The Open Group Base Specifications Issue 7
IEEE Std 1003.1-2008, 2016 Edition
Copyright © 2001-2016 The IEEE and The Open Group
NAME
atan2, atan2f, atan2l - arc tangent functions
SYNOPSIS
#include <math.h>
double atan2(double y, double x);
float atan2f(float y, float x);
long double atan2l(long double y, long double x);
DESCRIPTION
[CX] ![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif)
The functionality described on this reference page is aligned with the ISO C standard. Any conflict between the
requirements described here and the ISO C standard is unintentional. This volume of POSIX.1-2008 defers to the ISO C
standard.
![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
These functions shall compute the principal value of the arc tangent of y/ x, using the signs of both arguments to
determine the quadrant of the return value.
An application wishing to check for error situations should set errno to zero and call
feclearexcept(FE_ALL_EXCEPT) before calling these functions. On return, if errno is non-zero or
fetestexcept(FE_INVALID | FE_DIVBYZERO | FE_OVERFLOW | FE_UNDERFLOW) is non-zero, an error has occurred.
RETURN VALUE
Upon successful completion, these functions shall return the arc tangent of y/ x in the range [-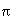 ,
, ] radians.
] radians.
If y is ±0 and x is < 0, ± shall be returned.
shall be returned.
If y is ±0 and x is > 0, ±0 shall be returned.
If y is < 0 and x is ±0, - /2 shall be returned.
/2 shall be returned.
If y is > 0 and x is ±0,  /2 shall be returned.
/2 shall be returned.
If x is 0, a pole error shall not occur.
[MX] ![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif) If
either x or y is NaN, a NaN shall be returned.
If
either x or y is NaN, a NaN shall be returned.
If the correct value would cause underflow, a range error may occur, and atan(),
atan2f(), and atan2l() shall return an implementation-defined value no greater in magnitude than DBL_MIN, FLT_MIN,
and LDBL_MIN, respectively. ![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
[MXX] ![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif) If the IEC 60559 Floating-Point option is supported, y/ x should be returned.
If the IEC 60559 Floating-Point option is supported, y/ x should be returned. ![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
[MX] ![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif) If
y is ±0 and x is -0, ±
If
y is ±0 and x is -0, ± shall be returned.
shall be returned.
If y is ±0 and x is +0, ±0 shall be returned.
For finite values of ± y > 0, if x is -Inf, ± shall be
returned.
shall be
returned.
For finite values of ± y > 0, if x is +Inf, ±0 shall be returned.
For finite values of x, if y is ±Inf, ± /2 shall be
returned.
/2 shall be
returned.
If y is ±Inf and x is -Inf, ±3 /4 shall be returned.
/4 shall be returned.
If y is ±Inf and x is +Inf, ± /4 shall be returned.
/4 shall be returned.
If both arguments are 0, a domain error shall not occur. ![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
ERRORS
These functions may fail if:
- Range Error
- [MX]
![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif) The result underflows.
The result underflows.
If the integer expression (math_errhandling & MATH_ERRNO) is non-zero, then errno shall be set to [ERANGE]. If
the integer expression (math_errhandling & MATH_ERREXCEPT) is non-zero, then the underflow floating-point exception
shall be raised. ![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
The following sections are informative.
EXAMPLES
Converting Cartesian to Polar Coordinates System
The function below uses atan2() to convert a 2d vector expressed in cartesian coordinates (x,y) to the
polar coordinates (rho,theta). There are other ways to compute the angle theta, using asin() acos(), or atan(). However, atan2() presents here two advantages:
Finally, this example uses hypot() rather than sqrt() since it is better for special cases; see hypot() for more information.
#include <math.h>
void
cartesian_to_polar(const double x, const double y,
double *rho, double *theta
)
{
*rho = hypot (x,y); /* better than sqrt(x*x+y*y) */
*theta = atan2 (y,x);
}
APPLICATION USAGE
On error, the expressions (math_errhandling & MATH_ERRNO) and (math_errhandling & MATH_ERREXCEPT) are
independent of each other, but at least one of them must be non-zero.
RATIONALE
None.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
None.
SEE ALSO
acos, asin, atan, feclearexcept, fetestexcept, hypot, isnan, sqrt, tan
XBD Treatment of Error Conditions for Mathematical Functions, <math.h>
CHANGE HISTORY
First released in Issue 1. Derived from Issue 1 of the SVID.
Issue 5
The DESCRIPTION is updated to indicate how an application should check for an error. This text was previously published in the
APPLICATION USAGE section.
Issue 6
The atan2f() and atan2l() functions are added for alignment with the ISO/IEC 9899:1999 standard.
The DESCRIPTION, RETURN VALUE, ERRORS, and APPLICATION USAGE sections are revised to align with the ISO/IEC 9899:1999
standard, and the IEC 60559:1989 standard floating-point extensions over the ISO/IEC 9899:1999 standard are marked.
IEEE Std 1003.1-2001/Cor 2-2004, item XSH/TC2/D6/18 is applied, adding to the EXAMPLES section.
Issue 7
POSIX.1-2008, Technical Corrigendum 1, XSH/TC1-2008/0038 [68,428] is applied.
End of informative text.
return to top of page
UNIX ® is a registered Trademark of The Open Group.
POSIX ® is a registered Trademark of The IEEE.
Copyright © 2001-2016 The IEEE and The Open Group, All Rights Reserved
[ Main Index | XBD | XSH | XCU | XRAT
]
![[Option Start]](../images/opt-start.gif) The functionality described on this reference page is aligned with the ISO C standard. Any conflict between the
requirements described here and the ISO C standard is unintentional. This volume of POSIX.1-2008 defers to the ISO C
standard.
The functionality described on this reference page is aligned with the ISO C standard. Any conflict between the
requirements described here and the ISO C standard is unintentional. This volume of POSIX.1-2008 defers to the ISO C
standard. ![[Option End]](../images/opt-end.gif)
 ,
,