is used in the gdsctl add shard command. Failure to grant SYSDG and SYSBACKUP to GSMUSER on a new shard causes gdsctl add shard to fail with an ORA-1031: insufficient privileges error.
If you use the gdsctl create shard command to create a new shard with the Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA), the GSMUSER account is automatically granted the SYSDG and SYSBACKUP privileges and assigned a random password during the deployment process. Because the GSMUSER account never needs to be logged into interactively, the value of the password does not need to be known by administrators; however, the password can be changed after deployment if required by using the alter user SQL command on the shard, in combination with the gdsctl modify shard -pwd command.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Sharding Database Users
10.2.2 About the GSMROOTUSER Account
GSMROOTUSER is a database account specific to Oracle Sharding that is only used when pluggable database (PDB) shards are present. The account is used by GDSCTL and global service managers to connect to the root container of container databases (CDBs) to perform administrative tasks.
If PDB shards are not in use, the GSMROOTUSER user should not by unlocked nor assigned a password on any database. However, in sharded configurations containing PDB shards, GSMROOTUSER must be unlocked and granted the SYSDG and SYSBACKUP privileges before a successful gdsctl add cdb command can be executed. The password for the GSMROOTUSER account can be changed after deployment if desired using the alter user SQL command in the root container of the CDB in combination with the gdsctl modify cdb -pwd command.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Sharding Database Users
10.3 Monitoring a Sharded Database
Sharded databases can be monitored using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control or GDSCTL.
See the following topics to use Enterprise Manager Cloud Control or GDSCTL to monitor sharded databases.
- Monitoring a Sharded Database with GDSCTL
There are numerousGDSCTL CONFIGcommands that you can use to obtain the health status of individual shards, shardgroups, shardspaces, and shard directors. - Monitoring a Sharded Database with Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control lets you discover, monitor, and manage the components of a sharded database. - Querying System Objects Across Shards
Use the SHARDS() clause to query Oracle-supplied tables to gather performance, diagnostic, and audit data from V$ views and DBA_* views.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.3.1 Monitoring a Sharded Database with GDSCTL
There are numerous GDSCTL CONFIG commands that you can use to obtain the health status of individual shards, shardgroups, shardspaces, and shard directors.
Monitoring a shard is just like monitoring a normal database, and standard Oracle best practices should be used to monitor the individual health of a single shard. However, it is also important to monitor the overall health of the entire sharded environment. The GDSCTL commands can also be scripted and through the use of a scheduler and can be done at regular intervals to help ensure that everything is running smoothly. When using Oracle GoldenGate for replication it is also important to monitor the lag of each replication stream.
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about using the GDSCTL CONFIG commands
Parent topic: Monitoring a Sharded Database
10.3.2 Monitoring a Sharded Database with Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control lets you discover, monitor, and manage the components of a sharded database.
Sharded database targets are found in the All Targets page.
Figure 10-1 Sharded Databases in the All Targets Refine Search pane
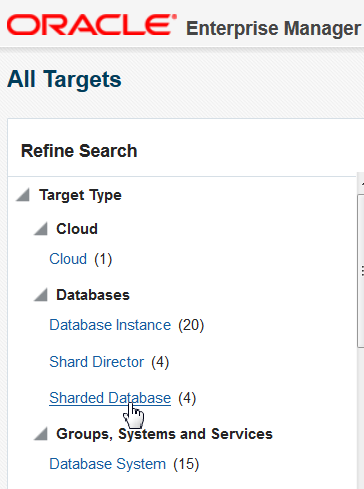
Description of "Figure 10-1 Sharded Databases in the All Targets Refine Search pane"
The target home page for a sharded database shows you a summary of the sharded database components and their statuses.
To monitor sharded database components you must first discover them. See Discovering Sharded Database Components for more information.
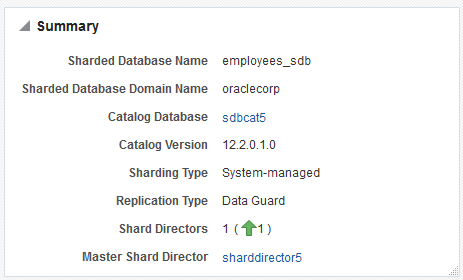
Summary
The Summary pane, in the top left of the page, shows the following information:
-
Sharded database name
-
Sharded database domain name
-
Shard catalog name. You can click the name to view more information about the shard catalog.
-
Shard catalog database version
-
Sharding method used to shard the database
-
Replication technology used for high availability
-
Number and status of the shard directors
-
Master shard director name. You can click the name to view more information about the master shard director.
Shard Load Map
The Shard Load Map, in the upper right of the page, shows a pictorial graph illustrating how transactions are distributed among the shards.
Figure 10-3 Sharded Database Shard Load Map
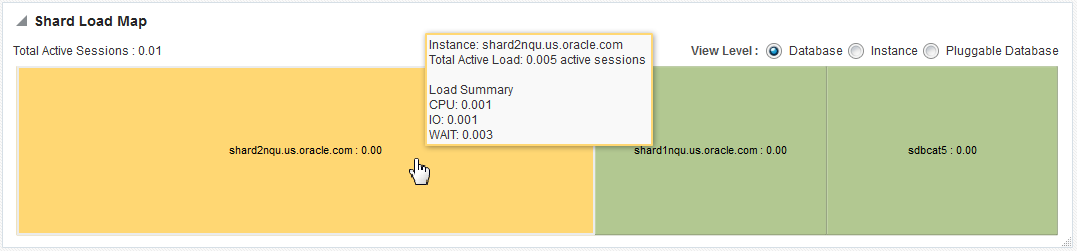
Description of "Figure 10-3 Sharded Database Shard Load Map"
You can select different View Levels above the graph.
