| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25519-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25519-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
The CASE statement chooses from a sequence of conditions and runs a corresponding statement.
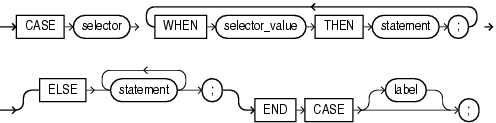
The simple CASE statement evaluates a single expression and compares it to several potential values.
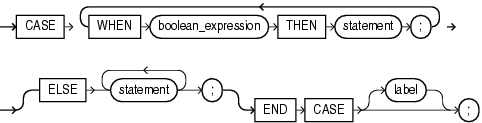
The searched CASE statement evaluates multiple Boolean expressions and chooses the first one whose value is TRUE.
See:
Expression whose value is evaluated once and used to select one of several alternatives. selector can have any PL/SQL data type except BLOB, BFILE, or a user-defined type.
WHEN selector_value THEN statement
selector_value can be an expression of any PL/SQL type except BLOB, BFILE, or a user-defined type.
The selector_values are evaluated sequentially. If the value of a selector_value equals the value of selector, then the statement associated with that selector_value runs, and the CASE statement ends. Subsequent selector_values are not evaluated.
Caution:
Astatement can modify the database and invoke nondeterministic functions. There is no fall-through mechanism, as there is in the C switch statement.ELSE statement [statement ]...
The statements run if and only if no selector_value has the same value as selector.
Without the ELSE clause, if no selector_value has the same value as selector, the system raises the predefined exception CASE_NOT_FOUND.
A label that identifies the statement (see "statement ::=" and "label").
WHEN boolean_expression THEN statement
The boolean_expressions are evaluated sequentially. If the value of a boolean_expression is TRUE, the statement associated with that boolean_expression runs, and the CASE statement ends. Subsequent boolean_expressions are not evaluated.
Caution:
Astatement can modify the database and invoke nondeterministic functions. There is no fall-through mechanism, as there is in the C switch statement.ELSE statement [statement ]...
The statements run if and only if no boolean_expression has the value TRUE.
Without the ELSE clause, if no boolean_expression has the value TRUE, the system raises the predefined exception CASE_NOT_FOUND.
A label that identifies the statement (see "statement ::=" and "label").
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the NULLIF function
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the COALESCE function