| Oracle® Database Administrator's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25494-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Administrator's Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E25494-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
The basic memory structures associated with Oracle Database include:
System Global Area (SGA)
The SGA is a group of shared memory structures, known as SGA components, that contain data and control information for one Oracle Database instance. The SGA is shared by all server and background processes. Examples of data stored in the SGA include cached data blocks and shared SQL areas.
Program Global Area (PGA)
A PGA is a memory region that contains data and control information for a server process. It is nonshared memory created by Oracle Database when a server process is started. Access to the PGA is exclusive to the server process. There is one PGA for each server process. Background processes also allocate their own PGAs. The total PGA memory allocated for all background and server processes attached to an Oracle Database instance is referred to as the total instance PGA memory, and the collection of all individual PGAs is referred to as the total instance PGA, or just instance PGA.
Figure 6-1 illustrates the relationships among these memory structures.
Figure 6-1 Oracle Database Memory Structures
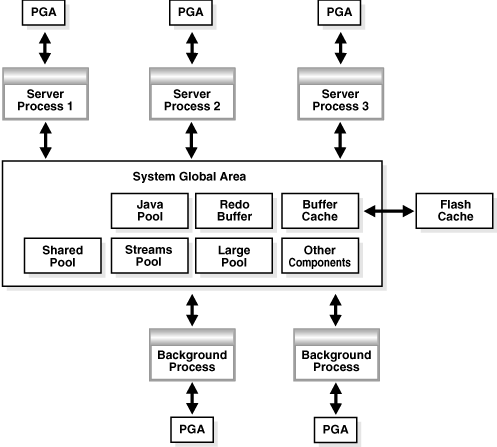
If your database is running on Solaris or Oracle Linux, you can optionally add another memory component: Database Smart Flash Cache (the flash cache). The flash cache is an extension of the SGA-resident buffer cache, providing a level 2 cache for database blocks. It can improve response time and overall throughput, especially for read-intensive online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads. The flash cache resides on one or more flash disk devices, which are solid state storage devices that use flash memory.
The flash cache is typically more economical than additional main memory, and is an order of magnitude faster than disk drives.
See Also:
Oracle Database Concepts for more information on memory architecture in an Oracle Database instance