-
Database
The database view aggregates database instances in Oracle RAC cluster databases into a single cell labeled with the Oracle RAC cluster database target name. This enables you to easily compare the total database load in Oracle RAC environments.
-
Instance
The instance view displays all database instances separately, but Oracle RAC instances are grouped together as sub-cells of the Oracle RAC database target. This view is essentially a two-level tree map, where the database level is the primary division, and the instance within the database is the secondary division. This allows load comparison of instances within Oracle RAC databases; for instance, to easily spot load imbalances across instances.
-
Pluggable Database
Although the PDB option is shown, PDB is not supported for Oracle Sharding in the current release.
Notice that the cells of the graph are not identical in size. Each cell corresponds to a shard target, either an instance or a cluster database. The cell size (its area) is proportional to the target database's load measured in average active sessions, so that targets with a higher load have larger cell sizes. Cells are ordered by size from left to right and top to bottom. Therefore, the target with the highest load always appears as the upper leftmost cell in the graph.
You can hover your mouse pointer over a particular cell of the graph to view the total active load (I/O to CPU ration), CPU, I/O, and wait times. Segments of the graph are colored to indicate the dominant load:
-
Green indicates that CPU time dominates the load
-
Blue indicates that I/O dominates the load
-
Yellow indicates that WAIT dominates the load
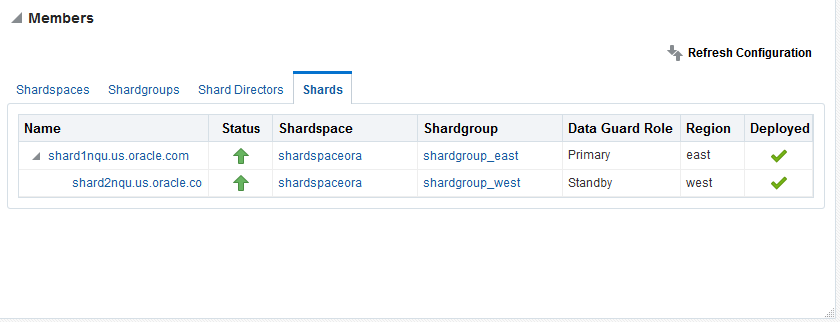
Members
The Members pane, in the lower left of the page, shows some relevant information about each of the components.
The pane is divided into tabs for each component: Shardspaces, Shardgroups, Shard Directors, and Shards. Click on a tab to view the information about each type of component
-
Shardspaces
The Shardspaces tab displays the shardspace names, status, number of chunks, and Data Guard protection mode. The shardspace names can be clicked to reveal more details about the selected shardspace.
-
Shardgroups
The Shardgroups tab displays the shardgroup names, status, the shardspace to which it belongs, the number of chunks, Data Guard role, and the region to which it belongs. You can click the shardgroup and shardspace names to reveal more details about the selected component.
-
Shard Directors
The Shard Directors tab displays the shard director names, status, region, host, and Oracle home. You can click the shard director names can be clicked to reveal more details about the selected shard director.
-
Shards
The Shards tab displays the shard names, deploy status, status, the shardspaces and shardgroups to which they belong, Data Guard roles, and the regions to which they belong. In the Names column, you can expand the Primary shards to display the information about its corresponding Standby shard. You can hover the mouse over the Deployed column icon and the deployment status details are displayed. You can click on the shard, shardspace, and shardgroup names to reveal more details about the selected component.
Services
The Services pane, in the lower right of the page, shows the names, status, and Data Guard role of the sharded database services. Above the list is shown the total number of services and an icon showing how many services are in a particular status. You can hover your mouse pointer over the icon to read a description of the status icon.
Figure 10-5 Sharded Database Services pane
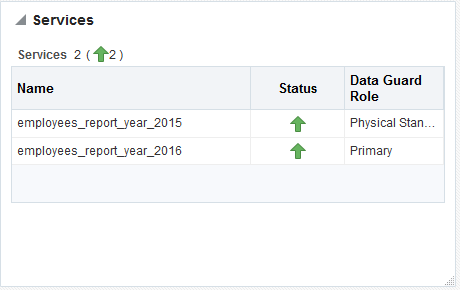
Description of "Figure 10-5 Sharded Database Services pane"
Incidents
The Incidents pane displays messages and warnings about the various components in the sharded database environment. More information about how to use this pane is in the Cloud Control online help.
Sharded Database Menu
The Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner, provides you with access to administrate the sharded database components.
Target Navigation
The Target Navigation pane gives you easy access to more details about any of the components in the sharded database.
Description of the illustration shard_em_navicon.png
Clicking the navigation tree icon on the upper left corner of the page opens the Target Navigation pane. This pane shows all of the discovered components in the sharded database in tree form.
Expanding a shardspace reveals the shardgroups in them. Expanding a shardgroup reveals the shards in that shardgroup.
Any of the component names can be clicked to view more details about them.
- Discovering Sharded Database Components
In Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, you can discover the shard catalog and shard databases, then add the shard directors, sharded databases, shardspaces, and shardgroups using guided discovery.
Parent topic: Monitoring a Sharded Database
10.3.2.1 Discovering Sharded Database Components
In Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, you can discover the shard catalog and shard databases, then add the shard directors, sharded databases, shardspaces, and shardgroups using guided discovery.
As a prerequisite, you must use Cloud Control to discover the shard director hosts and the.shard catalog database. Because the catalog database and each of the shards is a database itself, you can use standard database discovery procedures.
Monitoring the shards is only possible when the individual shards are discovered using database discovery. Discovering the shards is optional to discovering a sharded database, because you can have a sharded database configuration without the shards.
