| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E26088-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E26088-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the CREATE CONTEXT statement to:
Create a namespace for a context (a set of application-defined attributes that validates and secures an application)
Associate the namespace with the externally created package that sets the context
You can use the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure in your designated package to set or reset the attributes of the context.
See Also:
Oracle Database Security Guide for a discussion of contexts
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information on the DBMS_SESSION.SET_CONTEXT procedure
To create a context namespace, you must have CREATE ANY CONTEXT system privilege.
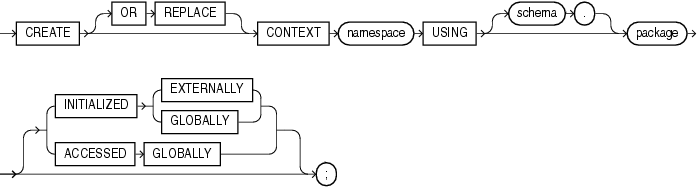
Specify OR REPLACE to redefine an existing context namespace using a different package.
Specify the name of the context namespace to create or modify. Context namespaces are always stored in the schema SYS.
See Also:
"Database Object Naming Rules" for guidelines on naming a context namespaceSpecify the schema owning package. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database uses the current schema.
Specify the PL/SQL package that sets or resets the context attributes under the namespace for a user session.
To provide some design flexibility, Oracle Database does not verify the existence of the schema or the validity of the package at the time you create the context.
The INITIALIZED clause lets you specify an entity other than Oracle Database that can initialize the context namespace.
EXTERNALLY EXTERNALLY indicates that the namespace can be initialized using an OCI interface when establishing a session.
See Also:
Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for information on using OCI to establish a sessionGLOBALLY GLOBALLY indicates that the namespace can be initialized by the LDAP directory when a global user connects to the database.
After the session is established, only the designated PL/SQL package can issue commands to write to any attributes inside the namespace.
See Also:
Oracle Database Security Guide for information on establishing globally initialized contexts
Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide for information on the connecting to the database through the LDAP directory
This clause indicates that any application context set in namespace is accessible throughout the entire instance. This setting lets multiple sessions share application attributes.
Creating an Application Context: Example This example uses a PL/SQL package emp_mgmt, which validates and secures a human resources application. See Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference for the example that creates that package. The following statement creates the context namespace hr_context and associates it with the package emp_mgmt:
CREATE CONTEXT hr_context USING emp_mgmt;
You can control data access based on this context using the SYS_CONTEXT function. For example, the emp_mgmt package has defined an attribute department_id as a particular department identifier. You can secure the base table employees by creating a view that restricts access based on the value of department_id, as follows:
CREATE VIEW hr_org_secure_view AS
SELECT * FROM employees
WHERE department_id = SYS_CONTEXT('hr_context', 'department_id');
See Also:
SYS_CONTEXT and Oracle Database Security Guide for more information on using application contexts to retrieve user information