When the target discovery procedure is finished, sharded database targets are added in Cloud Control. You can open the sharded database in Cloud Control to monitor and manage the components.
10.3.3 Querying System Objects Across Shards
Use the SHARDS() clause to query Oracle-supplied tables to gather performance, diagnostic, and audit data from V$ views and DBA_* views.
The shard catalog database can be used as the entry point for centralized diagnostic operations using the SQL SHARDS() clause. The SHARDS() clause allows you to query the same Oracle supplied objects, such as V$, DBA/USER/ALL views and dictionary objects and tables, on all of the shards and return the aggregated results.
As shown in the examples below, an object in the FROM part of the SELECT statement is wrapped in the SHARDS() clause to specify that this is not a query to local object, but to objects on all shards in the sharded database configuration. A virtual column called SHARD_ID is automatically added to a SHARDS()-wrapped object during execution of a multi-shard query to indicate the source of every row in the result. The same column can be used in predicate for pruning the query.
A query with the SHARDS() clause can only be run on the shard catalog database.
Examples
The following statement queries performance views
SQL> SELECT shard_id, callspersec FROM SHARDS(v$servicemetric)
WHERE service_name LIKE 'oltp%' AND group_id = 10;The following statement gathers statistics.
SQL> SELECT table_name, partition_name, blocks, num_rows
FROM SHARDS(dba_tab_partition) p
WHERE p.table_owner= :1;The following example statement shows how to find the SHARD_ID value for each shard.
SQL> select ORA_SHARD_ID, INSTANCE_NAME from SHARDS(sys.v_$instance);
ORA_SHARD_ID INSTANCE_NAME
------------ ----------------
1 sh1
11 sh2
21 sh3
31 sh4The following example statement shows how to use the SHARD_ID to prune a query.
SQL> select ORA_SHARD_ID, INSTANCE_NAME
from SHARDS(sys.v_$instance)
where ORA_SHARD_ID=21;
ORA_SHARD_ID INSTANCE_NAME
------------ ----------------
21 sh3
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the SHARDS() clause.
Parent topic: Monitoring a Sharded Database
10.4 Backing Up and Recovering a Sharded Database
Because shards are hosted on individual Oracle databases, you can use Oracle Maximum Availability best practices to back up and restore shards individually.
If you are using Data Guard and Oracle Active Data Guard for SDB high availability, be sure to take observers offline and disable Fast Start Failover before taking a primary or standby database offline.
Contact Oracle Support for specific steps to recover a shard in the event of a disaster.
See Also:
Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture for MAA best practices white papers
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.5 Modifying a Sharded Database Schema
When making changes to duplicated tables or sharded tables in a sharded database, these changes should be done from the shard catalog database.
Before executing any DDL operations on a sharded database, enable sharded DDL with
ALTER SESSION ENABLE SHARD DDL; This statement ensures that the DDL changes will be propagated to each shard in the sharded database.
The DDL changes that are propagated are commands that are defined as “schema related,” which include operations such as ALTER TABLE and CREATE TRIGGER. There are other operations that are propagated to each shard, such as the CREATE, ALTER, DROP user commands for simplified user management, and TABLESPACE operations to simplify the creation of tablespaces on multiple shards.
GRANT and REVOKE operations can be done from the shard catalog and are propagated to each shard, providing you have enabled shard DDL for the session. If more granular control is needed you can issue the command directly on each shard.
Operations such as DBMS package calls or similar operations are not propagated. For example, operations gathering statistics on the shard catalog are not propagated to each shard.
If you perform an operation that requires a lock on a table, such as adding a not null column, it is important to remember that each shard needs to obtain the lock on the table in order to perform the DDL operation. Oracle’s best practices for applying DDL in a single instance apply to sharded environments.
Multi-shard queries, which are executed on the shard catalog, issue remote queries across database connections on each shard. In this case it is important to ensure that the user has the appropriate privileges on each of the shards, whether or not the query will return data from that shard.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about operations used with duplicated tables and sharded tables
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.6 Propagation of Parameter Settings Across Shards
When you configure system parameter settings at the shard catalog, they are automatically propagated to all shards of the sharded database.
Before Oracle Database 19c, you had to configure ALTER SYSTEM parameter settings on each shard in a sharded database. In Oracle Database 19c, Oracle Sharding provides centralized management by allowing you to set parameters on the shard catalog. Then the settings are automatically propagated to all shards of the sharded database.
Propagation of system parameters happens only if done under ENABLE SHARD DDL on the shard catalog, then include SHARD=ALL in the ALTER statement.
SQL>alter session enable shard ddl;
SQL>alter system set enable_ddl_logging=true shard=all;Note:
Propagation of theenable_goldengate_replication parameter setting is not supported.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.7 Managing Sharded Database Software Versions
This section describes the version management of software components in the sharded database configuration. It contains the following topics:
- Patching and Upgrading a Sharded Database
Applying an Oracle patch to a sharded database environment can be done on a single shard or all shards; however, the method you use depends on the replication option used for the environment and the type of patch being applied. - Upgrading Sharded Database Components
The order in which sharded database components are upgraded is important for limiting downtime and avoiding errors as components are brought down and back online. - Downgrading a Sharded Database
Oracle Sharding does not support downgrading.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.7.1 Patching and Upgrading a Sharded Database
Applying an Oracle patch to a sharded database environment can be done on a single shard or all shards; however, the method you use depends on the replication option used for the environment and the type of patch being applied.
Patching a Sharded Database
Most patches can be applied to a single shard at a time; however, some patches should be applied across all shards. Use Oracle’s best practices for applying patches to single shards just as you would a non-sharded database, keeping in mind the replication method that is being used with the SDB. Oracle opatchauto can be used to apply patches to multiple shards at a time, and can be done in a rolling manner. Data Guard configurations are applied one after another, and in some cases (depending on the patch) you can use Standby First patching. When using Oracle GoldenGate be sure to apply patches in parallel across the entire shardspace. If a patch addresses an issue with multi-shard queries, replication, or the sharding infrastructure, it should be applied to all of the shards in the SDB.
Upgrading a Sharded Database
Upgrading the Oracle Sharding environment is not much different from upgrading other Oracle Database and global service manager environments; however, the components must be upgraded in a particular sequence such that the shard catalog is upgraded first, followed by the shard directors, and finally the shards.
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about upgrading the shard directors.
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about patching and upgrading in an Oracle Data Guard configuration.
Parent topic: Managing Sharded Database Software Versions
10.7.2 Upgrading Sharded Database Components
The order in which sharded database components are upgraded is important for limiting downtime and avoiding errors as components are brought down and back online.
Before upgrading any sharded database components you must
-
Complete any pending
MOVE CHUNKoperations that are in progress. -
Do not start any new
MOVE CHUNKoperations. -
Do not add any new shards during the upgrade process.
-
If you are upgrading an Oracle Database 18c sharded database configuration containing pluggable database (PDB) shards, follow the PDB-specific upgrade instructions in Using Oracle Multitenant with Oracle Sharding.
See Also:
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about using DBMS_ROLLING to perform a rolling upgrade.
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about patching and upgrading databases in an Oracle Data Guard configuration.
Parent topic: Managing Sharded Database Software Versions
10.7.3 Downgrading a Sharded Database
Oracle Sharding does not support downgrading.
Sharded database catalogs and shards cannot be downgraded.
Parent topic: Managing Sharded Database Software Versions
10.8 Shard Management
You can manage shards in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and GDSCTL.
The following topics describe shard management concepts and tasks:
- About Adding Shards
New shards can be added to an existing sharded database environment to scale out and to improve fault tolerance. - Resharding and Hot Spot Elimination
The process of redistributing data between shards, triggered by a change in the number of shards, is called resharding. Automatic resharding is a feature of the system-managed sharding method that provides elastic scalability of an SDB. - Removing a Shard From the Pool
It may become necessary to remove a shard from the sharded database environment, either temporarily or permanently, without losing any data that resides on that shard. - Adding Standby Shards
You can add Data Guard standby shards to an Oracle Sharding environment; however there are some limitations. - Managing Shards with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
You can manage database shards using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control - Managing Shards with GDSCTL
You can manage shards in your Oracle Sharding deployment using the GDSCTL command-line utility.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.8.1 About Adding Shards
New shards can be added to an existing sharded database environment to scale out and to improve fault tolerance.
For fault tolerance, it is beneficial to have many smaller shards than a few very large ones. As an application matures and the amount of data increases, you can add an entire shard or multiple shards to the SDB to increase capacity.
When you add a shard to a sharded database, if the environment is sharded by consistent hash, then chunks from existing shards are automatically moved to the new shard to rebalance the sharded environment.
When using user-defined sharding, populating a new shard with data may require manually moving chunks from existing shards to the new shard using the GDSCTL split chunk and move chunk commands.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control can be used to help identify chunks that would be good candidates to move, or split and move to the new shard.
When you add a shard to the environment, verify that the standby server is ready, and after the new shard is in place take backups of any shards that have been involved in a move chunk operation.
Parent topic: Shard Management
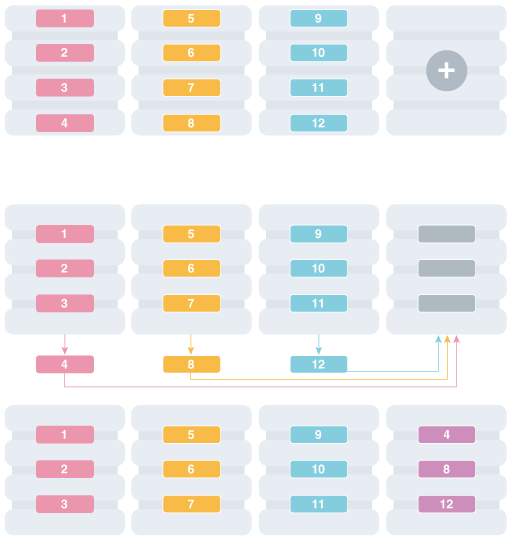
10.8.2 Resharding and Hot Spot Elimination
The process of redistributing data between shards, triggered by a change in the number of shards, is called resharding. Automatic resharding is a feature of the system-managed sharding method that provides elastic scalability of an SDB.
Sometimes data in an SDB needs to be migrated from one shard to another. Data migration across shards is required in the following cases:
-
When one or multiple shards are added to or removed from an SDB
-
When there is skew in the data or workload distribution across shards
The unit of data migration between shards is the chunk. Migrating data in chunks guaranties that related data from different sharded tables are moved together.
When a shard is added to or removed from an SDB, multiple chunks are migrated to maintain a balanced distribution of chunks and workload across shards.
Depending on the sharding method, resharding happens automatically (system-managed) or is directed by the user (composite). The following figure shows the stages of automatic resharding when a shard is added to an SDB with three shards.
A particular chunk can also be moved from one shard to another, when data or workload skew occurs, without any change in the number of shards. In this case, chunk migration can be initiated by the database administrator to eliminate the hot spot.
RMAN Incremental Backup, Transportable Tablespace, and Oracle Notification Service technologies are used to minimize impact of chunk migration on application availability. A chunk is kept online during chunk migration. There is a short period of time (a few seconds) when data stored in the chunk is available for read-only access only.
FAN-enabled clients receive a notification when a chunk is about to become read-only in the source shard, and again when the chunk is fully available in the destination shard on completion of chunk migration. When clients receive the chunk read-only event, they can either repeat connection attempts until the chunk migration is completed, or access the read-only chunk in the source chunk. In the latter case, an attempt to write to the chunk will result in a run-time error.
Note:
Running multi-shard queries while a sharded database is resharding can result in errors, so it is recommended that you do not deploy new shards during multi-shard workloads.
Parent topic: Shard Management
10.8.3 Removing a Shard From the Pool
It may become necessary to remove a shard from the sharded database environment, either temporarily or permanently, without losing any data that resides on that shard.
For example, removing a shard might become necessary if a sharded environment is scaled down after a busy holiday, or to replace a server or infrastructure within the data center. Prior to decommissioning the shard, you must move all of the chunks from the shard to other shards that will remain online. As you move them, try to maintain a balance of data and activity across all of the shards.
If the shard is only temporarily removed, keep track of the chunks moved to each shard so that they can be easily identified and moved back once the maintenance is complete.
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about using the GDSCTL REMOVE SHARD command
Parent topic: Shard Management
10.8.4 Adding Standby Shards
You can add Data Guard standby shards to an Oracle Sharding environment; however there are some limitations.
When using Data Guard as the replication method for a sharded database, Oracle Sharding supports only the addition of a primary or physical standby shard; other types of Data Guard standby databases are not supported when adding a new standby to the sharded database. However, a shard that is already part of the sharded database can be converted from a physical standby to a snapshot standby. When converting a physical standby to a snapshot standby, the following steps should be followed:
If the database is converted back to a physical standby, the global services can be enabled and started again, and the shard becomes an active member of the sharded database.
Parent topic: Shard Management
10.8.5 Managing Shards with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
You can manage database shards using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
To manage shards using Cloud Control, they must first be discovered. Because each database shard is a database itself, you can use standard Cloud Control database discovery procedures.
The following topics describe shard management using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control:
- Validating a Shard
Validate a shard prior to adding it to your Oracle Sharding deployment. - Adding Primary Shards
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to add a primary shards to your Oracle Sharding deployment. - Adding Standby Shards
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to add a standby shards to your Oracle Sharding deployment. - Deploying Shards
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to deploy shards that have been added to your Oracle Sharding environment.
Parent topic: Shard Management
10.8.5.1 Validating a Shard
Validate a shard prior to adding it to your Oracle Sharding deployment.
You can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to validate shards before adding them to your Oracle Sharding deployment. You can also validate a shard after deployment to confirm that the settings are still valid later in the shard lifecycle. For example, after a software upgrade you can validate existing shards to confirm correctness of their parameters and configuration.
To validate shards with Cloud Control, they should be existing targets that are being monitored by Cloud Control.
- From a shardgroup management page, open the Shardgroup menu, located in the top left corner of the shardgroup target page, and choose Manage Shards.
- If prompted, enter the shard catalog credentials, select the shard director to manage under Shard Director Credentials, select the shard director host credentials, and log in.
- Select a shard from the list and click Validate.
- Click OK to confirm you want to validate the shard.
- Click the link in the Information box at the top of the page to view the provisioning status of the shard.
When the shard validation script runs successfully check for errors reported in the output.
10.8.5.2 Adding Primary Shards
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to add a primary shards to your Oracle Sharding deployment.
Primary shards should be existing targets that are being monitored by Cloud Control.
It is highly recommended that you validate a shard before adding it to your Oracle Sharding environment. You can either use Cloud Control to validate the shard (see Validating a Shard), or run the DBMS_GSM_FIX.validateShard procedure against the shard using SQL*Plus (see Validating a Shard).
If you did not select Deploy All Shards in the sharded database in the procedure above, deploy the shard in your Oracle Sharding deployment using the Deploying Shards task.
10.8.5.3 Adding Standby Shards
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to add a standby shards to your Oracle Sharding deployment.
Standby shards should be existing targets that are being monitored by Cloud Control.
It is highly recommended that you validate a shard before adding it to your Oracle Sharding environment. You can either use Cloud Control to validate the shard (see Validating a Shard), or run the DBMS_GSM_FIX.validateShard procedure against the shard using SQL*Plus (see Validating a Shard).
If you did not select Deploy All Shards in the sharded database in the procedure above, deploy the shard in your Oracle Sharding deployment using the Deploying Shards task.
10.8.6 Managing Shards with GDSCTL
You can manage shards in your Oracle Sharding deployment using the GDSCTL command-line utility.
The following topics describe shard management using GDSCTL:
- Validating a Shard
Before adding a newly created shard to a sharding configuration, you must validate that the shard has been configured correctly for the sharding environment. - Adding Shards to a System-Managed SDB
Adding shards to a system-managed SDB elastically scales the SDB. In a system-managed SDB chunks are automatically rebalanced after the new shards are added. - Replacing a Shard
If a shard fails and is unrecoverable, or if you just want to move a shard to a new host for other reasons, you can replace it using the ADD SHARD -REPLACE command in GDSCTL.
Parent topic: Shard Management
10.8.6.1 Validating a Shard
Before adding a newly created shard to a sharding configuration, you must validate that the shard has been configured correctly for the sharding environment.
Before you run ADD SHARD, run the validateShard procedure against the database that will be added as a shard. The validateShard procedure verifies that the target database has the initialization parameters and characteristics needed to act successfully as a shard.
The validateShard procedure analyzes the target database and reports any issues that need to be addressed prior to running GDSCTL ADD SHARD on that database. The validateShard procedure does not make any changes to the database or its parameters; it only reports information and possible issues.
The validateShard procedure takes one optional parameter that specifies whether the shard will be added to a shard catalog using Data Guard or to a shard catalog using Oracle GoldenGate as its replication technology. If you are using Data Guard, call validateShard('DG'). If you are using Oracle GoldenGate, use validateShard('OGG'). The default value is Data Guard if no parameter is passed to validateShard.
The validateShard procedure can also be run after the deployment of a shard to confirm that the settings are still valid later in the shard lifecycle. For example, after a software upgrade or after shard deployment, validateShard can be run on existing shards to confirm correctness of their parameters and configuration.
Run validateShard as follows:
sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL> set serveroutput on
SQL> execute dbms_gsm_fix.validateShardThe following is an example of the output.
INFO: Data Guard shard validation requested.
INFO: Database role is PRIMARY.
INFO: Database name is DEN27B.
INFO: Database unique name is den27b.
INFO: Database ID is 718463507.
INFO: Database open mode is READ WRITE.
INFO: Database in archivelog mode.
INFO: Flashback is on.
INFO: Force logging is on.
INFO: Database platform is Linux x86 64-bit.
INFO: Database character set is WE8DEC. This value must match the character set of
the catalog database.
INFO: 'compatible' initialization parameter validated successfully.
INFO: Database is not a multitenant container database.
INFO: Database is using a server parameter file (spfile).
INFO: db_create_file_dest set to: '<ORACLE_BASE>/oracle/dbs2'
INFO: db_recovery_file_dest set to: '<ORACLE_BASE>/oracle/dbs2'
INFO: db_files=1000. Must be greater than the number of chunks and/or tablespaces
to be created in the shard.
INFO: dg_broker_start set to TRUE.
INFO: remote_login_passwordfile set to EXCLUSIVE.
INFO: db_file_name_convert set to: '/dbs/dt, /dbs/bt, dbs2/DEN27D/, dbs2/DEN27B/'
INFO: GSMUSER account validated successfully.
INFO: DATA_PUMP_DIR is '<ORACLE_BASE>//oracle/dbs2'.Any lines tagged with INFO are informational in nature and confirm correct settings. Lines tagged with WARNING may or may not be issues depending on your configuration. For example, issues related to Data Guard parameters are reported, but if your configuration will only include primary databases, then any Data Guard issues can be ignored. Finally, any output with the ERROR tag must be corrected for the shard to deploy and operate correctly in a sharding configuration.
Parent topic: Managing Shards with GDSCTL
10.8.6.2 Adding Shards to a System-Managed SDB
Adding shards to a system-managed SDB elastically scales the SDB. In a system-managed SDB chunks are automatically rebalanced after the new shards are added.
To prepare a new shard host, do all of the setup procedures as you did for the initial sharded database environment including:
-
Registering remote scheduler agents as described in Setting Up the Oracle Sharding Management and Routing Tier
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about GDSCTL command usage
Parent topic: Managing Shards with GDSCTL
10.8.6.3 Replacing a Shard
If a shard fails and is unrecoverable, or if you just want to move a shard to a new host for other reasons, you can replace it using the ADD SHARD -REPLACE command in GDSCTL.
When a shard database fails and the database can be recovered on the same host (using RMAN backup/restore or other methods), there is no need to replace the shard using the -replace parameter. If the shard cannot be recovered locally, or for some other reason you want to relocate the shard to another host or CDB, it is possible to create its replica on the new host. The sharding configuration can be updated with the new information by specifying the -replace option in GDSCTL command ADD SHARD.
The following are some cases where replacing a shard using ADD SHARD -REPLACE is useful.
-
The server (machine) where the shard database was running suffered irreparable damage and has to be replaced
-
You must replace a working server with another (more powerful, for example) server
-
A shard in a PDB was relocated from one CDB to another
In all of these cases the number of shards and data distribution across shards does not change after ADD SHARD is executed; a shard is replaced with another shard that holds the same data. This is different from ADD SHARD used without the -replace option when the number of shards increases and data gets redistributed.
Upon running ADD SHARD -REPLACE, the old shard parameters, such as connect_string, db_unique_name, and so on, are replaced with their new values. A new database can have different db_unique_name than the failed one. When replacing a standby in a Data Guard configuration, the DBID of the new database must match the old one, as Data Guard requires all of the members of the configuration to have same DBID.
Before Using Replace
Before you use ADD SHARD -REPLACE, verify the following:
-
You have restored the database correctly (for example, using RMAN restore or other method). The new database shard must have the same sharding metadata as the failed one. Perform basic validation to ensure that you do not accidently provide a connect string to the wrong shard.
-
The shard that failed must have been in a deployed state before failure happened.
-
The shard that failed must be down when executing the ADD SHARD -REPLACE command.
-
Fast-start failover observer must be running, if fast-start failover is enabled (which it is by default).
Replacing a Shard in a Data Guard Environment
The ADD SHARD -REPLACE command can only be used to replace a standby shard if the primary is still alive. In order to replace a primary shard that failed, wait for one of the remaining standbys to switch over to the primary role before trying to replace the failed shard.
When a switchover is not possible (primary and all the standbys are down), you must run ADD SHARD -REPLACE for each member starting with the primary. This creates a new broker configuration from scratch.
In MAXPROTECTION mode with no standbys alive, the primary database shuts down to maintain the protection mode. In this case, the primary database cannot be opened if the standby is not alive. To handle the replace operation in this scenario, you must first downgrade Data Guard protection mode using DGMGRL (to MAXAVAILABILITY or MAXPERFORMANCE) by starting up the database in mounted mode. After the protection mode is set, open the primary database and perform the replace operation using GDSCTL. After the replace operation finishes you can revert the protection mode back to the previous level using DGMGRL.
When replacing a standby in a Data Guard configuration, the DBID of the new database must match the old one, as Data Guard requires all of the members of the configuration to have same DBID.
Example 10-1 Example 1: Replacing the primary shard with no standbys in the configuration
The initial configuration has two primary shards deployed and no standbys, as shown in the following example. The Availability for shdc is shown as a dash because it has gone down in a disaster scenario.
$ gdsctl config shard
Name Shard Group Status State Region Availability
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------ ------------
shdb dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shdc dbs1 Ok Deployed east - To recover, you create a replica of the primary from the backup, using RMAN for example. For this example, a new shard is created with db_unique_name shdd and connect string inst4. Now, the old shard, shdc, can be replaced with the new shard, shdd, as follows:
$ gdsctl add shard -replace shdc -connect inst4 -pwd password
DB Unique Name: SHDDYou can verify the configuration as follows:
$ gdsctl config shard
Name Shard Group Status State Region Availability
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------ ------------
shdb dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shdd dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINEExample 10-2 Example 2: Replacing a standby shard
Note that you cannot replace a primary shard when the configuration contains a standby shard. In such cases, if the primary fails, the replace operation must be performed after one of the standbys becomes the new primary by automatic switchover.
The initial configuration has two shardgroups: one primary and one standby, each containing two shards, when the standby, shdd goes down.
$ gdsctl config shard
Name Shard Group Status State Region Availability
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------ ------------
shdb dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shdc dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shdd dbs2 Ok Deployed east -
shde dbs2 Ok Deployed east READ ONLYCreate a new standby. Because the primary is running, this should be done using the RMAN DUPLICATE command with the FOR STANDBY option. Once the new standby, shdf, is ready, replace the old shard, shdd, as follows:
$ gdsctl add shard -replace shdd -connect inst6 -pwd password
DB Unique Name: shdfYou can verify the configuration as follows:
$ gdsctl config shard
Name Shard Group Status State Region Availability
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------ ------------
shdb dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shdc dbs1 Ok Deployed east ONLINE
shde dbs2 Ok Deployed east READ ONLY
shdf dbs2 Ok Deployed east READ ONLYReplacing a Shard in an Oracle GoldenGate Environment
The GDSCTL command option ADD SHARD -REPLACE is not supported with Oracle GoldenGate.
Common Errors
ORA-03770: incorrect shard is given for replace
This error is thrown when the shard given for the replace operation is not the replica of the original shard. Specifically, the sharding metadata does not match the metadata stored in the shard catalog for this shard. Make sure that the database was copied correctly, preferably using RMAN. Note that this is not an exhaustive check. It is assumed that you created the replica correctly.
ORA-03768: The database to be replaced is still up: shardc
The database to be replaced must not be running when running the add shard -replace command. Verify this by looking at the output of GDSCTL command config shard. If the shard failed but still shows ONLINE in the output, wait for some time (about 2 minutes) and retry.
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about the ADD SHARD command.
Parent topic: Managing Shards with GDSCTL
10.9 Chunk Management
You can manage chunks in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and GDSCTL.
The following topics describe chunk management concepts and tasks:
- About Moving Chunks
Sometimes it becomes necessary to move a chunk from one shard to another. To maintain scalability of the sharded environment, it is important to attempt to maintain an equal distribution of the load and activity across all shards. - Moving Chunks
You can move chunks from one shard to another in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - About Splitting Chunks
Splitting a chunk in a sharded database is required when chunks become too big, or only part of a chunk must be migrated to another shard. - Splitting Chunks
You can split chunks in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.9.1 About Moving Chunks
Sometimes it becomes necessary to move a chunk from one shard to another. To maintain scalability of the sharded environment, it is important to attempt to maintain an equal distribution of the load and activity across all shards.
As the environment matures in a composite SDB, some shards may become more active and have more data than other shards. In order to keep a balance within the environment you must move chunks from more active servers to less active servers. There are other reasons for moving chunks:
-
When a shard becomes more active than other shards, you can move a chunk to a less active shard to help redistribute the load evenly across the environment.
-
When using range, list, or composite sharding, and you are adding a shard to a shardgroup.
-
When using range, list, or composite sharding, and you a removing a shard from a shardgroup.
-
After splitting a chunk it is often advisable to move one of the resulting chunks to a new shard.
When moving shards to maintain scalability, the ideal targets of the chunks are shards that are less active, or have a smaller portion of data. Oracle Enterprise Manager and AWR reports can help you identify the distribution of activity across the shards, and help identify shards that are good candidates for chunk movement.
Note:
Any time a chunk is moved from one shard to another, you should make a full backup of the databases involved in the operation (both the source of the chunk move, and the target of the chunk move.)
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about using the GDSCTL MOVE CHUNK command
Parent topic: Chunk Management
10.9.2 Moving Chunks
You can move chunks from one shard to another in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Chunk Management
10.9.3 About Splitting Chunks
Splitting a chunk in a sharded database is required when chunks become too big, or only part of a chunk must be migrated to another shard.
Oracle Sharding supports the online split of a chunk. Theoretically it is possible to have a single chunk for each shard and split it every time data migration is required. However, even though a chunk split does not affect data availability, the split is a time-consuming and CPU-intensive operation because it scans all of the rows of the partition being split, and then inserts them one by one into the new partitions. For composite sharding, it is time consuming and may require downtime to redefine new values for the shard key or super shard key.
Therefore, it is recommended that you pre-create multiple chunks on each shard and split them either when the number of chunks is not big enough for balanced redistribution of data during re-sharding, or a particular chunk has become a hot spot.
Even with system-managed sharding, a single chunk may grow larger than other chunks or may become more active. In this case, splitting that chunk and allowing automatic resharding to move one of the resulting chunks to another shard maintains a more equal balanced distribution of data and activity across the environment.
Oracle Enterprise Manager heat maps show which chunks are more active than other chunks. Using this feature will help identify which chunks could be split, and one of the resulting chunks could then be moved to another shard to help rebalance the environment.
See Also:
Oracle Database Global Data Services Concepts and Administration Guide for information about using the GDSCTL SPLIT CHUNK command
Parent topic: Chunk Management
10.9.4 Splitting Chunks
You can split chunks in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Chunk Management
10.10 Shard Director Management
You can add, edit, and remove shard directors in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
The following topics describe shard director management tasks:
- Creating a Shard Director
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to create and add a shard director to your Oracle Sharding deployment. - Editing a Shard Director Configuration
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to edit a shard director configuration in your Oracle Sharding deployment. - Removing a Shard Director
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to remove shard directors from your Oracle Sharding deployment.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.10.1 Creating a Shard Director
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to create and add a shard director to your Oracle Sharding deployment.
Parent topic: Shard Director Management
10.10.2 Editing a Shard Director Configuration
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to edit a shard director configuration in your Oracle Sharding deployment.
Parent topic: Shard Director Management
10.10.3 Removing a Shard Director
Use Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to remove shard directors from your Oracle Sharding deployment.
If the shard director you want to remove is the administrative shard director, as indicated by a check mark in that column of the Shard Directors list, you must choose another shard director to be the administrative shard director before removing it.
- Open the Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner of the Sharded Database target page, and choose Shard Directors.
- If prompted, enter the shard catalog credentials, select the shard director to manage under Shard Director Credentials, select the shard director host credentials, and log in.
- Select a shard director from the list and click Delete.
- Click the link in the Information box at the top of the page to view the provisioning status of the shard director removal.
Parent topic: Shard Director Management
10.11 Region Management
You can add, edit, and remove regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
The following topics describe region management tasks:
- Creating a Region
Create sharded database regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Editing a Region Configuration
Edit sharded database region configurations in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Removing a Region
Remove sharded database regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.11.1 Creating a Region
Create sharded database regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
- Open the Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner of the Sharded Database target page, and choose Regions.
- If prompted, enter the shard catalog credentials, select the shard director to manage under Shard Director Credentials, select the shard director host credentials, and log in.
- Click Create.
- Enter a unique name for the region in the Create Region dialog.
- Optionally, select a buddy region from among the existing regions.
- Click OK.
- Click the link in the Information box at the top of the page to view the provisioning status of the region.
Parent topic: Region Management
10.11.2 Editing a Region Configuration
Edit sharded database region configurations in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
- Open the Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner of the Sharded Database target page, and choose Regions.
- If prompted, enter the shard catalog credentials, select the shard director under Shard Director Credentials, select the shard director host credentials, and log in.
- Select a region from the list and click Edit.
- Select or remove a buddy region, and click OK.
- Click the link in the Information box at the top of the page to view the provisioning status of the region configuration changes.
When the region configuration is successfully updated the changes appear in the Regions list. You might need to refresh the page to see the updates.
Parent topic: Region Management
10.11.3 Removing a Region
Remove sharded database regions in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
- Open the Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner of the Sharded Database target page, and choose Regions.
- If prompted, enter the shard catalog credentials, select the shard director under Shard Director Credentials, select the shard director host credentials, and log in.
- Select a region from the list and click Delete.
- Click the link in the Information box at the top of the page to view the provisioning status of the region removal.
When the region configuration is successfully removed the changes appear in the Regions list. You might need to refresh the page to see the updates.
Parent topic: Region Management
10.12 Shardspace Management
You can add, edit, and remove shardspaces in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
The following topics describe shardspace management tasks:
- Creating a Shardspace
Create shardspaces in your composite Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. - Adding a Shardspace to a Composite Sharded Database
Learn to create a new shardspace, add shards to the shardspace, create a tablespace set in the new shardspace, and add a partitionset to the sharded table for the added shardspace. Then verify that the partitions in the tables are created in the newly added shards in the corresponding tablespaces.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.12.1 Creating a Shardspace
Create shardspaces in your composite Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Shardspace Management
10.12.2 Adding a Shardspace to a Composite Sharded Database
Learn to create a new shardspace, add shards to the shardspace, create a tablespace set in the new shardspace, and add a partitionset to the sharded table for the added shardspace. Then verify that the partitions in the tables are created in the newly added shards in the corresponding tablespaces.
Parent topic: Shardspace Management
10.13 Shardgroup Management
You can add, edit, and remove shardgroups in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
The following topics describe shardgroup management tasks:
- Creating a Shardgroup
Create shardgroups in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.13.1 Creating a Shardgroup
Create shardgroups in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Shardgroup Management
10.14 Services Management
You can manage services in your Oracle Sharding deployment with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
To manage Oracle Sharding services, open the Sharded Database menu, located in the top left corner of the Sharded Database target page, and choose Services. On the Services page, using the controls at the top of the list of services, you can start, stop, enable, disable, create, edit, and delete services.
Selecting a service opens a service details list which displays the hosts and shards on which the service is running, and the status, state, and Data Guard role of each of those instances. Selecting a shard in this list allows you to enable, disable, start, and stop the service on the individual shards.
The following topics describe services management tasks:
- Creating a Service
Create services in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Sharded Database Administration
10.14.1 Creating a Service
Create services in your Oracle Sharding deployment using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Parent topic: Services Management